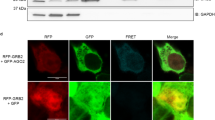
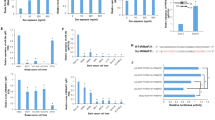
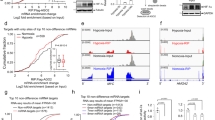
Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are generated by two-step processing to yield small RNAs that negatively regulate target gene expression at the post-transcriptional level1. Deregulation of miRNAs has been linked to diverse pathological processes, including cancer2,3. Recent studies have also implicated miRNAs in the regulation of cellular response to a spectrum of stresses4, such as hypoxia, which is frequently encountered in the poorly angiogenic core of a solid tumour5. However, the upstream regulators of miRNA biogenesis machineries remain obscure, raising the question of how tumour cells efficiently coordinate and impose specificity on miRNA expression and function in response to stresses. Here we show that epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is the product of a well-characterized oncogene in human cancers, suppresses the maturation of specific tumour-suppressor-like miRNAs in response to hypoxic stress through phosphorylation of argonaute 2 (AGO2) at Tyr 393. The association between EGFR and AGO2 is enhanced by hypoxia, leading to elevated AGO2-Y393 phosphorylation, which in turn reduces the binding of Dicer to AGO2 and inhibits miRNA processing from precursor miRNAs to mature miRNAs. We also identify a long-loop structure in precursor miRNAs as a critical regulatory element in phospho-Y393-AGO2-mediated miRNA maturation. Furthermore, AGO2-Y393 phosphorylation mediates EGFR-enhanced cell survival and invasiveness under hypoxia, and correlates with poorer overall survival in breast cancer patients. Our study reveals a previously unrecognized function of EGFR in miRNA maturation and demonstrates how EGFR is likely to function as a regulator of AGO2 through novel post-translational modification. These findings suggest that modulation of miRNA biogenesis is important for stress response in tumour cells and has potential clinical implications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim, V. N. MicroRNA biogenesis: coordinated cropping and dicing. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 6, 376–385 (2005)
van Kouwenhove, M., Kedde, M. & Agami, R. MicroRNA regulation by RNA-binding proteins and its implications for cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 11, 644–656 (2011)
Lu, J. et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435, 834–838 (2005)
Leung, A. K. & Sharp, P. A. MicroRNA functions in stress responses. Mol. Cell 40, 205–215 (2010)
Pouysségur, J., Dayan, F. & Mazure, N. M. Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour regression. Nature 441, 437–443 (2006)
Gould, G. W. & Lippincott-Schwartz, J. New roles for endosomes: from vesicular carriers to multi-purpose platforms. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 287–292 (2009)
Mosesson, Y., Mills, G. B. & Yarden, Y. Derailed endocytosis: an emerging feature of cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 8, 835–850 (2008)
Cikaluk, D. E. et al. GERp95, a membrane-associated protein that belongs to a family of proteins involved in stem cell differentiation. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 3357–3372 (1999)
Eulalio, A., Huntzinger, E. & Izaurralde, E. Getting to the root of miRNA-mediated gene silencing. Cell 132, 9–14 (2008)
Diederichs, S. & Haber, D. A. Dual role for argonautes in microRNA processing and posttranscriptional regulation of microRNA expression. Cell 131, 1097–1108 (2007)
Chendrimada, T. P. et al. TRBP recruits the Dicer complex to Ago2 for microRNA processing and gene silencing. Nature 436, 740–744 (2005)
Lemmon, M. A. & Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 141, 1117–1134 (2010)
Wang, Y. et al. Regulation of endocytosis via the oxygen-sensing pathway. Nature Med. 15, 319–324 (2009)
Franovic, A. et al. Translational up-regulation of the EGFR by tumor hypoxia provides a nonmutational explanation for its overexpression in human cancer. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 13092–13097 (2007)
Reynolds, A. R., Tischer, C., Verveer, P. J., Rocks, O. & Bastiaens, P. I. EGFR activation coupled to inhibition of tyrosine phosphatases causes lateral signal propagation. Nature Cell Biol. 5, 447–453 (2003)
Lee, O. H. et al. Genome-wide YFP fluorescence complementation screen identifies new regulators for telomere signaling in human cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 10, M110.001628 (2010)
Jiang, X., Huang, F., Marusyk, A. & Sorkin, A. Grb2 regulates internalization of EGF receptors through clathrin-coated pits. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 858–870 (2003)
Bertout, J. A., Patel, S. A. & Simon, M. C. The impact of O2 availability on human cancer. Nature Rev. Cancer 8, 967–975 (2008)
Ventura, A. & Jacks, T. MicroRNAs and cancer: short RNAs go a long way. Cell 136, 586–591 (2009)
Nicoloso, M. S., Spizzo, R., Shimizu, M., Rossi, S. & Calin, G. A. MicroRNAs – the micro steering wheel of tumour metastases. Nature Rev. Cancer 9, 293–302 (2009)
Leung, A. K. & Sharp, P. A. MicroRNAs: a safeguard against turmoil? Cell 130, 581–585 (2007)
Schirle, N. T. & MacRae, I. J. The crystal structure of human Argonaute2. Science 336, 1037–1040 (2012)
Elkayam, E. et al. The structure of human Argonaute-2 in complex with miR-20a. Cell 150, 100–110 (2012)
Tahbaz, N. et al. Characterization of the interactions between mammalian PAZ PIWI domain proteins and Dicer. EMBO Rep. 5, 189–194 (2004)
Maniataki, E. & Mourelatos, Z. A human, ATP-independent, RISC assembly machine fueled by pre-miRNA. Genes Dev. 19, 2979–2990 (2005)
Tsutsumi, A., Kawamata, T., Izumi, N., Seitz, H. & Tomari, Y. Recognition of the pre-miRNA structure by Drosophila Dicer-1. Nature Struct. Mol. Biol. 18, 1153–1158 (2011)
Suzuki, H. I. et al. Modulation of microRNA processing by p53. Nature 460, 529–533 (2009)
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Pickering, D. Yu, and A.-B. Shyu for suggestions and technical assistance with northern blot analysis. This work was supported by the US National Institutes of Health (CA109311 and CA099031 to M.-C.H., and CCSG Core Grant CA16672), the US National Breast Cancer Foundation, The Center for Biological Pathway at the UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, S. G. Komen (SAC110016 to M.-C.H.), The Sister Institution Fund of China Medical University and Hospital and the UT MD Anderson Cancer Center, the Cancer Research Center of Excellence (D0H102-TD-C-111-005, Taiwan), a Private University grant (NSC99-2632-B-039-001-MY3, Taiwan), and the Program for Stem Cell and Regenerative Medicine Frontier Research (NSC101-2321-B-039-001, Taiwan).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
J.S. and M.-C.H. designed and conceived the study; J.S. and M.-C.H. wrote the manuscript; J.L.H. contributed to the preparation of the manuscript. J.S., W.X., Y.B.K., L.H., S.-O.L., Y.D., Y. Wang, W.-C.C. and C.-H.C. did the experiments; Y. Wu provided human primary breast tumour samples; Y.C.L. provided the split-half-YFP-fused constructs; X.L. and C.-G.L. assisted in next-generation RNA deep sequencing; B.P.J. provided the pipeline analysis service for RNA sequencing data; and K.N. and D.-J.P. analysed the crystal structure of human AGO2.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1–41, Supplementary Table 1, Supplementary Methods and Supplementary References. (PDF 15146 kb)
Supplementary Data
This file contains the Normalized Expression (RPKM) of mRNAs that are regulated by EGFR and likely to be targeted by Top-Scoring mHESM. (XLS 68 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Xia, W., Khotskaya, Y. et al. EGFR modulates microRNA maturation in response to hypoxia through phosphorylation of AGO2. Nature 497, 383–387 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12080
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12080
This article is cited by
-
CEBPD is a master transcriptional factor for hypoxia regulated proteins in glioblastoma and augments hypoxia induced invasion through extracellular matrix-integrin mediated EGFR/PI3K pathway
Cell Death & Disease (2023)
-
Regulation of microRNA expression by the adaptor protein GRB2
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
AGO2 silences mobile transposons in the nucleus of quiescent cells
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology (2023)
-
Hsa-microRNA-27b-3p inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by inactivating transforming growth factor-activated kinase-binding protein 3/nuclear factor kappa B signalling
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters (2022)
-
MicroRNA-21 guide and passenger strand regulation of adenylosuccinate lyase-mediated purine metabolism promotes transition to an EGFR-TKI-tolerant persister state
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)