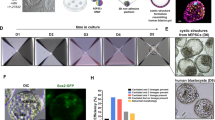
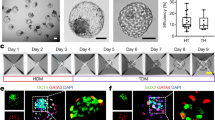
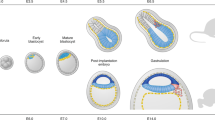
Abstract
During in vitro fertilization, embryos deemed clinically useless based on poor morphology are typically discarded. Here we demonstrate a statistical correlation between the developmental stage of such poor-quality embryos and the yield of human embryonic stem (hES) cell lines. Early-arrested or highly fragmented embryos only rarely yield cell lines, whereas those that have achieved blastocyst stage are a robust source of normal hES cells.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cowan, C.A. et al. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 1353–1356 (2004).
Gardner, D.K. & Schoolcraft, W.B. In Vitro Development of Human Blastocyst (Parthenon Press, Carnforth, UK, 1999).
Racowsky, C. et al. Reprod. Biomed. Online 6, 323–331 (2003).
Mitalipova, M. et al. Stem Cells 21, 521–526 (2003).
Hovatta, O. et al. Hum. Reprod. 18, 1404–1409 (2003).
Mateizel, I. et al. Hum. Reprod. 21, 503–511 (2006).
Genbacev, O. et al. Fertil. Steril. 83, 1517–1529 (2005).
Chen, H. et al. Hum. Reprod. 20, 2201–2206 (2005).
Zhang, X. et al. Derivation of human embryonic stem cells from developing and arrested embryos. Stem Cells 24, 2669–2676 (2006).
Strelchenko, N., Verlinsky, O., Kukharenko, V. & Verlinsky, Y . Reprod. Biomed. Online 9, 623–629 (2004).
Klimanskaya, I., Chung, Y., Becker, S., Lu, S.J. & Lanza, R . Nature 444, 481–485 (2006).
Boiani, M., Eckardt, S., Leu, N.A., Scholer, H.R. & McLaughlin, K.J. 123. EMBO J. 22, 5304–5312 (2003).
Watanabe, K. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 25, 681–686 (2007).
Bendall, S.C. et al. Nature 448, 1015–1021 (2007).
Draper, J.S. et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 22, 53–54 (2004).
Daphnis, D.D. et al. Hum. Reprod. 20, 129–137 (2005).
Landry, D.W. & Zucker, H.A. J. Clin. Invest. 114, 1184–1186 (2004).
2005 Assisted Reproductive Technology (ART) Report, Department of Health and Human Servicies. Center for Disease Control and Prevention http://www.cdc.gov/ART/ARTReports.htm.
Acknowledgements
This work was made possible through the generosity and vision of Joshua and Anita Bekenstein, the Harvard Stem Cell Institute and Children's Hospital Boston. G.Q.D. is a recipient of the Burroughs Wellcome Fund Clinical Scientist Award in Translational Research. T.A.I. was supported by grants from the Breast Cancer Research Foundation and Mesothelioma Applied Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.H.L., A.Y., project planning, experimental work, preparation of manuscript; H.H., A.T., J.S., experimental work; T.C., research coordinator at clinical site; T.A.I., interpretation of teratoma pathology; E.G., C.R., G.Q.D., project planning, preparation of manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–14, Tables 1–2, Methods (PDF 3357 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lerou, P., Yabuuchi, A., Huo, H. et al. Human embryonic stem cell derivation from poor-quality embryos. Nat Biotechnol 26, 212–214 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1378
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1378