Abstract
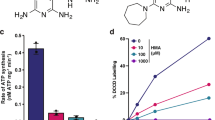
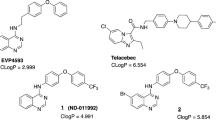
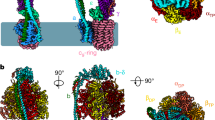
The diarylquinoline R207910 (TMC207) is a promising candidate in clinical development for the treatment of tuberculosis. Though R207910-resistant mycobacteria bear mutations in ATP synthase, the compound's precise target is not known. Here we establish by genetic, biochemical and binding assays that the oligomeric subunit c (AtpE) of ATP synthase is the target of R207910. Thus targeting energy metabolism is a new, promising approach for antibacterial drug discovery.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dye, C., Scheele, S., Dolin, P., Pathania, V. & Raviglione, M.C. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 282, 677–686 (1999).
Andries, K. et al. Science 307, 223–227 (2005).
Ji, B. et al. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 50, 1921–1926 (2006).
Junge, W. & Nelson, N. Science 308, 642–644 (2005).
Walsh, C. Nature 406, 775–781 (2000).
Telenti, A. et al. J. Clin. Microbiol. 35, 719–723 (1997).
de Jonge, M.R., Koymans, L.H., Guillemont, J.E., Koul, A. & Andries, K. Proteins published online 23 March 2007 (doi:10.1002/prot.21376).
Telenti, A. et al. Nat. Med. 3, 567–570 (1997).
Wang, R., Prince, J.T. & Marcotte, E.M. Genome Res. 15, 1118–1126 (2005).
Tran, S.L. & Cook, G.M. J. Bacteriol. 187, 5023–5028 (2005).
Ferrandiz, M.J. & de la Campa, A.G. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 212, 133–138 (2002).
Acknowledgements
We thank P. Janssens, T. Gevers, H. Szel, J. Hendrickx, A. Shanmugham, E. Pasquier, A. Poncelet, P. Palandjian, S. Masure, W. Bruinzeel and P. Verhasselt for technical help; N. Lounis, L. Geeraert and M. Haxaire-Theeuwes for critical reading; E. Mortz (Alphalyse, Denmark) for mass spectrometry analysis; H. Van Vlijmen for R207910-docking figure; L. Leijssen for help with figures; and Vichem (Budapest) for coupling experiments. Z.R., H.L. and D.B. acknowledge EU financial support (Marie-Curie MRTN-CT-2005-019481).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K. wrote the manuscript as a project team leader, with contributions from K.A., D.B. and N.D. A.K., K.A., N.D. and D.B. contributed to study design and data analysis. K.V. did ATP synthesis assay; N.D. made constructs for subunit c purification; N.D. and B.M. did affinity chromatography assays and complementation studies; R.W. contributed to DARQ screening; L.V. did ATP measurements, MIC determinations and isolation of resistant mutants; J.G. and I.D. synthesized DARQs, separated isomers and performed chemical characterizations; and H.L. and Z.R. contributed to the BIAcore binding experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Research for this project is mainly provided by Johnson & Johnson Pharmaceuticals. A.K., N.D., K.V., B.M., L.V., R.W., I.D., J.G and K.A. are employees of Johnson & Johnson.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Chemical structure of R207910 (R,S) and related isomers. (PDF 19 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Genetic organization of mycobacterial ATP synthase and homology model of subunit-c. (PDF 96 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 3
Characterization of R207910-resistant M. tuberculosis strains. (PDF 27 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 4
Binding studies using affinity capture chromatography. (PDF 76 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 5
BIAcore interaction analysis of purified whole ATP synthase from Bacillus PS3 or its α3β3γ sub-complex with R207910. (PDF 46 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
MICs of R207910 stereoisomers in different mycobacterial species. (PDF 44 kb)
Supplementary Table 2
Inhibition of M. smegmatis ATP synthase activity by DARQ compounds. (PDF 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koul, A., Dendouga, N., Vergauwen, K. et al. Diarylquinolines target subunit c of mycobacterial ATP synthase. Nat Chem Biol 3, 323–324 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio884
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio884
This article is cited by
-
The pathogenic mechanism of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: implication for new drug development
Molecular Biomedicine (2022)
-
Targeting the cytochrome bc1 complex for drug development in M. tuberculosis: review
Molecular Diversity (2022)
-
Efficacy of bedaquiline in the treatment of drug-resistant tuberculosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
BMC Infectious Diseases (2021)
-
Complex effects of macrolide venturicidins on bacterial F-ATPases likely contribute to their action as antibiotic adjuvants
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Hit movie reveals how a tuberculosis drug halts ATP synthesis
Nature (2021)