Abstract
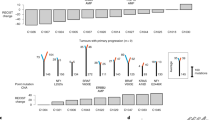
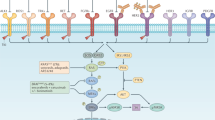
Colorectal tumours that are wild type for KRAS are often sensitive to EGFR blockade, but almost always develop resistance within several months of initiating therapy1,2. The mechanisms underlying this acquired resistance to anti-EGFR antibodies are largely unknown. This situation is in marked contrast to that of small-molecule targeted agents, such as inhibitors of ABL, EGFR, BRAF and MEK, in which mutations in the genes encoding the protein targets render the tumours resistant to the effects of the drugs3,4,5,6. The simplest hypothesis to account for the development of resistance to EGFR blockade is that rare cells with KRAS mutations pre-exist at low levels in tumours with ostensibly wild-type KRAS genes. Although this hypothesis would seem readily testable, there is no evidence in pre-clinical models to support it, nor is there data from patients. To test this hypothesis, we determined whether mutant KRAS DNA could be detected in the circulation of 28 patients receiving monotherapy with panitumumab, a therapeutic anti-EGFR antibody. We found that 9 out of 24 (38%) patients whose tumours were initially KRAS wild type developed detectable mutations in KRAS in their sera, three of which developed multiple different KRAS mutations. The appearance of these mutations was very consistent, generally occurring between 5 and 6 months following treatment. Mathematical modelling indicated that the mutations were present in expanded subclones before the initiation of panitumumab treatment. These results suggest that the emergence of KRAS mutations is a mediator of acquired resistance to EGFR blockade and that these mutations can be detected in a non-invasive manner. They explain why solid tumours develop resistance to targeted therapies in a highly reproducible fashion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amado, R. G. et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 26, 1626–1634 (2008)
Karapetis, C. S. et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 1757–1765 (2008)
Pao, W. et al. KRAS mutations and primary resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib. PLoS Med. 2, e17 (2005)
Engelman, J. A. et al. MET amplification leads to gefitinib resistance in lung cancer by activating ERBB3 signaling. Science 316, 1039–1043 (2007)
Corcoran, R. B. et al. BRAF gene amplification can promote acquired resistance to MEK inhibitors in cancer cells harboring the BRAF V600E mutation. Sci. Signal. 3, ra84 (2010)
Johannessen, C. M. et al. COT drives resistance to RAF inhibition through MAP kinase pathway reactivation. Nature 468, 968–972 (2010)
Diehl, F. et al. Circulating mutant DNA to assess tumor dynamics. Nature Med. 14, 985–990 (2008)
Diehl, F. et al. Detection and quantification of mutations in the plasma of patients with colorectal tumors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 16368–16373 (2005)
Holdhoff, M., Schmidt, K., Donehower, R. & Diaz, L. A., Jr Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to confirm somatic KRAS mutations. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 101, 1284–1285 (2009)
Hecht, J. R. et al. Lack of correlation between epidermal growth factor receptor status and response to panitumumab monotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 16, 2205–2213 (2010)
Wu, J. et al. Recurrent GNAS mutations define an unexpected pathway for pancreatic cyst development. Sci. Transl. Med. 3, 92ra66 (2011)
Diehl, F. et al. BEAMing: single-molecule PCR on microparticles in water-in-oil emulsions. Nature Methods 3, 551–559 (2006)
Jones, S. et al. Comparative lesion sequencing provides insights into tumor evolution. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 4283–4288 (2008)
Dewanji, A., Luebeck, E. G. & Moolgavkar, S. H. A generalized Luria–Delbrück model. Math. Biosci. 197, 140–152 (2005)
Luria, S. E. & Delbrück, M. Mutations of bacteria from virus sensitivity to virus resistance. Genetics 28, 491–511 (1943)
Iwasa, Y., Nowak, M. A. & Michor, F. Evolution of resistance during clonal expansion. Genetics 172, 2557–2566 (2006)
Tomasetti, C. & Levy, D. Role of symmetric and asymmetric division of stem cells in developing drug resistance. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 16766–16771 (2010)
Montagut, C. et al. Identification of a mutation in the extracellular domain of the epidermal growth factor receptor conferring cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer. Nature Med. 18, 221–223 (2012)
Maheswaran, S. et al. Detection of mutations in EGFR in circulating lung-cancer cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 359, 366–377 (2008)
Turke, A. B. et al. Preexistence and clonal selection of MET amplification in EGFR mutant NSCLC. Cancer Cell 17, 77–88 (2010)
Leder, K. et al. Fitness conferred by BCR-ABL kinase domain mutations determines the risk of pre-existing resistance in chronic myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 6, e27682 (2011)
Durrett, R. & Moseley, S. Evolution of resistance and progression to disease during clonal expansion of cancer. Theor. Popul. Biol. 77, 42–48 (2010)
Lenaerts, T., Pacheco, J. M., Traulsen, A. & Dingli, D. Tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy can cure chronic myeloid leukemia without hitting leukemic stem cells. Haematologica 95, 900–907 (2010)
Komarova, N. L. & Wodarz, D. Drug resistance in cancer: principles of emergence and prevention. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 9714–9719 (2005)
Lu, Y. et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) ubiquitination as a mechanism of acquired resistance escaping treatment by the anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody cetuximab. Cancer Res. 67, 8240–8247 (2007)
Yonesaka, K. et al. Activation of ERBB2 signaling causes resistance to the EGFR-directed therapeutic antibody cetuximab. Sci. Transl. Med. 3, 99ra86 (2011)
Rago, C. et al. Serial assessment of human tumor burdens in mice by the analysis of circulating DNA. Cancer Res. 67, 9364–9370 (2007)
Fan, H. C., Blumenfeld, Y. J., Chitkara, U., Hudgins, L. & Quake, S. R. Noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by shotgun sequencing DNA from maternal blood. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 16266–16271 (2008)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank J. Schaeffer, J. Ptak, N. Silliman and L. Dobbyn for technical assistance and M. Ekdahl for operational assistance. This work was supported by The Virginia and D. K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, the National Colorectal Cancer Research Alliance, NIH grants CA129825, CA43460, CA57345, CA62924, CA095103, and R01GM078986, NCI contract N01-CN-43309, ERC Start grant (279307: Graph Games), FWF NFN Grant No S11407-N23 (Rise), and the John Templeton Foundation. Simulations were performed on the Orchestra cluster supported by the Harvard Medical School Research Information Technology Group.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.A.D., K.S.O. and B.V. designed experiments, analysed data and wrote the paper. B.V., I.K. and J.W. performed experiments, analysed data and provided input to the manuscript. R.T.W., J.B. and J.R.H. provided critical materials, reagents, analysed data and provided input to the manuscript. B.A., I.B., J.G.R. and M.A.N. analysed data, performed the mathematical modelling and provided input to the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
L.A.D., K.W.K. and B.V. are Founding Scientific Advisors of Personal Genome Diagnostics, Inc., a company focused on the identification of genetic alterations in human cancer for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. L.A.D., K.W.K. and B.V. are members of the Scientific Advisory Board of Inostics, a company that is developing technologies for the molecular diagnosis of cancer. L.A.D., B.V. and K.W.K. also own stock in Inostics. K.W.K. and B.V. are entitled to a share of the royalties received by the University on sales of products related to BEAMing. Spouse of L.A.D. is an employee of Amgen. The terms of these arrangements are being managed by Johns Hopkins University in accordance with their conflict of interest policies.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Table 1-6, Supplementary Figures 1-3 and a Supplementary Appendix, which contains Supplementary Text and Data 1-4, Supplementary Figure 1 and additional references. (PDF 843 kb)
PowerPoint slides
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Diaz Jr, L., Williams, R., Wu, J. et al. The molecular evolution of acquired resistance to targeted EGFR blockade in colorectal cancers. Nature 486, 537–540 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11219
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11219