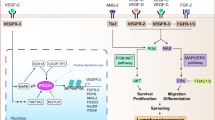
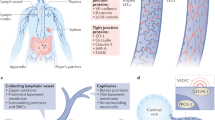
Abstract
The lymphatic vasculature forms a vessel network that drains interstitial fluid from tissues and returns it to the blood. Lymphatic vessels are also an essential part of the body's immune defence. They have an important role in the pathogenesis of several diseases, such as cancer, lymphoedema and various inflammatory conditions. Recent biological and technological developments in lymphatic vascular biology will lead to a better understanding and treatment of these diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hirakawa, S. & Detmar, M. New insights into the biology and pathology of the cutaneous lymphatic system. J. Dermatol. Sci. 35, 1–8 (2004).
Oliver, G. Lymphatic vasculature development. Nature Rev. Immunol. 4, 35–45 (2004).
Tammela, T., Petrova, T. V. & Alitalo, K. Molecular lymphangiogenesis: new players. Trends Cell Biol. 15, 434–441 (2005).
Kaipainen, A. et al. Expression of the fms-like tyrosine kinase FLT4 gene becomes restricted to lymphatic endothelium during development. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3566–3570 (1995).
Achen, M. G. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor D (VEGF-D) is a ligand for the tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (Flk1) and VEGF receptor 3 (Flt4). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 548–553 (1998).
Joukov, V. et al. A novel vascular endothelial growth factor, VEGF-C, is a ligand for the Flt4 (VEGFR-3) and KDR (VEGFR-2) receptor tyrosine kinases. EMBO J. 15, 290–298 (1996).
Jeltsch, M. et al. Hyperplasia of lymphatic vessels in VEGF-C transgenic mice. Science 276, 1423–1425 (1997).
Mäkinen, T. et al. Isolated lymphatic endothelial cells transduce growth, survival and migratory signals via the VEGF-C/D receptor VEGFR-3. EMBO J. 20, 4762–4773 (2001).
Karkkainen, M. J. et al. A model for gene therapy of human hereditary lymphedema. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 98, 12677–12682 (2001).
Yuan, L. et al. Abnormal lymphatic vessel development in neuropilin 2 mutant mice. Development 129, 4797–4806 (2002).
Joukov, V. et al. Proteolytic processing regulates receptor specificity and activity of VEGF-C. EMBO J. 16, 3898–3911 (1997).
Cao, Y. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C induces angiogenesis in vivo. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14389–14392 (1998).
Stacker, S. A. et al. Biosynthesis of vascular endothelial growth factor-D involves proteolytic processing which generates non-covalent homodimers. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 32127–32136 (1999).
Rissanen, T. T. et al. VEGF-D is the strongest angiogenic and lymphangiogenic effector among VEGFs delivered into skeletal muscle via adenoviruses. Circ. Res. 92, 1098–1106 (2003).
Nagy, J. A. et al. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor induces lymphangiogenesis as well as angiogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 196, 1497–1506 (2002).
Karkkainen, M. J. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C is required for sprouting of the first lymphatic vessels from embryonic veins. Nature Immunol. 5, 74–80 (2004).
Gannon, G. et al. Overexpression of vascular endothelial growth factor-A165 enhances tumor angiogenesis but not metastasis during beta-cell carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 62, 603–608 (2002).
Oh, S. J. et al. VEGF and VEGF-C: specific induction of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis in the differentiated avian chorioallantoic membrane. Dev. Biol. 188, 96–109 (1997).
Cursiefen, C. et al. VEGF-A stimulates lymphangiogenesis and hemangiogenesis in inflammatory neovascularization via macrophage recruitment. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 1040–1050 (2004).
Baluk, P. et al. Pathogenesis of persistent lymphatic vessel hyperplasia in chronic airway inflammation. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 247–257 (2005).
Wang, J. F., Zhang, X. F. & Groopman, J. E. Stimulation of beta 1 integrin induces tyrosine phosphorylation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 and modulates cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 41950–41957 (2001).
Vlahakis, N. E., Young, B. A., Atakilit, A. & Sheppard, D. The lymphangiogenic vascular endothelial growth factors VEGF-C and -D are ligands for the integrin alpha9beta1. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 4544–4552 (2005).
Huang, X. Z. et al. Fatal bilateral chylothorax in mice lacking the integrin alpha9beta1. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 5208–5215 (2000).
Zhang, X. et al. KSHV activation of VEGFR-3 alters endothelial function and enhances infection. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 26216–26224 (2005).
Kubo, H. et al. Blockade of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 signaling inhibits fibroblast growth factor-2-induced lymphangiogenesis in mouse cornea. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 8868–8873 (2002).
Cao, R. et al. PDGF-BB induces intratumoral lymphangiogenesis and promotes tumour metastasis. Cancer Cell 6, 333–345 (2004).
Kajiya, K., Hirakawa, S., Ma, B., Drinnenberg, I. & Detmar, M. Hepatocyte growth factor promotes lymphatic vessel formation and function. EMBO J. 24, 2885–2895 (2005).
Sabin, F. R. The lymphatic system in human embryos, with a consideration of the morphology of the system as a whole. Am. J. Anat. 9, 43–91 (1909).
Wigle, J. T. & Oliver, G. Prox1 function is required for the development of the murine lymphatic system. Cell 98, 769–778 (1999).
Wigle, J. T. et al. An essential role for Prox1 in the induction of the lymphatic endothelial cell phenotype. EMBO J. 21, 1505–1513 (2002).
Hong, Y. K. et al. Prox1 is a master control gene in the program specifying lymphatic endothelial cell fate. Dev. Dyn. 225, 351–357 (2002).
Petrova, T. V. et al. Lymphatic endothelial reprogramming of vascular endothelial cells by the Prox-1 homeobox transcription factor. EMBO J. 21, 4593–4599. (2002).
Harvey, N. L. et al. Lymphatic vascular defects promoted by Prox1 haploinsufficiency cause adult-onset obesity. Nature Genet. 37, 1072–1081 (2005).
Baldwin, M. E. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor D is dispensable for development of the lymphatic system. Mol. Cell Biol. 25, 2441–2449 (2005).
Dumont, D. J. et al. Cardiovascular failure in mouse embryos deficient in VEGF receptor-3. Science 282, 946–949 (1998).
Karkkainen, M. J. et al. Missense mutations interfere with VEGFR-3 signaling in primary lymphoedema. Nature Genet. 25, 153–159 (2000).
Jackson, D. G. Biology of the lymphatic marker LYVE-1 and applications in research into lymphatic trafficking and lymphangiogenesis. APMIS 112, 526–538 (2004).
Makinen, T. et al. PDZ interaction site in ephrinB2 is required for the remodeling of lymphatic vasculature. Genes Dev. 19, 397–410 (2005).
Jeltsch, M., Tammela, T., Alitalo, K. & Wilting, J. Genesis and pathogenesis of lymphatic vessels. Cell Tissue Res. 314, 69–84 (2003).
Aalami, O. O., Allen, D. B. & Organ, C. H. Jr. Chylous ascites: a collective review. Surgery 128, 761–778 (2000).
Abtahian, F. et al. Regulation of blood and lymphatic vascular separation by signaling proteins SLP-76 and Syk. Science 299, 247–251 (2003).
Saharinen, P. et al. Multiple angiopoietin recombinant proteins activate the Tie1 receptor tyrosine kinase and promote its interaction with Tie2. J. Cell Biol. 169, 239–243 (2005).
Gale, N. W. et al. Angiopoietin-2 is required for postnatal angiogenesis and lymphatic patterning, and only the latter role is rescued by Angiopoietin-1. Dev. Cell 3, 411–423 (2002).
Morisada, T. et al. Angiopoietin-1 promotes LYVE-1-positive lymphatic vessel formation. Blood 105, 4649–4656 (2005).
Tammela, T. et al. Angiopoietin-1 promotes lymphatic sprouting and hyperplasia. Blood 105, 4642–4648 (2005).
Adams, R. H. & Klein, R. Eph receptors and ephrin ligands. essential mediators of vascular development. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 10, 183–188 (2000).
Petrova, T. V. et al. Defective valves and abnormal mural cell recruitment underlie lymphatic vascular failure in lymphedema distichiasis. Nature Med. 10, 974–981 (2004).
Dagenais, S. L. et al. Foxc2 is expressed in developing lymphatic vessels and other tissues associated with lymphedema-distichiasis syndrome. Gene Expr. Patterns 4, 611–619 (2004).
Ferrell, R. E. Research perspectives in inherited lymphatic disease. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 979, 39–51 (2002).
Brice, G. et al. Analysis of the phenotypic abnormalities in lymphoedema-distichiasis syndrome in 74 patients with FOXC2 mutations or linkage to 16q24. J. Med. Genet. 39, 478–483 (2002).
Schacht, V. et al. T1alpha/podoplanin deficiency disrupts normal lymphatic vasculature formation and causes lymphedema. EMBO J. 22, 3546–3556 (2003).
Kriehuber, E. et al. Isolation and characterization of dermal lymphatic and blood endothelial cells reveal stable and functionally specialized cell lineages. J. Exp. Med. 194, 797–808 (2001).
Makinen, T. et al. Isolated lymphatic endothelial cells transduce growth, survival and migratory signals via the VEGF-C/D receptor VEGFR-3. EMBO J. 20, 4762–4773. (2001).
Podgrabinska, S. et al. Molecular characterization of lymphatic endothelial cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 99, 16069–16074 (2002).
Hirakawa, S. et al. Identification of vascular lineage-specific genes by transcriptional profiling of isolated blood vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 162, 575–586 (2003).
Rockson, S. G. Lymphedema. Am. J. Med. 110, 288–295 (2001).
Yla-Herttuala, S. & Alitalo, K. Gene transfer as a tool to induce therapeutic vascular growth. Nature Med. 9, 694–701 (2003).
Saaristo, A. et al. Lymphangiogenic gene therapy with minimal blood vascular side effects. J. Exp. Med. 196, 719–730 (2002).
Thurston, G. et al. Angiopoietin-1 protects the adult vasculature against plasma leakage. Nature Med. 6, 460–463 (2000).
Weis, S. & Cheresh, D. A. Pathophysiological consequences of VEGF-induced vascular permeability. Nature 65, 9789–9798 (2005).
Pepper, M. S. Lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis: myth or reality? Clin. Cancer Res. 7, 462–468 (2001).
Stacker, S. A., Achen, M. G., Jussila, L., Baldwin, M. E. & Alitalo, K. Lymphangiogenesis and cancer metastasis. Nature Rev. Cancer 2, 573–583 (2002).
He, Y. et al. Suppression of tumor lymphangiogenesis and lymph node metastasis by blocking vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 signaling. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 94, 819–825 (2002).
Skobe, M. et al. Induction of tumor lymphangiogenesis by VEGF-C promotes breast cancer metastasis. Nature Med. 7, 192–198 (2001).
Mandriota, S. J. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-C-mediated lymphangiogenesis promotes tumour metastasis. EMBO J. 20, 672–682 (2001).
Stacker, S. A. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor-D promotes the metastatic spread of cancer via the lymphatics. Nature Med. 7, 186–191 (2001).
Karpanen, T. et al. Vacular endothelial growth factor C promotes tumor lymphangiogenesis and intralymphatic tumor growth. Cancer Res. 61, 1786–1790 (2001).
Valtola, R. et al. VEGFR-3 and its ligand VEGF-C are associated with angiogenesis in breast cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 154, 1381–1390 (1999).
Krishnan, J. et al. Differential in vivo and in vitro expression of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C and VEGF-D in tumors and its relationship to lymphatic metastasis in immunocompetent rats. Cancer Res. 63, 713–722 (2003).
Dadras, S. S. et al. Tumor lymphangiogenesis: a novel prognostic indicator for cutaneous melanoma metastasis and survival. Am. J. Pathol. 162, 1951–1960 (2003).
Maula, S. M. et al. Intratumoral lymphatics are essential for the metastatic spread and prognosis in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck region. Cancer Res. 63, 1920–1926 (2003).
Padera, T. P. et al. Pathology: cancer cells compress intratumour vessels. Nature 427, 695 (2004).
Wong, S. Y. et al. Tumor-secreted VEGF-C is necessary for prostate cancer lymphangiogenesis, but lymphangiogenesis is unnecessary for lymph node metastasis. Cancer Res. 65, 9789–9798.
Padera, T. P. et al. Lymphatic metastasis in the absence of functional intratumor lymphatics. Science 296, 1883–1886 (2002).
He, Y. et al. Vascular endothelial cell growth factor receptor 3-mediated activation of lymphatic endothelium is crucial for tumor cell entry and spread via lymphatic vessels. Cancer Res. 65, 4739–4746 (2005).
Laakkonen, P., Porkka, K., Hoffman, J. A. & Ruoslahti, E. A tumor-homing peptide with a targeting specificity related to lymphatic vessels. Nature Med. 8, 751–755 (2002).
Zlotnik, A. Chemokines in neoplastic progression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 14, 181–185 (2004).
Hirakawa, S. et al. VEGF-A induces tumor and sentinel lymph node lymphangiogenesis and promotes lymphatic metastasis. J. Exp. Med. 201, 1089–1099 (2005).
Pullinger, B. D. & Florey, H. W. Proliferation of lymphatics in inflammation. J. Pathol. Bact. 45, 157–170 (1937).
Ristimaki, A., Narko, K., Enholm, B., Joukov, V. & Alitalo, K. Proinflammatory cytokines regulate expression of the lymphatic endothelial mitogen vascular endothelial growth factor-C. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 8413–8418 (1998).
Saban, M. R. et al. Visualization of lymphatic vessels through NF-kappaB activity. Blood 104, 3228–3230 (2004).
Kerjaschki, D. et al. Lymphatic neoangiogenesis in human kidney transplants is associated with immunologically active lymphocytic infiltrates. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 15, 603–612 (2004).
Hamrah, P., Chen, L., Zhang, Q. & Dana, M. R. Novel expression of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR)-3 and VEGF-C on corneal dendritic cells. Am. J. Pathol. 163, 57–68 (2003).
Chen, L. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 mediates induction of corneal alloimmunity. Nature Med. 10, 813–815 (2004).
Ohl, L. et al. CCR7 governs skin dendritic cell migration under inflammatory and steady-state conditions. Immunity 21, 279–288 (2004).
Irjala, H. et al. Mannose receptor is a novel ligand for L-selectin and mediates lymphocyte binding to lymphatic endothelium. J. Exp. Med. 194, 1033–1041 (2001).
Salmi, M., Koskinen, K., Henttinen, T., Elima, K. & Jalkanen, S. CLEVER-1 mediates lymphocyte transmigration through vascular and lymphatic endothelium. Blood 104, 3849–3857 (2004).
Nibbs, R. J. et al. The beta-chemokine receptor D6 is expressed by lymphatic endothelium and a subset of vascular tumors. Am. J. Pathol. 158, 867–877 (2001).
Kriederman, B. M. et al. FOXC2 haploinsufficient mice are a model for human autosomal dominant lymphedema-distichiasis syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 12, 1179–1185 (2003).
Ayadi, A. et al. Net-targeted mutant mice develop a vascular phenotype and up-regulate egr-1. EMBO J. 20, 5139–5152 (2001).
Fruman, D. A. et al. Hypoglycaemia, liver necrosis and perinatal death in mice lacking all isoforms of phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85 alpha. Nature Genet. 26, 379–382 (2000).
Pennisi, D. et al. Mutations in Sox18 underlie cardiovascular and hair follicle defects in ragged mice. Nature Genet. 24, 434–437 (2000).
Gittenberger-De Groot, A. C. et al. Abnormal lymphatic development in trisomy 16 mouse embryos precedes nuchal edema. Dev. Dyn. 230, 378–384 (2004).
Dixelius, J. et al. Ligand-induced vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3 (VEGFR-3) heterodimerization with VEGFR-2 in primary lymphatic endothelial cells regulates tyrosine phosphorylation sites. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 40973–40979 (2003).
Salameh, A., Galvagni, F., Bardelli, M., Bussolino, F. & Oliviero, S. Direct recruitment of CRK and GRB2 to VEGFR-3 induce proliferation, migration and survival of endothelial cells through the activation of ERK, AKT and JNK pathways. Blood 15, 3423–3431 (2005).
Ny, A. et al. A genetic Xenopus laevis tadpole model to study lymphangiogenesis. Nature Med. 11, 998–1004 (2005).
Schneider, M., Othman-Hassan, K., Christ, B. & Wilting, J. Lymphangioblasts in the avian wing bud. Dev. Dyn. 216, 311–319 (1999).
Rajantie, I. et al. Adult bone marrow-derived cells recruited during angiogenesis comprise precursors for periendothelial vascular mural cells. Blood 104, 2084–2086 (2004).
Wang, H. W. et al. Kaposi sarcoma herpesvirus-induced cellular reprogramming contributes to the lymphatic endothelial gene expression in Kaposi sarcoma. Nature Genet. 36, 687–693 (2004).
Hong, Y. K. et al. Lymphatic reprogramming of blood vascular endothelium by Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Nature Genet. 36, 683–685 (2004).
Acknowledgements
We extend our gratitude to the many colleagues who have contributed to the field, but whose work could not be cited here owing to space limitations. We thank C. Norrmén for providing confocal image of lymphatic vessels, A. Parsons for assistance in editing, and H. Schmidt for the drawing of figures. The work in the authors' laboratories is supported by the US National Institutes of Health, the European Union, the Finnish Academy, the Sigrid Juselius Foundation and the Finnish Cancer Organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare competing financial interests: Kari Alitalo is a board member and minority owner of Lymphatix Ltd. (Anti-VEGFR-3 monoclonal antibodies have been licenced to ImClone Systems Inc by the University of Helsinki.)
Additional information
Author Information Reprints and permissions information is available at npg.nature.com/reprintsandpermissions.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alitalo, K., Tammela, T. & Petrova, T. Lymphangiogenesis in development and human disease. Nature 438, 946–953 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04480
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04480
This article is cited by
-
An advanced 3D lymphatic system for assaying human cutaneous lymphangiogenesis in a microfluidic platform
NPG Asia Materials (2024)
-
15-Lipoxygenase promotes resolution of inflammation in lymphedema by controlling Treg cell function through IFN-β
Nature Communications (2024)
-
Overexpression of Long Non-coding RNA uc.246 Facilitates Angiogenesis, Migration, and EMT Phenotype of Human Breast Cancer Cells
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology (2024)
-
A new lymphedema treatment using pyro-drive jet injection
Human Cell (2024)
-
Molecular and metabolic orchestration of the lymphatic vasculature in physiology and pathology
Nature Communications (2023)