Abstract
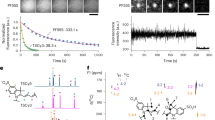
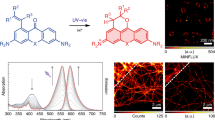
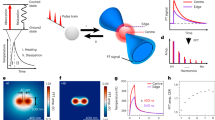
The ideal fluorescent probe for bioimaging is bright, absorbs at long wavelengths and can be implemented flexibly in living cells and in vivo. However, the design of synthetic fluorophores that combine all of these properties has proved to be extremely difficult. Here, we introduce a biocompatible near-infrared silicon–rhodamine probe that can be coupled specifically to proteins using different labelling techniques. Importantly, its high permeability and fluorogenic character permit the imaging of proteins in living cells and tissues, and its brightness and photostability make it ideally suited for live-cell super-resolution microscopy. The excellent spectroscopic properties of the probe combined with its ease of use in live-cell applications make it a powerful new tool for bioimaging.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hinner, M. & Johnsson, K. How to obtain labeled proteins and what to do with them. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 21, 766–776 (2010).
Schneckenburger, H. et al. Light exposure and cell viability in fluorescence microscopy. J. Microsc. 245, 311–318 (2012).
Pellett, P. A. et al. Two-color STED microscopy in living cells. Biomed Opt Express 2, 2364–2371 (2011).
Wombacher, R. et al. Live-cell super-resolution imaging with trimethoprim conjugates. Nature Methods 7, 717–719 (2010).
Jones, S. A., Shim, S. H., He, J. & Zhuang, X. Fast, three-dimensional super-resolution imaging of live cells. Nature Methods 8, 499–508 (2011).
van de Linde, S., Heilemann, M. & Sauer, M. Live-cell super-resolution imaging with synthetic fluorophores. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 61, 519–540 (2012).
Koide, Y., Urano, Y., Hanaoka, K., Terai, T. & Nagano, T. Evolution of group 14 rhodamines as platforms for near-infrared fluorescence probes utilizing photoinduced electron transfer. ACS Chem. Biol. 6, 600–608 (2011).
Egawa, T. et al. Development of a far-red to near-infrared fluorescence probe for calcium ion and its application to multicolor neuronal imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 14157–14159 (2011).
Koide, Y., Urano, Y., Hanaoka, K., Terai, T. & Nagano, T. Development of an Si-rhodamine-based far-red to near-infrared fluorescence probe selective for hypochlorous acid and its applications for biological imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133, 5680–5682 (2011).
Keppler, A. et al. A general method for the covalent labeling of fusion proteins with small molecules in vivo. Nature Biotechnol. 21, 86–89 (2003).
Keppler, A., Pick, H., Arrivoli, C., Vogel, H. & Johnsson, K. Labeling of fusion proteins with synthetic fluorophores in live cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 101, 9955–9959 (2004).
Wang, T. et al. Spirolactonized Si-rhodamine: a novel NIR fluorophore utilized as a platform to construct Si-rhodamine-based probes. Chem. Commun. 48, 8781–8783 (2012).
Åkerlöf, G. & Short, A. O. The dielectric constant of dioxane–water mixtures between 0 and 80°. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 58, 1241–1243 (1936).
Gautier, A. et al. An engineered protein tag for multiprotein labeling in living cells. Chem. Biol. 15, 128–136 (2008).
Los, G. V. et al. HaloTag: a novel protein labeling technology for cell imaging and protein analysis. ACS Chem. Biol. 3, 373–382 (2008).
Held, M. et al. CellCognition: time-resolved phenotype annotation in high-throughput live cell imaging. Nature Methods 7, 747–754 (2010).
Hell, S. W. Microscopy and its focal switch. Nature Methods 6, 24–32 (2009).
Dempsey, G. T., Vaughan, J. C., Chen, K. H., Bates, M. & Zhuang, X. Evaluation of fluorophores for optimal performance in localization-based super-resolution imaging. Nature Methods 8, 1027–1036 (2011).
Schnell, U., Dijk, F., Sjollema, K. A. & Giepmans, B. N. Immunolabeling artifacts and the need for live-cell imaging. Nature Methods 9, 152–158 (2012).
Rust, M. J., Bates, M. & Zhuang, X. Sub-diffraction-limit imaging by stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM). Nature Methods 3, 793–795 (2006).
Betzig, E. et al. Imaging intracellular fluorescent proteins at nanometer resolution. Science 313, 1642–1645 (2006).
Folling, J. et al. Fluorescence nanoscopy by ground-state depletion and single-molecule return. Nature Methods 5, 943–945 (2008).
Heilemann, M. et al. Subdiffraction-resolution fluorescence imaging with conventional fluorescent probes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 47, 6172–6176 (2008).
Steinhauer, C., Forthmann, C., Vogelsang, J. & Tinnefeld, P. Superresolution microscopy on the basis of engineered dark states. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16840–16841 (2008).
Hell, S. W. & Wichmann, J. Breaking the diffraction resolution limit by stimulated emission: stimulated-emission-depletion fluorescence microscopy. Opt. Lett. 19, 780–782 (1994).
Hein, B. et al. Stimulated emission depletion nanoscopy of living cells using SNAP-tag fusion proteins. Biophys. J. 98, 158–163 (2010).
Berning, S., Willig, K. I., Steffens, H., Dibaj, P. & Hell, S. W. Nanoscopy in a living mouse brain. Science 335, 551 (2012).
Morozova, K. S. et al. Far-red fluorescent protein excitable with red lasers for flow cytometry and superresolution STED nanoscopy. Biophys. J. 99, L13–L15 (2010).
David, R. Cell cycle: building the centriole. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12, 342 (2011).
Azimzadeh, J. & Marshall, W. F. Building the centriole. Curr. Biol. 20, R816–R825 (2010).
Bettencourt-Dias, M. & Glover, D. M. Centrosome biogenesis and function: centrosomics brings new understanding. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8, 451–463 (2007).
Gache, V. et al. Xenopus meiotic microtubule-associated interactome. PLoS One 5, e9248 (2010).
Korvatska, O. et al. Mutations in the TSGA14 gene in families with autism spectrum disorders. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 156, 303–311 (2011).
Lee, J. E. et al. CEP41 is mutated in Joubert syndrome and is required for tubulin glutamylation at the cilium. Nature Genet. 44, 193–199 (2012).
Lang, K. et al. Genetically encoded norbornene directs site-specific cellular protein labelling via a rapid bioorthogonal reaction. Nature Chem. 4, 298–304 (2012).
Plass, T. et al. Amino acids for Diels–Alder reactions in living cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 51, 4166–4170 (2012).
Lang, K. et al. Genetic encoding of bicyclononynes and trans-cyclooctenes for site-specific protein labeling in vitro and in live mammalian cells via rapid fluorogenic Diels–Alder reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 10317–10320 (2012).
Liu, C. C. & Schultz, P. G. Adding new chemistries to the genetic code. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 79, 413–444 (2010).
Plass, T., Milles, S., Koehler, C., Schultz, C. & Lemke, E. A. Genetically encoded copper-free click chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 50, 3878–3881 (2011).
Saito, T. & Nakatsuji, N. Efficient gene transfer into the embryonic mouse brain using in vivo electroporation. Dev. Biol. 240, 237–246 (2001).
Niu, L. & Yu, J. Investigating intracellular dynamics of FtsZ cytoskeleton with photoactivation single-molecule tracking. Biophys. J. 95, 2009–2016 (2008).
Mueller, V. et al. STED nanoscopy reveals molecular details of cholesterol- and cytoskeleton-modulated lipid interactions in living cells. Biophys. J. 101, 1651–1660 (2011).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation, the Chemical National Centre of Competence in Research Biology, European Research Council grant no. 243016-PALMassembly and the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne. G.L. was supported by a Federation of European Biochemical Societies long-term fellowship. K.U. was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Postdoctoral Fellowships for Foreign Researchers Fellows. C.S. is supported by TRR83, and T.P. by the Fonds der Chemischen Industrie. E.A.L. acknowledges funding from the Emmy Noether program of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. E.A.L. and C.S. also acknowledge funding from the SPP 1623 of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft. The authors thank A. Schena, B. Mollwitz and P. Gönczy for sharing reagents and cell lines, S. Hell and S. Jakobs (MPI Göttingen) for excellent support, Tanja Gilat (Max-Planck Institut (MPI) Göttingen) for preparation of the cells and A. Schönle (MPI Göttingen) for support with the software ImSpector.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors planned the experiments and co-wrote the paper. K.U. designed the structure of SiR-carboxyl. K.U., L.R. and I.C. performed the chemical syntheses. G.L., K.U. and L.R. characterized the dyes. G.L., A.H. and V.M. performed the confocal and STED microscopy with subsequent data analysis. N.O. and S.M. performed the GSDIM/STORM imaging and data analysis. T.P., C.S. and E.A.L performed the amber suppression experiments and analysis. G.Y., Z-G.L. and P.H. performed the labelling in brain sections.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information
Supplementary information (PDF 2206 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary movie 1 (AVI 12822 kb)
Supplementary information
Supplementary movie 2 (AVI 836 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lukinavičius, G., Umezawa, K., Olivier, N. et al. A near-infrared fluorophore for live-cell super-resolution microscopy of cellular proteins. Nature Chem 5, 132–139 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1546
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1546
This article is cited by
-
Tracking endogenous proteins based on RNA editing-mediated genetic code expansion
Nature Chemical Biology (2024)
-
A general strategy to develop fluorogenic polymethine dyes for bioimaging
Nature Chemistry (2024)
-
Quantitative determination of fluorescence labeling implemented in cell cultures
BMC Biology (2023)
-
A general method for the development of multicolor biosensors with large dynamic ranges
Nature Chemical Biology (2023)
-
Deep learning enables fast, gentle STED microscopy
Communications Biology (2023)