Abstract
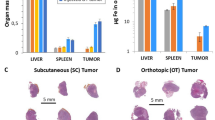
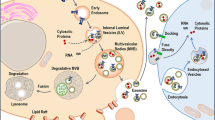
The tumour microenvironment regulates tumour progression and the spread of cancer in the body. Targeting the stromal cells that surround cancer cells could, therefore, improve the effectiveness of existing cancer treatments. Here, we show that magnetic nanoparticle clusters encapsulated inside a liposome can, under the influence of an external magnet, target both the tumour and its microenvironment. We use the outstanding T2 contrast properties (r2 = 573–1,286 s−1 mM−1) of these ferri-liposomes, which are ∼95 nm in diameter, to non-invasively monitor drug delivery in vivo. We also visualize the targeting of the tumour microenvironment by the drug-loaded ferri-liposomes and the uptake of a model probe by cells. Furthermore, we used the ferri-liposomes to deliver a cathepsin protease inhibitor to a mammary tumour and its microenvironment in a mouse, which substantially reduced the size of the tumour compared with systemic delivery of the same drug.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liotta, L. A. & Kohn, E. C. The microenvironment of the tumour-host interface. Nature 411, 375–379 (2001).
Mueller, M. M. & Fusenig, N. E. Friends or foes—bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 4, 839–849 (2004).
Santos, A. M., Jung, J., Aziz, N., Kissil, J. L. & Puré, E. Targeting fibroblast activation protein inhibits tumor stromagenesis and growth in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 119, 3613–3625 (2009).
Rosi, N. L. & Mirkin, C. A. Nanostructures in biodiagnostics. Chem. Rev. 105, 1547–1562 (2005).
Arrueboa, M., Fernández-Pachecoa, R., Ibarraa, M. R. & Santamaría, S. Magnetic nanoparticles for drug delivery. Nanotoday 2, 22–32 (2007).
Galanzha, E. I. et al. In vivo magnetic enrichment and multiplex photoacoustic detection of circulating tumour cells. Nature Nanotech. 4, 855–860 (2009).
Namiki, Y. et al. A novel magnetic crystal–lipid nanostructure for magnetically guided in vivo gene delivery. Nature Nanotech. 4, 598–606 (2009).
Kim, J. W., Galanzha, E. I., Shashkov, E. V., Moon, H. M. & Zharov, V. P. Golden carbon nanotubes as multimodal photoacoustic and photothermal high-contrast molecular agents. Nature Nanotech. 4, 688–694 (2009).
Vlaskou, D. et al. Magnetic and acoustically active lipospheres for magnetically targeted nucleic acid delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 20, 3881–3894 (2010).
Bulte, J. W. M. et al. Selective Mr imaging of labeled human peripheral-blood mononuclear-cells by liposome mediated incorporation of dextran-magnetite particles. Magn. Reson. Med. 29, 32–37 (1993).
Bulte, J. W., de Cuyper, M., Despres, D. & Frank, J. A. Short- vs. long-circulating magnetoliposomes as bone marrow-seeking MR contrast agents. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 9, 329–335 (1999).
Bulte, J. W. M., de Cuyper, M., Despres, D. & Frank, J. A. Preparation, relaxometry, and biokinetics of PEGylated magnetoliposomes as MR contrast agent. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 194, 204–209 (1999).
Lee, J. et al. Artificially engineered magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-sensitive molecular imaging. Nature Med. 13, 95–99 (2007).
Torchilin, V. Multifunctional and stimuli-sensitive pharmaceutical nanocarriers. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 71, 431–444 (2009).
Medarova, Z., Pham, W., Farrar, C., Petkova, V. & Moore, A. In vivo imaging of siRNA delivery and silencing in tumors. Nature Med. 13, 372–377 (2007).
Naiden, E. et al. Magnеtiс pгopеrtiеs and stгuсtural parameters of nanosizеd oхidе fеrrimagnеt powdеrs produсеd by mесhanoсhemiсal synthеsis frоm salt solutions. Phys. Solid State 5, 891–900 (2003).
Bogdanov, A. A., Martin, C., Weissleder, R. & Brady, T. J. Trapping of dextran-coated colloids in liposomes by transient binding to aminophospholipid—preparation of ferrosomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembranes 1193, 212–218 (1994).
Di Paolo, D. et al. Liposome-mediated therapy of neuroblastoma. Methods Enzymol. 465, 225–249 (2009).
Torchilin, V. P. et al. Poly(ethylene glycol) on the liposome surface - on the mechanism of polymer-coated liposome longevity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembranes 1195, 11–20 (1994).
Fortin-Ripoche, J. P. et al. Magnetic targeting of magnetoliposomes to solid tumors with MR imaging monitoring in mice: feasibility. Radiology 239, 415–424 (2005).
Martina, M. S. et al. Generation of superparamagnetic liposomes revealed as highly efficient MRI contrast agents for in vivo imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 127, 10676–10685 (2005).
Stollfuss, J. C. et al. Rectal carcinoma: high-spatial-resolution MR imaging and T2 quantification in rectal cancer specimens. Radiology 241, 132–141 (2006).
Seo, W. S. et al. FeCo/graphitic-shell nanocrystals as advanced magnetic-resonance-imaging and near-infrared agents. Nature Mater. 5, 971–976 (2006).
Ai, H. et al. Magnetite-loaded polymeric micelles as ultrasensitive magnetic-resonance probes. Adv. Mater. 17, 1949–1952 (2005).
Shapiro, M. G., Atanasijevic, T., Faas, H., Westmeyer, G. G. & Jasanoff, A. Dynamic imaging with MRI contrast agents: quantitative considerations. Magn. Reson. Imaging 24, 449–462 (2006).
Na, H. B. et al. Development of a T1 contrast agent for magnetic resonance imaging using MnO nanoparticles. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 46, 5397–5401 (2007).
Zhao, M., Josephson, L., Tang, Y. & Weissleder, R. Magnetic sensors for protease assays. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. 42, 1375–1378 (2003).
Atanasijevic, T., Shusteff, M., Fam, P. & Jasanoff, A. Calcium-sensitive MRI contrast agents based on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and calmodulin. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 103, 14707–14712 (2006).
Guy, C. T., Cardiff, R. D. & Muller, W. J. Induction of mammary tumors by expression of polyomavirus middle T oncogene: a transgenic mouse model for metastatic disease. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 954–961 (1992).
Wender, P. A. et al. Real-time analysis of uptake and bioactivatable cleavage of luciferin-transporter conjugates in transgenic reporter mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 10340–10345 (2007).
Greenbaum, D., Medzihradszky, K. F., Burlingame, A. & Bogyo, M. Epoxide electrophiles as activity-dependent cysteine protease profiling and discovery tools. Chem. Biol. 7, 569–581 (2000).
Greenbaum, D. et al. Chemical approaches for functionally probing the proteome. Mol. Cell Proteomics 1, 60–68 (2002).
Joyce, J. A. et al. Cathepsin cysteine proteases are effectors of invasive growth and angiogenesis during multistage tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 5, 443–453 (2004).
Bell-McGuinn, K., Garfall, A., Bogyo, M., Hanahan, D. & Joyce, J. A. Inhibition of cysteine cathepsin protease activity enhances chemotherapy regimens by decreasing tumor growth and invasiveness in a mouse model of multistage cancer. Cancer Res. 67, 7378–7385 (2007).
Schurigt, U. et al. Trial of the cysteine cathepsin inhibitor JPM-OEt on early and advanced mammary cancer stages in the MMTV-PyMT-transgenic mouse model. Biol. Chem. 389, 1067–1074 (2008).
Vasiljeva, O. et al. Tumor cell-derived and macrophage-derived cathepsin B promotes progression and lung metastasis of mammary cancer. Cancer Res. 66, 5242–5250 (2006).
Vasiljeva, O. & Turk, B. Dual contrasting roles of cysteine cathepsins in cancer progression: apoptosis versus tumour invasion. Biochimie 90, 380–386 (2008).
Sevenich, L. et al. Synergistic antitumor effects of combined cathepsin B and cathepsin Z deficiencies on breast cancer progression and metastasis in mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 2497–2502 (2010).
Gocheva, V. & Joyce, J. A. Cysteine cathepsins and the cutting edge of cancer invasion. Cell Cycle 6, 60–64 (2007).
Turk, V., Kos, J. & Turk, B. Cysteine cathepsins (proteases)—on the main stage of cancer? Cancer Cell 5, 409–410 (2004).
Rossi, A., Deveraux, Q., Turk, B. & Sali, A. Comprehensive search for cysteine cathepsins in the human genome. Biol. Chem. 385, 363–372 (2004).
Mohamed, M. M. & Sloane, B. F. Cysteine cathepsins: multifunctional enzymes in cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 6, 764–775 (2006).
Vasiljeva, O. et al. Emerging roles of cysteine cathepsins in disease and their potential as drug targets. Curr. Pharm. Des. 13, 387–403 (2007).
Sloane, B. F. et al. Cathepsin B and tumor proteolysis: contribution of the tumor microenvironment. Semin. Cancer Biol. 15, 149–157 (2005).
Gocheva, V. et al. IL-4 induces cathepsin protease activity in tumor-associated macrophages to promote cancer growth and invasion. Genes Dev. 24, 241–255 (2010).
Ceelen, W. P. & Flessner, M. F. Intraperitoneal therapy for peritoneal tumors: biophysics and clinical evidence. Nature Rev. Clin. Oncol. 7, 108–115 (2010).
Sadaghiani, A. M. et al. Design, synthesis, and evaluation of in vivo potency and selectivity of epoxysuccinyl-based inhibitors of papain-family cysteine proteases. Chem. Biol. 14, 499–511 (2007).
Vasiljeva, O. et al. Reduced tumour cell proliferation and delayed development of high-grade mammary carcinomas in cathepsin B-deficient mice. Oncogene 27, 4191–4199 (2008).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Yu.F. Ivanov (Tomsk Scientific Center) for transmission electron microscopy, G. Kapun (National Institute of Chemistry) for scanning electron microscopy, M. Škarabot (Jozef Stefan Institute) for atomic force microscopy, J. Ščančar and M. Vahčič (Jozef Stefan Institute) for flame atomic absorption spectrometry, I.V. Sukhodolo, R.I. Pleshko, A.N. Dzuman, I.V. Milto and L.M. Ogorodova (Siberian State Medical University) for help in the acute toxicity study, and A. Sepe, M. Butinar, M. Trstenjak-Prebanda and A. Petelin (Jozef Stefan Institute), O.G. Terekhova (Tomsk Scientific Center), M. Tacke and N. Klemm (Institut für Molekulare Medizin und Zellforschung) for technical and methodological assistance, G. Salvesen (Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute) for valuable discussions, and R.H. Pain (Jozef Stefan Institute) for critical reading of the manuscript. JPM-565 was kindly provided by the Drug Synthesis and Chemistry Branch, Developmental Therapeutics Program, Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis, National Cancer Institute. The research leading to these results was supported in part by the European Community's Seventh Framework Programme FP7/2007-2011 (grant agreement no. 201279, Microenvimet, O.V., T.R., C.P. and B.T.), the Slovenian Research Agency (research grant no. P1-0140, B.T.), the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 07-04-12170, E.P.N.), the United States Civilian Research and Development Foundation (project no. Y4-C16-05, A.A.M and V.I.I.) and the DFG SFB 850 (to T.R., C.P. and R.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
G.M., U.M., I.P., S.G.P., B.T. and O.V. conceived and designed the experiments. G.M., U.M., L.B. and O.V. performed the experiments. G.M., U.M., S.G.P., B.T. and O.V. analysed the data. T.R., C.P. and R.Z. contributed transgenic mouse models and animal imaging. M.B. contributed JPM-565 inhibitor. A.A.M., V.I.I., E.P.N. and S.G.P. supplied the magnetic nanoparticles. S.G.P., V.T., B.T. and O.V. supervised the project. G.M., S.G.P., B.T. and O.V. wrote the manuscript. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 3236 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikhaylov, G., Mikac, U., Magaeva, A. et al. Ferri-liposomes as an MRI-visible drug-delivery system for targeting tumours and their microenvironment. Nature Nanotech 6, 594–602 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.112
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2011.112
This article is cited by
-
Delivery of Corn-Derived Nanoparticles with Anticancer Activity to Tumor Tissues by Modification with Polyethylene Glycol for Cancer Therapy
Pharmaceutical Research (2023)
-
Evaluation of novel cathepsin-X inhibitors in vitro and in vivo and their ability to improve cathepsin-B-directed antitumor therapy
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
Rat Blood Leukocytes after Intravenous Injection of Magnetoliposomes on the Basis of Nanomagnetite
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2021)