Abstract
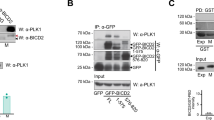
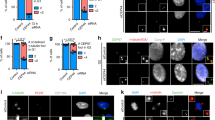
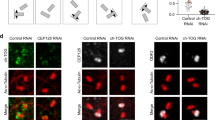
Dynamin 2 (Dyn2) is a large GTPase involved in vesicle formation and actin reorganization1,2,3. In this study, we report a novel role for Dyn2 as a component of the centrosome that is involved in centrosome cohesion. By light microscopy, Dyn2 localized aside centrin and colocalized with γ-tubulin at the centrosome; by immunoelectron microscopy, however, Dyn2 was detected in the pericentriolar material as well as on centrioles. Exogenously expressed green fluorescent protein (GFP)-tagged Dyn2 also localized to the centrosome, whereas glutathione S-transferase (GST)-tagged Dyn2 pulled down a protein complex(es) containing actin, α-tubulin and γ-tubulin from liver homogenate. Furthermore, gel overlay and immunoprecipitation indicated a direct interaction between γ-tubulin and a 219-amino-acid middle domain of Dyn2. Reduction of Dyn2 protein levels with small-interfering RNA (siRNA) resulted in centrosome splitting, whereas microtubule nucleation from centrosomes was not affected, suggesting a role for Dyn2 in centrosome cohesion. Finally, fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) analysis of a GFP-tagged Dyn2 middle domain indicated that Dyn2 is a dynamic exchangeable component of the centrosome. These findings suggest a novel function for Dyn2 as a participant in centrosome cohesion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Orth, J.D. & McNiven, M.A. Dynamin at the actin–membrane interface. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 31–39 (2003).
McNiven, M.A., Cao, H., Pitts, K.R. & Yoon, Y. The dynamin family of mechanoenzymes: pinching in new places. Trends Biochem. Sci. 25, 115–120 (2000).
Hinshaw, J.E. Dynamin and its role in membrane fission. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 16, 483–519 (2000).
Doxsey, S.J. Re-evaluating centrosome function. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 688–698 (2001).
Lange, B.M.H. Integration of the centrosome in cell-cycle control, stress response and signal transduction pathways. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 35–43 (2002).
Julian, M. et al. γ-tubulin participates in the formation of the midbody during cytokinesis in mammalian cells. J. Cell Sci. 105, 145–156 (1993).
Karki, S., LaMonte, B. & Holzbaur, E.L. Characterization of the p22 subunit of dynactin reveals the localization of cytoplasmic dynein and dynactin to the midbody of dividing cells. J. Cell Biol. 142, 1023–1034 (1998).
Ha Kim, Y., Yeol Choi, J., Jeong, Y., Wolgemuth, D.J. & Rhee, K. Nek2 localizes to multiple sites in mitotic cells, suggesting its involvement in multiple cellular functions during the cell cycle. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 290, 730–736 (2002).
Herrmann, L., Dittmar, T. & Erdmann, K.S. The protein tyrosine phosphatase PTP-BL associates with the midbody and is involved in the regulation of cytokinesis. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 230–240 (2003).
Jang, Y.J., Lin, C.Y., Ma, S. & Erikson, R.L. Functional studies on the role of the C-terminal domain of mammalian polo-like kinase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 1984–1989 (2002).
Thompson, H.M., Skop, A.R., Euteneuer, U., Meyer, B.J. & McNiven, M.A. The large GTPase dynamin associates with the spindle midzone and is required for cytokinesis. Curr. Biol. 12, 2111–2117 (2002).
Moudjou, M., Bordes, N., Paintrand, M. & Bornens, M. γ-tubulin in mammalian cells: the centrosomal and the cytosolic forms. J. Cell Sci. 109, 875–887 (1996).
Mitchison, T.J. & Kirschner, M.W. in Methods in Enzymology Vol. 134 (ed. Vallee, R.B.) 261–268 (Academic Press, San Diego, 1986).
Mitchison, T.J. & Kirschner, M.W. Microtubule assembly nucleated by isolated centrosomes. Nature 312, 232–237 (1984).
Moudjou, M. & Bornens, M. in Cell biology: A laboratory handbook, Vol. 1 (ed. Celis, J.E.) 595–604 (Academic Press, San Diego, 1994).
Herskovits, J.S., Shpetner, H.S., Burgess, C.C. & Vallee, R.B. Microtubules and Src-homology 3 domains stimulate the dynamin GTPase via its C-terminal domain. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 11468–11472 (1993).
Warnock, D.E., Baba, T. & Schmid, S.L. Ubiquitously expressed dynamin-II has a higher intrinsic GTPase activity and a greater propensity for self-assembly than neuronal dynamin-I. Mol. Biol. Cell 8, 2553–2562 (1997).
van der Bliek, A.M. et al. Mutations in human dynamin block an intermediate stage in coated vesicle formation. J. Cell Biol. 122, 553–563 (1993).
Elbashir, S.M. et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature 411, 428–429 (2001).
Paintrand, M., Moudjou, M., Delacroix, H. & Bornens, M. Centrosome organization and centriole architecture: their sensitivity to divalent cations. J. Struct. Biol. 108, 107–128 (1992).
Dictenberg, J.B. et al. Pericentrin and γ-tubulin form a protein complex and are organized into a novel lattice at the centrosome. J. Cell Biol. 141, 163–174 (1998).
Khodjakov, A. & Rieder, C.L. The sudden recruitment of γ-tubulin to the centrosome at the onset of mitosis and its dynamic exchange throughout the cell cycle, do not require microtubules. J. Cell Biol. 146, 585–596 (1999).
Henley, J.R. & McNiven, M.A. Association of a dynamin-like protein with the Golgi apparatus in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 133, 761–775 (1996).
Henley, J.R., Krueger, E.W., Oswald, B.J. & McNiven, M.A. Dynamin-mediated internalization of caveolae. J. Cell Biol. 141, 85–99 (1998).
Euteneuer, U., Gräf, R., Kube-Granderath, E. & Schliwa, M. Dictyostelium γ-tubulin: molecular characterization and ultrastructural localization. J. Cell Sci. 111, 405–412 (1998).
Jones, S.M., Howell, K.E., Henley, J.R., Cao, H. & McNiven, M.A. Role of dynamin in the formation of transport vesicles from the trans-Golgi network. Science 279, 573–577 (1998).
Cao, H., Garcia, F. & McNiven, M.A. Differential distribution of dynamin isoforms in mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 9, 2595–2609 (1998).
Marks, D.L., Larkin, J.M. & McNiven, M.A. Association of kinesin with the Golgi apparatus in rat hepatocytes. J. Cell Sci. 107, 2417–2426 (1994).
Okamoto, P.M., Gamby, C., Wells, D., Fallon, J. & Vallee, R.B. Dynamin isoform-specific interaction with the Shank/ProSAP scaffolding proteins of the postsynaptic density and actin cytoskeleton. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 48458–48465 (2001).
Cao, H., Thompson, H.M., Krueger, E.W. & McNiven, M.A. Disruption of Golgi structure and function in mammalian cells expressing a mutant dynamin. J. Cell Sci. 113, 1993–2002 (2000).
Acknowledgements
The authors thank E.W. Krueger, S.G. Weller and Dr. Y. Yoon for technical advice, and the entire McNiven lab for helpful suggestions and critically reading the manuscript. The authors also thank J.L. Salisbury and S.L. Schmid for anti-centrin and anti-Dyn1 antibodies, respectively, and D.J. Tindall for the scrambled siRNA oligonucleotides.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information Figures
Supplementary Information, Fig. S1 (PDF 878 kb)
Supplementary Information, Fig. S2
Legends to accompany movies
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, H., Cao, H., Chen, J. et al. Dynamin 2 binds γ-tubulin and participates in centrosome cohesion. Nat Cell Biol 6, 335–342 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1112
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1112
This article is cited by
-
Dynamin 2 is essential for mammalian spermatogenesis
Scientific Reports (2016)
-
Intermediate Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
Neuroscience Bulletin (2014)
-
Protein adaptation: mitotic functions for membrane trafficking proteins
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2013)
-
Dynamin 2 homozygous mutation in humans with a lethal congenital syndrome
European Journal of Human Genetics (2013)
-
Neuromuscular junction abnormalities in DNM2-related centronuclear myopathy
Journal of Molecular Medicine (2013)