Abstract
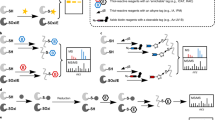
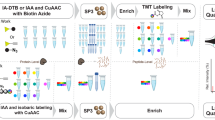
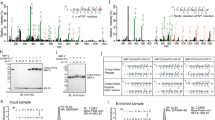
We have modified the biotin switch assay for protein S-nitrosothiols (SNOs), using resin-assisted capture (SNO-RAC). Compared with existing methodologies, SNO-RAC requires fewer steps, detects high-mass S-nitrosylated proteins more efficiently, and facilitates identification and quantification of S-nitrosylated sites by mass spectrometry. When combined with iTRAQ labeling, SNO-RAC revealed that intracellular proteins may undergo rapid denitrosylation on a global scale. This methodology is readily adapted to analyzing diverse cysteine-based protein modifications, including S-acylation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hess, D.T. et al. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 150–166 (2005).
Cho, D.H. et al. Science 324, 102–105 (2009).
Lim, K.H. et al. Nature 452, 646–649 (2008).
Foster, M.W. et al. Trends Mol. Med. 9, 160–168 (2003).
Jaffrey, S.R. et al. Nat. Cell Biol. 3, 193–197 (2001).
Greco, T.M. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 7420–7425 (2006).
Paige, J.S. et al. Chem. Biol. 15, 1307–1316 (2008).
Hao, G. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 1012–1017 (2006).
Roth, A.F. et al. Cell 125, 1003–1013 (2006).
Hara, M.R. et al. Nat. Cell Biol. 7, 665–674 (2005).
Forrester, M.T. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 13977–13983 (2007).
Benhar, M. et al. Science 320, 1050–1054 (2008).
Liu, L. et al. Cell 116, 617–628 (2004).
Ross, P.L. et al. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 3, 1154–1169 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Nimkar (Applied Biosystems) for providing iTRAQ reagents, and Q. Sun, K. Ozawa, A. Hausladen and D. Hess for expert advice. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants U19-ES012496, P01-HL075443, HL075443 and HL059130.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.T.F., M.W.F. and L.N. performed experiments and analyzed data. J.W.T. and M.A.M. acquired and analyzed mass spectrometry data. M.T.F. and J.S.S. wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
Duke University (M.T.F., M.W.F., J.S.S.) has applied for a patent based on this methodology.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–7, Supplementary Tables 1–3 (PDF 1291 kb)
Supplementary Table 4
MS spectra from all identified SNO-sites in CysNO-treated RAW264.7 macrophages and MG1655 E. coli. MSE (IdentityE) database search matches for the macrophage experiment are presented as Mascot searches for the purposes of display. (PDF 12223 kb)
Supplementary Table 5
Data from MS analyses of iTRAQ-coupled SNO-RAC. (ZIP 12668 kb)
Supplementary Table 6
MS/MS spectra from high mass protein-SNO identifications. (ZIP 1156 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forrester, M., Thompson, J., Foster, M. et al. Proteomic analysis of S-nitrosylation and denitrosylation by resin-assisted capture. Nat Biotechnol 27, 557–559 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1545
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt.1545
This article is cited by
-
TRAP1 S-nitrosylation as a model of population-shift mechanism to study the effects of nitric oxide on redox-sensitive oncoproteins
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Nitrosative stress in Parkinson’s disease
npj Parkinson's Disease (2022)
-
eNOS-dependent S-nitrosylation of the NF-κB subunit p65 has neuroprotective effects
Cell Death & Disease (2021)
-
TCA cycle metabolic compromise due to an aberrant S-nitrosoproteome in HIV-associated neurocognitive disorder with methamphetamine use
Journal of NeuroVirology (2021)
-
Nitric Oxide Enhances Rice Resistance to Rice Black-Streaked Dwarf Virus Infection
Rice (2020)