Abstract
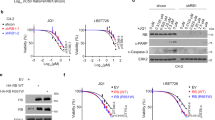
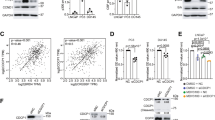
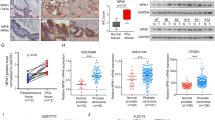
The bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) family of proteins comprises four members—BRD2, BRD3, BRD4 and the testis-specific isoform BRDT—that largely function as transcriptional coactivators1,2,3 and play critical roles in various cellular processes, including the cell cycle, apoptosis, migration and invasion4,5. BET proteins enhance the oncogenic functions of major cancer drivers by elevating the expression of these drivers, such as c-Myc in leukemia6,7, or by promoting the transcriptional activities of oncogenic factors, such as AR and ERG in prostate cancer8. Pathologically, BET proteins are frequently overexpressed and are clinically linked to various types of human cancer5,9,10; they are therefore being pursued as attractive therapeutic targets for selective inhibition in patients with cancer. To this end, a number of bromodomain inhibitors, including JQ1 and I-BET, have been developed11,12 and have shown promising outcomes in early clinical trials. Although resistance to BET inhibitors has been documented in preclinical models13,14,15, the molecular mechanisms underlying acquired resistance are largely unknown. Here we report that cullin-3SPOP earmarks BET proteins, including BRD2, BRD3 and BRD4, for ubiquitination-mediated degradation. Pathologically, prostate cancer–associated SPOP mutants fail to interact with and promote the degradation of BET proteins, leading to their elevated abundance in SPOP-mutant prostate cancer. As a result, prostate cancer cell lines and organoids derived from individuals harboring SPOP mutations are more resistant to BET-inhibitor-induced cell growth arrest and apoptosis. Therefore, our results elucidate the tumor-suppressor role of SPOP in prostate cancer in which it acts as a negative regulator of BET protein stability and also provide a molecular mechanism for resistance to BET inhibitors in individuals with prostate cancer bearing SPOP mutations.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeng, L. & Zhou, M.M. Bromodomain: an acetyl-lysine binding domain. FEBS Lett. 513, 124–128 (2002).
Wu, S.Y. & Chiang, C.M. The double bromodomain–containing chromatin adaptor Brd4 and transcriptional regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 13141–13145 (2007).
Filippakopoulos, P. & Knapp, S. The bromodomain interaction module. FEBS Lett. 586, 2692–2704 (2012).
Filippakopoulos, P. & Knapp, S. Targeting bromodomains: epigenetic readers of lysine acetylation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13, 337–356 (2014).
Belkina, A.C. & Denis, G.V. BET domain co-regulators in obesity, inflammation and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 12, 465–477 (2012).
Delmore, J.E. et al. BET bromodomain inhibition as a therapeutic strategy to target c-Myc. Cell 146, 904–917 (2011).
Mertz, J.A. et al. Targeting MYC dependence in cancer by inhibiting BET bromodomains. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 108, 16669–16674 (2011).
Asangani, I.A. et al. Therapeutic targeting of BET bromodomain proteins in castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 510, 278–282 (2014).
French, C.A. et al. BRD4-NUT fusion oncogene: a novel mechanism in aggressive carcinoma. Cancer Res. 63, 304–307 (2003).
Crawford, N.P. et al. Bromodomain 4 activation predicts breast cancer survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 6380–6385 (2008).
Filippakopoulos, P. et al. Selective inhibition of BET bromodomains. Nature 468, 1067–1073 (2010).
Nicodeme, E. et al. Suppression of inflammation by a synthetic histone mimic. Nature 468, 1119–1123 (2010).
Fong, C.Y. et al. BET inhibitor resistance emerges from leukaemia stem cells. Nature 525, 538–542 (2015).
Rathert, P. et al. Transcriptional plasticity promotes primary and acquired resistance to BET inhibition. Nature 525, 543–547 (2015).
Shu, S. et al. Response and resistance to BET bromodomain inhibitors in triple-negative breast cancer. Nature 529, 413–417 (2016).
Holohan, C., Van Schaeybroeck, S., Longley, D.B. & Johnston, P.G. Cancer drug resistance: an evolving paradigm. Nat. Rev. Cancer 13, 714–726 (2013).
Gottesman, M.M. Mechanisms of cancer drug resistance. Annu. Rev. Med. 53, 615–627 (2002).
Housman, G. et al. Drug resistance in cancer: an overview. Cancers (Basel) 6, 1769–1792 (2014).
Genschik, P., Sumara, I. & Lechner, E. The emerging family of CULLIN3–RING ubiquitin ligases (CRL3s): cellular functions and disease implications. EMBO J. 32, 2307–2320 (2013).
Vitari, A.C. et al. COP1 is a tumour suppressor that causes degradation of ETS transcription factors. Nature 474, 403–406 (2011).
Jang, M.K. et al. The bromodomain protein Brd4 is a positive regulatory component of P-TEFb and stimulates RNA polymerase II–dependent transcription. Mol. Cell 19, 523–534 (2005).
Yang, Z. et al. Recruitment of P-TEFb for stimulation of transcriptional elongation by the bromodomain protein Brd4. Mol. Cell 19, 535–545 (2005).
Wu, S.Y., Lee, A.Y., Lai, H.T., Zhang, H. & Chiang, C.M. Phospho switch triggers Brd4 chromatin binding and activator recruitment for gene-specific targeting. Mol. Cell 49, 843–857 (2013).
Zhuang, M. et al. Structures of SPOP–substrate complexes: insights into molecular architectures of BTB–Cul3 ubiquitin ligases. Mol. Cell 36, 39–50 (2009).
Barbieri, C.E. et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent SPOP, FOXA1 and MED12 mutations in prostate cancer. Nat. Genet. 44, 685–689 (2012).
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. The molecular taxonomy of primary prostate cancer. Cell 163, 1011–1025 (2015).
Theurillat, J.P. et al. Ubiquitylome analysis identifies dysregulation of effector substrates in SPOP-mutant prostate cancer. Science 346, 85–89 (2014).
Gan, W. et al. SPOP promotes ubiquitination and degradation of the ERG oncoprotein to suppress prostate cancer progression. Mol. Cell 59, 917–930 (2015).
Zhong, Q. et al. Image-based computational quantification and visualization of genetic alterations and tumour heterogeneity. Sci. Rep. 6, 24146 (2016).
Lu, G. et al. The myeloma drug lenalidomide promotes the cereblon-dependent destruction of Ikaros proteins. Science 343, 305–309 (2014).
Krönke, J. et al. Lenalidomide causes selective degradation of IKZF1 and IKZF3 in multiple myeloma cells. Science 343, 301–305 (2014).
Winter, G.E. et al. Phthalimide conjugation as a strategy for in vivo target protein degradation. Science 348, 1376–1381 (2015).
Kumar-Sinha, C., Tomlins, S.A. & Chinnaiyan, A.M. Recurrent gene fusions in prostate cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 8, 497–511 (2008).
Rubin, M.A., Maher, C.A. & Chinnaiyan, A.M. Common gene rearrangements in prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 29, 3659–3668 (2011).
Gao, D. et al. Organoid cultures derived from patients with advanced prostate cancer. Cell 159, 176–187 (2014).
Wei, W. et al. Degradation of the SCF component Skp2 in cell-cycle phase G1 by the anaphase-promoting complex. Nature 428, 194–198 (2004).
Boehm, J.S., Hession, M.T., Bulmer, S.E. & Hahn, W.C. Transformation of human and murine fibroblasts without viral oncoproteins. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 6464–6474 (2005).
Inuzuka, H. et al. Phosphorylation by casein kinase I promotes the turnover of the Mdm2 oncoprotein via the SCFβ-TRCP ubiquitin ligase. Cancer Cell 18, 147–159 (2010).
Drost, J. et al. Organoid culture systems for prostate epithelial and cancer tissue. Nat. Protoc. 11, 347–358 (2016).
Gao, J. et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 6, pl1 (2013).
Humphrey, P.A., Moch, H., Cubilla, A.L., Ulbright, T.M. & Reuter, V.E. The 2016 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs—Part B: Prostate and Bladder Tumours. Eur. Urol. 70, 106–119 (2016).
Acknowledgements
We thank N. Mitsiades (Baylor College of Medicine), P. Zhou (Weill Cornell Medical College), W. Kaelin (Dana-Farber Cancer Institute), C. French (Brigham and Women's Hospital), R.-H. Chen (Institute of Biological Chemistry, Academia Sinica), S. Uchida (Tokyo Medical and Dental University), J. Yuan (Harvard Medical School) and S.-Y. Shao (Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center) for their contributed materials. We thank F. Wu, B. Wang, N.T. Nihira and B. North for critical reading of the manuscript and members of the Wei and Bradner laboratories for useful discussions. X.D. and J.G. are supported by a National Research Service Award T-32 training grant. W.G. is supported by 1K99CA207867 from the National Cancer Institute. D.L.B. is a Merck Fellow of the Damon Runyon Cancer Research Foundation (DRG-2196-14). P.J.W. is funded in part by a H2020 grant from the European Commission (PrECISE) and a research grant from the University of Zurich, Switzerland. W.W. is an American Cancer Society research scholar. This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants (W.W., GM094777 and CA177910).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.D., W.G. and X.L. designed and performed most of the experiments with assistance from J.G., J.Z., K.S., H.I., P.L., L.W. and L.A.G. W.Z., Q.Z., L.B., P.J.W. and J.H. performed IHC. X.D., W.G., J.G., J.Z., S.L., T.C. and K.-K.W. performed the xenograft assays. L.H., S.W., S.K.M. and Y.C. performed the 3D cell culture assays. F.B. and A.H.B. performed the bioinformatics analysis. D.V., M.B., M.A.R. and C.E.B. performed assays with transgenic mice. D.L.B., J.Q. and J.E.B. provided BET inhibitors and performed related drug treatment. W.W. designed the experiments and supervised the study. W.G., X.D. and W.W. wrote the manuscript. All authors commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–14. (PDF 18106 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, X., Gan, W., Li, X. et al. Prostate cancer–associated SPOP mutations confer resistance to BET inhibitors through stabilization of BRD4. Nat Med 23, 1063–1071 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4378
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4378