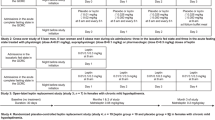
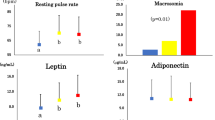
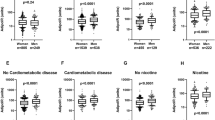
Abstract
Leptin, the gene product of the obese gene, may play an important role in regulating body weight by signalling the size of the adipose tissue mass. Plasma leptin was found to be highly correlated with body mass index (BMI) in rodents and in 87 lean and obese humans. In humans, there was variability in plasma leptin at each BMI suggesting that there are differences in its secretion rate from fat. Weight loss due to food restriction was associated with a decrease in plasma leptin in samples from mice and obese humans.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halaas, J.L. et al. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 269, 543–546 (1995).
Campfield, L.A., Smith, F.J., Guisez, Y., Devos, R. & Burn, P. Recombinant mouse OB protein: Evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science 269, 546–549 (1995).
Pelleymounter, M.A. et al. Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 269, 540–543 (1995).
Zhang, Y. et al. Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372, 425–432 (1994).
Maffei, M. et al. Increased expression in adipocytes of ob RNA in mice with lesions of the hypothalamus and with mutations at the db locus. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 6957–6960 (1995).
Green, E.D. et al. The human obese (OB) gene: RNA expression pattern and mapping on the physical, cytogenetic, and genetic maps of chromosome 7. Genome Res. 5, 5–12 (1995).
Masuzaki, H. et al. Adipocyte-specific expression and regional differences in the adipose tissue. Diabetes 44, 855–858 (1995).
Kennedy, G.C. The role of depot fat in the hypothalamic control of food intake in the rat. Proc. R. Soc. (London)(B) 140, 578–592 (1953).
Coleman, D.L. Obese and diabetes: Two mutant genes causing diabetes-obesity syndromes in mice Diabetologia 14, 141–148 (1978).
Bennett, W.I. Beyond overeating. New Engl. J. Med. 332, 673–674 (1995).
Lindpaintner, K. Clinical implications of basic research: Finding an obesity gene — A tale of mice and man. New Engl. J. Med. 332, 679–680 (1995).
Friedman, J.M., Leibel, R.L., Siegel, D., Walsh, J. & Bahary, N. Molecular mapping of the mouse ob mutation. Genomics 11, 1054–1062 (1991).
Truett, G.E., Bahary, N., Friedman, J.M. & Leibel, R.L. The rat obesity gene fatty (fa) maps to chromosome 5: Evidence for homology with the mouse gene diabetes (db). Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U. S.A. 88, 7806–7809 (1991).
Debons, A.F., Krimsky, I., Maayan, M.L., Fani, K. & Jimenez, F.A. Gold thioglucose obesity syndrome. Fed. Proc. 36, 143–147 (1977).
West, D.B., Boozer, C.N., Moody, D.L. & Atkinson, R.L. Obesity induced by a high fat diet in nine strains of inbred mice. Am. J. Physiol. 262, R1025–R1032 (1992).
Barrows, C.H. & Kokkonen, C.G. Relationship between nutrition and aging. Adv. Nutr. Res. 1, 253–298 (1977).
MacDougald, O.A., Hwang, C.S., Fan, F. & Lane, M.D. Regulated expression of the obese gene product (leptin) in white adipose tissue and 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (in the press).
Knowler, W.C., Pettitt, D.J. & Saad, M.F. Obesity in the Pima Indians: Its magnitude and relationship with diabetes. Am. J. clin. Nutr. 53, 1543S–1551S (1991).
Dawson-Saunders, B. & Trapp, R.G. Basic and Clinical Biostatistics (Appleton & Lange, Norwalk, Connecticut, 1990).
Pouliot, M.C. et al. Waist circumference and abdominal sagittal diameter: Best simple anthropometric indexes of abdominal visceral adipose tissue accumulation and related cardiovascular risk in men and women. Am. J. Cardiol. 73, 460–468 (1994).
Mohan, S. & Baylink, D.J. Development of a simple valid method for the complete removal of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding proteins from IGFs in human serum and other biological fluids: Comparison with acid-ethanol treatment and C18 Sep-Pak separation. J. clin. Endocrin. Metab. 80, 637–647 (1995).
Tannenbaum, G.S. & Martin, J.B. Evidence for an endogenous ultradian rhythm governing growth hormone secretion in the rat. Endocrinology 98, 562–570 (1976).
Murakami, T. & Shima, K. Cloning of rat obese cDNA and Its expression in obese rats. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 209, 944–952 (1995).
Bultman, S.J., Michaud, E.J. & Woychik, R.P. Molecular characterization of the mouse agouti locus. Cell 71, 1195–1204 (1992).
Miller, M.W. et al. Cloning of the mouse agouti gene predicts a secreted protein ubiquitously expressed in mice carrying the lethal yellow mutation. Genes Devl. 7, 454–467 (1993).
Lu, D. et al. Agouti protein is an antagonist of the melanocyte-stimulating-hormone receptor. Nature 371, 799–802 (1994).
Coleman, D.L. & Eicher, E.M. Fat (fat) and tubby (tub), two autosomal recessive mutations causing obesity syndromes in the mouse. J. Hered. 81, 424–427 (1990).
Naggert, J.K. et al. Hyperproinsulinaemia in obese fat/fat mice associated with a carboxypeptidase E mutation which reduces enzyme activity. Nature Genet. 10, 135–142 (1995).
Funahashl, T. et al. Enhanced expression of rat obese (ob) gene in adipose tissues of ventromedial hypothalamus (VMH)-lesioned rats. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 211, 469–475 (1995).
Hervey, G.R. The effects of lesions in the hypothalamus in parabiotic rats. J. Physiol. 145, 336–352 (1959).
Trayhurn, P., Thomas, M.E.A., Duncan, J.S. & Rayner, D.V. Effects of fasting and refeeding on ob gene expression in white adipose tissue of lean and obese (ob/ob) mice. FEBS Letters 368, 488–490 (1995).
Lonnqvist, F., Arner, P., Nordfors, L. & Schalling, M. Overexpression of the obese (ob) gene in adipose tissue of human obese subjects. Nature Med. 1, 950–953 (1995).
Hamilton, B.S., Paglia, D., Kwan, A.Y.M. & Deitel, M. Increased obese mRNA expression in omental fat cells from massively obese humans. Nature Med. 1, 953–956 (1995).
Leibel, R.L., Rosenbaum, M. & Hirsch, J. Changes in energy expenditure resulting from altered body weight. New Engl. J. Med. 332, 621–628 (1995).
Leibel, R.L. A biologic radar system for the assessment of body mass. The model of a geometry sensitive endocrine system is presented. J. theor. Biol. 66, 297–306 (1977).
Weigle, D.S. Appetite and the regulation of body composition. FASEB J. 8, 302–310 (1994).
Abrams, J.S. et al. Strategies of anti-cytokine monoclonal antibody development: Immunoassay of IL-10 and IL-5 in clinical samples. Immunol. Rev. 127, 5–24 (1992).
Harlow, E. & Lane, D. Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 1988).
Kern, P.A., Ong, J.M., Saffari, B. & Carty, J. The effects of weight loss on the activity and expression of adipose-tissue lipoprotein lipase in very obese humans. New Engl. J. Med. 322, 1053–1059 (1990).
Kern, P.A. et al. The expression of tumor necrosis factor in human adipose tissue. Regulation by obesity, weight loss, and relationship to lipoprotein lipase. J. clin. Invest. 95, 2111–2119 (1995).
Diabetes Mellitus: Report of a WHO Study Group. WHO Tech. Rep. 727, 796–769 (World Health Organization, Geneva, 1985).
Lillioja, S. et al. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction as precursors of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. New Engl. J. Med. 329, 1988–1992 (1993).
Goldman, R.F. & Bushkirk, E.R. Body volume measurement by underwater weighing: Description of a method. in Techniques for Measuring Body Composition: Proceedings of a Conference: Quartermaster Research and Engineering Center (eds Brozek, J. & Henschel, A.) 78–89 (National Research Council, Washington, DC, 1959).
Siri, W.E. Body composition from fluid spaces and density: Analysis of methods. In Techniques for Measuring Body Composition: Proceedings of a Conference: Quartermaster Research and Engineering Center (eds Brozek, J. & Henschel, A.) 223–244 (National Research Council, Washington, DC, 1959).
Chomczynski, P. & Sacchi, N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Analyt. Biochem. 162, 156–159 (1987).
Simsolo, R.B., Ong, J.M. & Kern, P.A. The regulation of adipose tissue and muscle lipoprotein lipase in runners by detraining. J. clin. Invest, 92, 2124–2130 (1993).
Feinberg, A.P. & Vogelstein, B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Analyt. Biochem. 132, 6–13 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maffei, M., Halaas, J., Ravussin, E. et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med 1, 1155–1161 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1195-1155
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1195-1155
This article is cited by
-
Hypothalamic-Ovarian axis and Adiposity Relationship in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Physiopathology and Therapeutic Options for the Management of Metabolic and Inflammatory Aspects
Current Obesity Reports (2024)
-
Leptin and ghrelin dynamics: unraveling their influence on food intake, energy balance, and the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2024)
-
Serum levels of adiponectin differentiate generalized lipodystrophies from anorexia nervosa
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation (2024)
-
Associations between chronic widespread pain, pressure pain thresholds, leptin, and metabolic factors in individuals with knee pain
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2023)
-
Implications of immunometabolism for smouldering MS pathology and therapy
Nature Reviews Neurology (2023)