Abstract
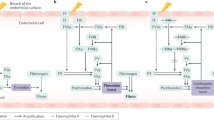
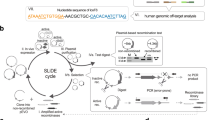
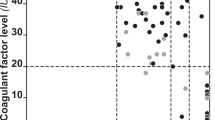
Mutations in the factor VIII gene have been discovered for barely more than half of the examined cases of severe haemophilia A. To account for the unidentified mutations, we propose a model based on the possibility of recombination between homologous sequences located in intron 22 and upstream of the factor VIII gene. Such a recombination would lead to an inversion of all intervening DNA and a disruption of the gene. We present evidence to support this model and describe a Southern blot assay that detects the inversion. These findings should be valuable for genetic prediction of haemophilia A in ∼45% of families with severe disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verkerk, A.J.M.H. et al. Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell 65, 905–914 (1991).
Kunkel, L.M. Analysis of deletions in DNA from patients with Becker and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Nature 322, 73–77 (1986).
Tuddenham, E.G.D. et al. Haemophilia A: Database of nucleotide substitutions, deletions, insertions and rearrangements of the factor VIII gene. Nucl. Acids Res. 19, 4821–4833 (1991).
Higuchi, M. et al. Molecular characterization of mild-to-moderate hemophilia A: Detection of the mutation in 25 of 29 patients by denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 8307–8311 (1991).
Higuchi, M. et al. Molecular characterization of severe hemophilia A suggests that about half the mutations are not within the coding regions and splice junctions of the factor VIII gene. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 7405–7409 (1991).
Naylor, J.A., Green, P.M., Rizza, C.R. & Giannelli, F. Analysis of factor VIII mRNA defects in everyone of 28 haemophilia A patients. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 11–17 (1993).
Gitschier, J. et al. Characterization of the human factor VIII gene. Nature 312, 326–330 (1984).
Levinson, B., Kenwrick, S., Lakich, D., Hammonds, G. & Gitschier, J. A transcribed gene in an intron of the human factor VIM gene. Genomics 7, 1–11 (1990).
Levinson, B., Kenwrick, S., Gamel, P., Fisher, K. & Gitschier, J. Evidence for a third transcript from the human factor VIII gene. Genomics 14, 585–589 (1992).
Freije, D. & Schlessinger, D. A 1.6-Mb contig of yeast artificial chromosomes around the human factor VIII gene reveals three regions homologous to probes for the DXS115 locus and two for the DXYS64 locus. Am. J. hum. Genet. 51, 66–80 (1992).
Patterson, M. et al. An intronic region within the human factor VIM gene is duplicated within Xq28 and is homologous to the polymorphic locus DXS115 (767). Am. J. hum. Genet. 44, 679–685 (1989).
Smithies, O. Chromosomal rearrangements and protein structure. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 29, 309–319 (1964).
Efremov, G.D. Hemoglobins Lepore and anti-Lepore. Hemoglobin 2, 197–233 (1978).
Yen, P.H. et al. Frequent deletions of the human X chromosome distal short arm result from recombination between low copy repetitive elements. Cell 61, 603–610 (1990).
Pentao, L., Wise, C.A., Chinault, A.C., Patel, P.I. & Lupski, J.R. Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 1A duplication appears to arise from recombination at repeat sequences flanking the 1.5 Mb monomer unit. Nature Genet. 2, 292–300 (1992).
Jones, R.W., Old, J.M., Trent, R.J., Clegg, J.B. & Weatherall, D.J. Major rearrangement in the human β-globin gene cluster. Nature 291, 39–44 (1981).
Karathanasis, S.K., Ferris, E. & Haddad, I.A. DNA inversion within the apolipoproteins AI/CIII/AIV-encoding gene cluster of certain patients with premature atherosclerosis. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 7198–7202 (1987).
Kulozik, A.E., Bellan-Koch, A., Kohne, E. & Kleihauer, E. A deletion/inversion rearrangement of the β-globin gene cluster in a Turkish family with λβo-Thalassemia Intermedia. Blood 79, 2455–2459 (1992).
Rizza, C.R. & Spooner, R.J.D. Treatment of haemophilia and related disorders in Britain and Northern Ireland during 1976–1980: report on behalf of the directors of haemophilia centres in the United Kingdom. Brit Med. J. 286, 929–933 (1983).
Katz, B.Z., Raab-Traub, N. & Miller, G. Latent and replicating forms of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in lymphomas and lymphoproliferative disease. J. inf. Dis. 160, 589–598 (1989).
Kenwrick, S. & Gitschier, J. A contiguous, 3-Mb physical map of Xq28 extending from the color-blindness locus to DXS15. Am. J. hum. Genet. 45, 873–882 (1989).
Carle, G.F. & Olson, M.V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 3756–3760 (1985).
Church, G. & Gilbert, W. Genomic sequencing. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 1991–1995 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lakich, D., Kazazian, H., Antonarakis, S. et al. Inversions disrupting the factor VIII gene are a common cause of severe haemophilia A. Nat Genet 5, 236–241 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1193-236
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1193-236