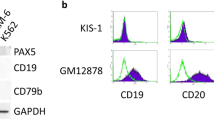
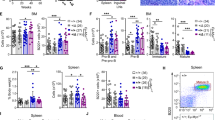
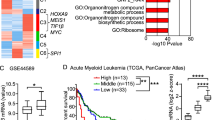
Abstract
The BCL6 proto-oncogene encodes a transcriptional repressor that is required for germinal center formation and has been linked to lymphomagenesis. BCL6 functions by directly binding to specific DNA sequences and suppressing the transcription of target genes. Here we report an alternative mechanism by which BCL6 controls the transcription of genes lacking a BCL6 binding site and show that this mechanism was required for the prevention of tumor suppressor p53–independent cell cycle arrest in germinal center B cells. BCL6 interacted with the transcriptional activator Miz-1 and, via Miz-1, bound to the promoter and suppressed transcription of the cell cycle arrest gene CDKN1A. Through this mechanism, BCL6 may facilitate the proliferative expansion of germinal centers during the normal immune response and, when deregulated, the pathological expansion of B cell lymphomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye, B.H. et al. Alterations of a zinc finger-encoding gene, BCL-6, in diffuse large-cell lymphoma. Science 262, 747–750 (1993).
Chang, C.C., Ye, B.H., Chaganti, R.S. & Dalla-Favera, R. BCL-6, a POZ/zinc-finger protein, is a sequence-specific transcriptional repressor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 6947–6952 (1996).
Seyfert, V.L., Allman, D., He, Y. & Staudt, L.M. Transcriptional repression by the proto-oncogene BCL-6. Oncogene 12, 2331–2342 (1996).
Dhordain, P. et al. Corepressor SMRT binds the BTB/POZ repressing domain of the LAZ3/BCL6 oncoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10762–10767 (1997).
Wong, C.W. & Privalsky, M.L. Components of the SMRT corepressor complex exhibit distinctive interactions with the POZ domain oncoproteins PLZF, PLZF-RARα, and BCL-6. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 27695–27702 (1998).
Fujita, N. et al. MTA3 and the Mi-2/NuRD complex regulate cell fate during B lymphocyte differentiation. Cell 119, 75–86 (2004).
Pasqualucci, L. et al. Molecular pathogenesis of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: the role of Bcl-6. Leuk. Lymphoma 44, S5–12 (2003).
Cattoretti, G. et al. BCL-6 protein is expressed in germinal-center B cells. Blood 86, 45–53 (1995).
Allman, D. et al. BCL-6 expression during B-cell activation. Blood 87, 5257–5268 (1996).
MacLennan, I.C. Germinal centers. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12, 117–139 (1994).
Rajewsky, K. Clonal selection and learning in the antibody system. Nature 381, 751–758 (1996).
Ye, B.H. et al. The BCL-6 proto-oncogene controls germinal-centre formation and Th2-type inflammation. Nat. Genet. 16, 161–170 (1997).
Dent, A.L., Shaffer, A.L., Yu, X., Allman, D. & Staudt, L.M. Control of inflammation, cytokine expression, and germinal center formation by BCL-6. Science 276, 589–592 (1997).
Niu, H., Ye, B.H. & Dalla-Favera, R. Antigen receptor signaling induces MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation and degradation of the BCL-6 transcription factor. Genes Dev. 12, 1953–1961 (1998).
Bereshchenko, O.R., Gu, W. & Dalla-Favera, R. Acetylation inactivates the transcriptional repressor BCL6. Nat. Genet. 32, 606–613 (2002).
Tunyaplin, C. et al. Direct repression of prdm1 by Bcl-6 inhibits plasmacytic differentiation. J. Immunol. 173, 1158–1165 (2004).
Fearon, D.T., Manders, P.M. & Wagner, S.D. Bcl-6 uncouples B lymphocyte proliferation from differentiation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 512, 21–28 (2002).
Lo Coco, F. et al. Rearrangements of the BCL6 gene in diffuse large cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Blood 83, 1757–1759 (1994).
Ye, B.H. et al. Chromosomal translocations cause deregulated BCL6 expression by promoter substitution in B cell lymphoma. EMBO J. 14, 6209–6217 (1995).
Chen, W., Iida, S., Louie, D.C., Dalla-Favera, R. & Chaganti, R.S. Heterologous promoters fused to BCL6 by chromosomal translocations affecting band 3q27 cause its deregulated expression during B-cell differentiation. Blood 91, 603–607 (1998).
Shen, H.M., Peters, A., Baron, B., Zhu, X. & Storb, U. Mutation of BCL-6 gene in normal B cells by the process of somatic hypermutation of Ig genes. Science 280, 1750–1752 (1998).
Pasqualucci, L. et al. BCL-6 mutations in normal germinal center B cells: evidence of somatic hypermutation acting outside Ig loci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11816–11821 (1998).
Migliazza, A. et al. Frequent somatic hypermutation of the 5′ noncoding region of the BCL6 gene in B-cell lymphoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 12520–12524 (1995).
Pasqualucci, L. et al. Mutations of the BCL6 proto-oncogene disrupt its negative autoregulation in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 101, 2914–2923 (2003).
Wang, X., Li, Z., Naganuma, A. & Ye, B.H. Negative autoregulation of BCL-6 is bypassed by genetic alterations in diffuse large B cell lymphomas. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 15018–15023 (2002).
Cattoretti, G. et al. Deregulated BCL6 expression recapitulates the pathogenesis of human diffuse large B cell lymphomas in mice. Cancer Cell 7, 445–455 (2005).
Shaffer, A.L. et al. BCL-6 represses genes that function in lymphocyte differentiation, inflammation, and cell cycle control. Immunity 13, 199–212 (2000).
Niu, H., Cattoretti, G. & Dalla-Favera, R. BCL6 controls the expression of the B7–1/CD80 costimulatory receptor in germinal center B cells. J. Exp. Med. 198, 211–221 (2003).
Phan, R.T. & Dalla-Favera, R. The BCL6 proto-oncogene suppresses p53 expression in germinal-centre B cells. Nature 432, 635–639 (2004).
Seoane, J. et al. TGFβ influences Myc, Miz-1 and Smad to control the CDK inhibitor p15INK4b. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 400–408 (2001).
Gaidano, G. et al. p53 mutations in human lymphoid malignancies: association with Burkitt lymphoma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 5413–5417 (1991).
el-Deiry, W.S. et al. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75, 817–825 (1993).
Yu, J. et al. Identification and classification of p53-regulated genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 14517–14522 (1999).
Seoane, J., Le, H.V. & Massague, J. Myc suppression of the p21(Cip1) Cdk inhibitor influences the outcome of the p53 response to DNA damage. Nature 419, 729–734 (2002).
Wu, S. et al. Myc represses differentiation-induced p21 expression via Miz-1-dependent interaction with the p21 core promoter. Oncogene 22, 351–360 (2003).
Herold, S. et al. Negative regulation of the mammalian UV response by Myc through association with Miz-1. Mol. Cell 10, 509–521 (2002).
Klein, U. et al. Transcriptional analysis of the B cell germinal center reaction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 2639–2644 (2003).
Shaffer, A.L. et al. Signatures of the immune response. Immunity 15, 375–385 (2001).
Allday, M.J., Inman, G.J., Crawford, D.H. & Farrell, P.J. DNA damage in human B cells can induce apoptosis, proceeding from G1/S when p53 is transactivation competent and G2/M when it is transactivation defective. EMBO J. 14, 4994–5005 (1995).
Chan, T.A., Hwang, P.M., Hermeking, H., Kinzler, K.W. & Vogelstein, B. Cooperative effects of genes controlling the G2/M checkpoint. Genes Dev. 14, 1584–1588 (2000).
Wanzel, M. et al. Akt and 14–3-3eta regulate Miz1 to control cell-cycle arrest after DNA damage. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 30–41 (2005).
Sheikh, M.S. et al. Mechanisms of regulation of WAF1/Cip1 gene expression in human breast carcinoma: role of p53-dependent and independent signal transduction pathways. Oncogene 9, 3407–3415 (1994).
Tang, D. et al. ERK activation mediates cell cycle arrest and apoptosis after DNA damage independently of p53. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 12710–12717 (2002).
Staller, P. et al. Repression of p15INK4b expression by Myc through association with Miz-1. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 392–399 (2001).
Seoane, J., Le, H.V., Shen, L., Anderson, S.A. & Massague, J. Integration of Smad and forkhead pathways in the control of neuroepithelial and glioblastoma cell proliferation. Cell 117, 211–223 (2004).
Papavasiliou, F.N. & Schatz, D.G. Cell-cycle-regulated DNA double-stranded breaks in somatic hypermutation of immunoglobulin genes. Nature 408, 216–221 (2000).
Sale, J.E. & Neuberger, M.S. TdT-accessible breaks are scattered over the immunoglobulin V domain in a constitutively hypermutating B cell line. Immunity 9, 859–869 (1998).
Bross, L. et al. DNA double-strand breaks in immunoglobulin genes undergoing somatic hypermutation. Immunity 13, 589–597 (2000).
Offit, K. et al. BCL6 gene rearrangement and other cytogenetic abnormalities in diffuse large cell lymphoma. Leuk. Lymphoma 20, 85–89 (1995).
Polo, J.M. et al. Specific peptide interference reveals BCL6 transcriptional and oncogenic mechanisms in B-cell lymphoma cells. Nat. Med. 10, 1329–1335 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Seoane and J. Massague (Sloan Kettering Memorial Cancer Center, New York, New York) for advice and for the Miz-1 construct; R. Tjian (University of California, Berkeley, California) for anti-Miz-1; and A. Iavarone and R. Baer for advice, discussions and critically reading the manuscript. Supported by the National Institutes of Health (R.D.-F. and R.T.P.) and the American-Italian Cancer Foundation (K.B.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phan, R., Saito, M., Basso, K. et al. BCL6 interacts with the transcription factor Miz-1 to suppress the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21 and cell cycle arrest in germinal center B cells. Nat Immunol 6, 1054–1060 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1245
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1245
This article is cited by
-
BCR-ABL triggers a glucose-dependent survival program during leukemogenesis through the suppression of TXNIP
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
RegEnrich gene regulator enrichment analysis reveals a key role of the ETS transcription factor family in interferon signaling
Communications Biology (2022)
-
BTB/POZ zinc finger protein ZBTB16 inhibits breast cancer proliferation and metastasis through upregulating ZBTB28 and antagonizing BCL6/ZBTB27
Clinical Epigenetics (2020)
-
Frequent mutations in the amino-terminal domain of BCL7A impair its tumor suppressor role in DLBCL
Leukemia (2020)
-
CHK1 dosage in germinal center B cells controls humoral immunity
Cell Death & Differentiation (2019)