Abstract
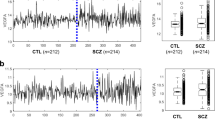
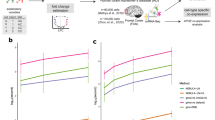
Human diseases are often accompanied by histological changes that confound interpretation of molecular analyses and identification of disease-related effects. We developed population-specific expression analysis (PSEA), a computational method of analyzing gene expression in samples of varying composition that can improve analyses of quantitative molecular data in many biological contexts. PSEA of brains from individuals with Huntington's disease revealed myelin-related abnormalities that were undetected using standard differential expression analysis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Hodges, A. et al. Hum. Mol. Genet. 15, 965–977 (2006).
Reiner, A. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5733–5737 (1988).
Vonsattel, J.P. et al. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 44, 559–577 (1985).
Lu, P., Nakorchevskiy, A. & Marcotte, E.M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 10370–10375 (2003).
Shen-Orr, S.S. et al. Nat. Methods 7, 287–289 (2010).
Venet, D., Pecasse, F., Maenhaut, C. & Bersini, H. Bioinformatics 17 (suppl. 1) S279–S287 (2001).
Stuart, R.O. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 615–620 (2004).
Lähdesmäki, H., Shmulevich, L., Dunmire, V., Yli-Harja, O. & Zhang, W. BMC Bioinformatics 6, 54 (2005).
Abbas, A.R., Wolslegel, K., Seshasayee, D., Modrusan, Z. & Clark, H.F. PLoS ONE 4, e6098 (2009).
Ghosh, D. Bioinformatics 20, 1663–1669 (2004).
Wang, M., Master, S.R. & Chodosh, L.A. BMC Bioinformatics 7, 328 (2006).
Ciarmiello, A. et al. J. Nucl. Med. 47, 215–222 (2006).
Rosas, H.D. et al. Neuroimage 49, 2995–3004 (2010).
Fox, J. Applied Regression Analysis, Linear Models, and Related Methods (Sage Publications, Inc., 1997).
Irizarry, R.A. et al. Biostatistics 4, 249–264 (2003).
Leong, H.S., Yates, T., Wilson, C. & Miller, C.J. Bioinformatics 21, 2552–2553 (2005).
Akaike, H. IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr. 19, 716–723 (1974).
Burnham, K.P. & Anderson, D.R. Model selection and multi-model inference (Springer, 2002).
Cook, R.D. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 74, 169–174 (1979).
Benjamini, Y. & Hochberg, Y. J. R. Stat. Soc. B 57, 289–300 (1995).
Gautier, L., Cope, L., Bolstad, B.M. & Irizarry, R.A. Bioinformatics 20, 307–315 (2004).
Steiner, P. et al. Neuroscience 113, 893–905 (2002).
Levison, S. & McCarthy, K. in Culturing Nerve Cells (eds. Banker, G. and Goslin, K.) 309–335 (The MIT Press, 1991).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Huntington's Disease Society of America, the Novartis Foundation and the Swiss National Science; Foundation. We thank L. Glauser for technical assistance; F. Brunet, S. Lengacher, I. Allamand, M. Marti, L. Claivaz, M. Delorenzi, T. Sengstag, D. Goldstein and S. Brahmachari for helpful discussions; B. Deplancke, J. Rougemont, I. Krier and M. Nalls for critically reading the manuscript; members of Vital-IT and the Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics for providing computing infrastructure, and members of the Lausanne DNA Array facility for assistance in processing microarray samples from primary cell cultures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K. developed and applied PSEA, performed experiments with cultured cells, and wrote the manuscript, with input from R.L.-C; D.T., H.J.W. and R.L.M.F. performed immunohistochemical experiments with brain sections; and R.L.-C. conceptualized the project and directed the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–21, Supplementary Tables 1–15,17–18, Supplementary Data 1–7, Supplementary Discussion (PDF 7675 kb)
Supplementary Table 16
Standard differential expression analysis showing differential total expression (HD grade 1 versus control samples). (XLSX 3345 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhn, A., Thu, D., Waldvogel, H. et al. Population-specific expression analysis (PSEA) reveals molecular changes in diseased brain. Nat Methods 8, 945–947 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1710
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1710