Abstract
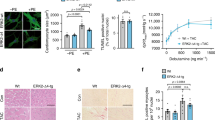
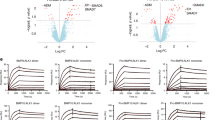
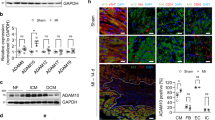
G-protein–coupled receptor (GPCR) agonists are well-known inducers of cardiac hypertrophy. We found that the shedding of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) resulting from metalloproteinase activation and subsequent transactivation of the epidermal growth factor receptor occurred when cardiomyocytes were stimulated by GPCR agonists, leading to cardiac hypertrophy. A new inhibitor of HB-EGF shedding, KB-R7785, blocked this signaling. We cloned a disintegrin and metalloprotease 12 (ADAM12) as a specific enzyme to shed HB-EGF in the heart and found that dominant-negative expression of ADAM12 abrogated this signaling. KB-R7785 bound directly to ADAM12, suggesting that inhibition of ADAM12 blocked the shedding of HB-EGF. In mice with cardiac hypertrophy, KB-R7785 inhibited the shedding of HB-EGF and attenuated hypertrophic changes. These data suggest that shedding of HB-EGF by ADAM12 plays an important role in cardiac hypertrophy, and that inhibition of HB-EGF shedding could be a potent therapeutic strategy for cardiac hypertrophy.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katz, A.M. Cardiomyopathy of overload. A major determinant of prognosis in congestive heart failure. N. Engl. J. Med. 322, 100–110 (1990).
Levy, D., Garrison, R.J., Savage, D.D., Kannel, W.B. & Castelli, W.P. Prognostic implications of echocardiographically determined left ventricular mass in the Framingham Heart Study. N. Engl. J. Med 322, 1561–1566 (1990).
Simpson, P., McGrath, A. & Savion, S. Myocyte hypertrophy in neonatal rat heart cultures and its regulation by serum and by catecholamines. Circ. Res. 51, 787–801 (1982).
Ito, H. et al. Endothelin-1 induces hypertrophy with enhanced expression of muscle-specific genes in cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 69, 209–215 (1991).
Sadoshima, J., Xu, Y., Slayter, H.S. & Izumo, S. Autocrine release of angiotensin II mediates stretch-induced hypertrophy of cardiac myocytes in vitro. Cell 75, 977–984 (1993).
Schmieder, R.E., Martus, P. & Klingbeil, A. Reversal of left ventricular hypertrophy in essential hypertension. A meta-analysis of randomized double-blind studies. JAMA 275, 1507–1513 (1996).
Effects of enalapril on mortality in severe congestive heart failure. Results of the Cooperative North Scandinavian Enalapril Survival Study (CONSENSUS). The CONSENSUS Trial Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 316, 1429–1435 (1987).
Chien, K.R. et al. Transcriptional regulation during cardiac growth and development. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 55, 77–95 (1993).
Sadoshima, J. & Izumo, S. The cellular and molecular response of cardiac myocytes to mechanical stress. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 59, 551–571 (1997).
Daub, H., Weiss, F.U., Wallasch, C. & Ullrich, A. Role of transactivation of the EGF receptor in signalling by G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature 379, 557–560 (1996).
Tsai, W., Morielli, A.D. & Peralta, E.G. The m1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor transactivates the EGF receptor to modulate ion channel activity. EMBO J. 16, 4597–4605 (1997).
Zwick, E. et al. Critical role of calcium-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation in PC12 cell membrane depolarization and bradykinin signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 24767–24770 (1997).
Eguchi, S. et al. Calcium-dependent epidermal growth factor receptor transactivation mediates the angiotensin II-induced mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8890–8896 (1998).
Prenzel, N. et al. EGF receptor transactivation by G-protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage of proHB-EGF. Nature 402, 884–888 (1999).
Spinale, F.G. et al. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibition during the development of congestive heart failure: effects on left ventricular dimensions and function. Circ. Res. 85, 364–376 (1999).
Tokumaru, S. et al. Ectodomain shedding of epidermal growth factor receptor ligands is required for keratinocyte migration in cutaneous wound healing. J. Cell Biol. 151, 209–220 (2000)
Goishi, K. et al. Phorbol ester induces the rapid processing of cell surface heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor: Conversion from juxtacrine to paracrine growth factor activity. Mol. Biol. Cell 6, 967–980 (1995).
Izumi, Y. et al. A metalloprotease-disintegrin, MDC9/meltrin-γ/ADAM9 and PKCδ are involved in TPA-induced ectodomain shedding of membrane-anchored heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor. EMBO J. 17, 7260–7272 (1998).
Moss, M.L. et al. Cloning of a disintegrin metalloproteinase that processes precursor tumour-necrosis factor-α. Nature 385, 733–736 (1997).
Friddle, C.J., Koga, T., Rubin, E.M. & Bristow, J. Expression profiling reveals distinct sets of genes altered during induction and regression of cardiac hypertrophy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6745–6750 (2000).
Saadane, N., Alpert, L. & Chalifour, L.E. Expression of immediate early genes, GATA-4, and Nkx-2.5 in adrenergic-induced cardiac hypertrophy and during regression in adult mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 127, 1165–1176 (1999).
Higashiyama, S., Lau, K., Besner, G., Abraham, J. A. & Klagsbrun, M. Structure of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor: Multiple forms, primary structure, and glycosylation of the mature protein. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 6205–6212 (1992).
Acknowledgements
We thank J.A. Abraham for helpful comments and advice; and J. Yamada, A. Ohno, T. Fukushima, A. Ogai and S. Mori for technical assistance. This study is supported by Grant-in-aid for Scientific Research (No. 09281102, 12370153 and 12877107) from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asakura, M., Kitakaze, M., Takashima, S. et al. Cardiac hypertrophy is inhibited by antagonism of ADAM12 processing of HB-EGF: Metalloproteinase inhibitors as a new therapy. Nat Med 8, 35–40 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0102-35
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0102-35
This article is cited by
-
Serum biomarkers associated with SARS-CoV-2 severity
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
ADAM10 and ADAM17 regulate EGFR, c-Met and TNF RI signalling in liver regeneration and fibrosis
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Contribution of ADAM17 and related ADAMs in cardiovascular diseases
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2021)
-
Role of hypoxia-related proteins in adenoid cystic carcinoma invasion
Diagnostic Pathology (2020)
-
Propofol affects the growth and metastasis of pancreatic cancer via ADAM8
Pharmacological Reports (2020)