Abstract
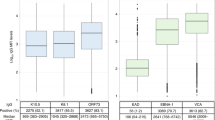
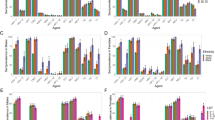
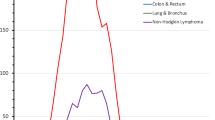
Striking differences in Kaposi's sarcoma (KS) risk for AIDS patients who acquire HIV via homosexual activity and those whose HIV infections derive from blood product exposure suggest the presence of a sexually transmitted agent other than HIV in the development of KS. Using an immunofluorescence assay, we examined serum samples from 913 patients for the presence of antibody specific for infection by human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8), an agent whose genome is regularly found in KS tissue. The distribution of HHV8 seropositivity conforms to that expected for a sexually transmitted pathogen and tracks closely with the risk for KS development. Our data support the inference that this virus is the etiologic cofactor predicted by the epidemiology of KS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beral, V. Epidemiology of Kaposi's sarcoma. Cancer Surv. 10, 5–22 (1991).
Ziegler, J., Templeton, A.C. & Voegel, G.L. KS: A comparison of classical, endemic and epidemic forms. Semin. Oncol. 11, 47–52 (1984).
Penn, I. Kaposi's sarcoma in organ transplant recipients. Transplantation 27, 8–11 (1979).
Beral, V., Peterman, T., Berkelman, R. & Jaffe, H.W. Kaposi's sarcoma among persons with AIDS: A sexually transmitted infection? Lancet 335, 123–128 (1990).
Friedman-Kien, A.E. et al. Kaposi's sarcoma in HIV-negative homosexual men. Lancet 335, 168–169 (1990).
Chang, Y. et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science 266, 1865–1869 (1994).
Ambroziak, J. et al. Herpesvirus-like sequences in HIV-infected and uninfected Kaposi's sarcoma patients (Technical Comment). Science 268, 582–583 (1995).
Moore, P. & Chang, Y. Detection of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in Kaposi's sarcoma patients with and those without HIV infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1181–1185 (1995).
Schalling, M., Ekman, M., Kaaya, E.E., Linde, A. & Biberfeld, P. A role for a new herpes virus (KSHV) in different forms of Kaposi's sarcoma. Nature Med. 1, 707–708 (1995).
Chuck, S., Grant, R.M., Katongole-Mbidde, E., Conant, M. & Ganem, D. Frequent presence of herpesviral-like DNA sequences in lesions of HIV-negative Kaposi's sarcoma. J. Infect. Dis. 173, 248–251 (1996).
Huang, Y.-Q. et al. Human herpesvirus-like DNA sequence in various forms of Kaposi's sarcoma. Lancet 345, 759–761 (1995).
Soulier, J. et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in multicentric Castleman's disease. Blood 86, 1276–1280 (1995).
Cesarmen, E., Chang, Y., Moore, P.S., Said, J.W. & Knowles, D.M. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity-based lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1186–1191 (1995).
Boshoff, C. et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infects endothelial and spindle cells. Nature Med. 1, 1274–1278 (1995).
Whitby, D. et al. Detection of Kaposi sarcoma associated herpesvirus in peripheral blood of HIV-infected individuals and progression to Kaposi's sarcoma. Lancet 346, 799–802 (1995).
Moore, P. et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection prior to onset of Kaposi's sarcoma. AIDS 10, 175–180 (1995).
Lin, J.C. et al. Is Kaposi's-sarcoma-associated herpesvirus detectable in semen of HIV-infected homosexual men? Lancet 346, 1601–1602 (1995).
Monini, P., DeLellis, L., Fabris, M., Rigolin, F. & Cassai, E. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus DNA sequences in prostate tissue and human semen. N. Engl. J. Med. 334, 1168–1172 (1996).
Rady, P.L. et al. Herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in non-Kaposi's sarcoma skin lesions of transplant patients. Lancet 345, 1339–1340 (1995).
Adams, V. et al. Absence of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in skin cancers of non-immunosuppressed patients. Lancet 346, 1715–1716 (1995).
Boshoff, C. et al. HHV8 and skin cancers in immunosuppressed patients. Lancet 347, 338–339 (1996).
Strauss, S. Introduction to herpesviridae. in Principles and Practice of Infectious Diseases (eds. MandelG., Bennett.W. & Dolin, R.) 1330–1334 (Churchill-Livingstone, New York, 1995).
Henle, G., Henle, W. & Horwitz, C. Antibodies to Epstein Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen in infectious mononucleosis. /. Infect. Dis. 130, 231–239 (1974).
Rickinson, A. & Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus. in Virology 3rd edn. (eds. Fields B., Knipe D. Howley, P.) 2397–2446 (Raven, New York, 1995.
Renne, R. et al. Lytic growth of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (human herpesvirus 8) in culture. Nature Med. 2, 342–346 (1996).
Cesarman, E. et al. In vitro establishment and characterization of two AIDS-related lymphoma cell lines containing Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences. Blood 86, 2708–2714 (1995).
Moore, P. et al. Primary characterization of a herpesvirus agent associated with Kaposi's sarcoma. J. Virol. 70, 549–558 (1996).
Operskalski, E.A. et al. and the Transfusion Safety Study Group. Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection: Relationship of risk group and age to rate of progression to AIDS. J. Infect. Dis. 172, 648–655 (1995).
Kieff, E. Epstein-Barr virus and its replication. in Virology, 3rd edn. (eds. Fields, B., Knipe, D. Howley, P.) 2343–2396 (Raven, New York, 1995
Miller, G. et al. Antibodies to butyrate-inducible antigens of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus in patients with HIV-1 infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 334, 1292–1297 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kedes, D., Operskalski, E., Busch, M. et al. The seroepidemiology of human herpesvirus 8 (Kaposi's sarcoma–associated herpesvirus): Distribution of infection in KS risk groups and evidence for sexual transmission. Nat Med 2, 918–924 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0896-918
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0896-918
This article is cited by
-
Seroprevalence and risk factors for Kaposi’s Sarcoma associated herpesvirus among men who have sex with men in Shanghai, China
BMC Infectious Diseases (2023)
-
Seroprevalence of antibodies against Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus among HIV-negative people in China
Infectious Agents and Cancer (2017)
-
Prevalence of Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus among intravenous drug users: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Virologica Sinica (2017)
-
The Role of Nuclear Medicine in the Staging and Management of Human Immune Deficiency Virus Infection and Associated Diseases
Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging (2017)
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Kaposi Sarcoma
American Journal of Clinical Dermatology (2017)