Abstract
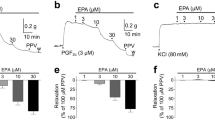
TRPV4 is a widely expressed cation channel of the ‘transient receptor potential’ (TRP) family1 that is related to the vanilloid receptor VR1 (TRPV1). It functions as a Ca2+ entry channel2 and displays remarkable gating promiscuity by responding to both physical stimuli (cell swelling, innoxious heat2,3,4,5,6,7) and the synthetic ligand 4αPDD8. An endogenous ligand for this channel has not yet been identified. Here we show that the endocannabinoid anandamide and its metabolite arachidonic acid activate TRPV4 in an indirect way involving the cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-dependent formation of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids. Application of 5′,6′-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid at submicromolar concentrations activates TRPV4 in a membrane-delimited manner and causes Ca2+ influx through TRPV4-like channels in vascular endothelial cells. Activation of TRPV4 in vascular endothelial cells might therefore contribute to the relaxant effects of endocannabinoids and their P450 epoxygenase-dependent metabolites on vascular tone9,10,11,12.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clapham, D. E., Runnels, L. W. & Strübing, C. The TRP ion channel family. Nature Rev. Neurosci. 2, 387–396 (2001)
Strotmann, R., Harteneck, C., Nunnenmacher, K., Schultz, G. & Plant, T. D. OTRPC4, a nonselective cation channel that confers sensitivity to extracellular osmolarity. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 695–702 (2000)
Güler, A. et al. Heat-evoked activation of the ion channel, TRPV4. J. Neurosci. 22, 6408–6414 (2002)
Wissenbach, U., Bödding, M., Freichel, M. & Flockerzi, V. Trp12, a novel Trp related protein from kidney. FEBS Lett. 485, 127–134 (2000)
Liedtke, W. et al. Vanilloid receptor-related osmotically activated channel (VR-OAC), a candidate vertebrate osmoreceptor. Cell 103, 525–535 (2000)
Nilius, B., Prenen, J., Wissenbach, U., Bödding, M. & Droogmans, G. Differential activation of the volume-sensitive cation channel TRP12 (OTRPC4) and the volume-regulated anion currents in HEK-293 cells. Pflügers Arch. 443, 227–233 (2001)
Watanabe, H. et al. Heat-evoked activation of TRPV4 channels in an HEK293 cell expression system and in native mouse aorta endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 47044–47051 (2002)
Watanabe, H. et al. Activation of TRPV4 channels (hVRL-2/mTRP12) by phorbol derivatives. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 13569–13577 (2002)
Seegers, H. C., Gross, R. W. & Boyle, W. A. Calcium-independent phospholipase A2-derived arachidonic acid is essential for endothelium-dependent relaxation by acetylcholine. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 302, 918–923 (2002)
Tan, J. Z., Kaley, G. & Gurtner, G. H. Nitric oxide and prostaglandins mediate vasodilation to 5,6-EET in rabbit lung. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 407, 561–566 (1997)
Fuloria, M., Smith, T. K. & Aschner, J. L. Role of 5,6-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid in the regulation of newborn piglet pulmonary vascular tone. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 283, L383–L389 (2002)
Jarai, Z. et al. Cannabinoid-induced mesenteric vasodilation through an endothelial site distinct from CB1 or CB2 receptors. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 14136–14141 (1999)
Voets, T. et al. Molecular determinants of permeation through the cation channel TRPV4. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 33704–33710 (2002)
Ueda, N. Endocannabinoid hydrolases. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 68–69, 521–534 (2002)
Fleming, I. Cytochrome P450 enzymes in vascular homeostasis. Circ. Res. 89, 753–762 (2001)
Roman, R. J. P-450 metabolites of arachidonic acid in the control of cardiovascular function. Physiol. Rev. 82, 131–185 (2002)
Randall, M. D. & Kendall, D. A. Endocannabinoids: A new class of vasoactive substances. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 19, 55–58 (1998)
Zygmunt, P. M. et al. Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature 400, 452–457 (1999)
Randall, M. D. & Kendall, D. A. Anandamide and endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor act via a common vasorelaxant mechanism in rat mesentery. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 346, 51–53 (1998)
Rzigalinski, B. A., Willoughby, K. A., Hoffman, S. W., Falck, J. R. & Ellis, E. F. Calcium influx factor, further evidence it is 5,6-epoxyeicosatrienoic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 175–182 (1999)
Xie, Q., Zhang, Y., Zhai, C. & Bonanno, J. A. Calcium influx factor from cytochrome P-450 metabolism and secretion-like coupling mechanisms for capacitative calcium entry in corneal endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 16559–16566 (2002)
Graier, W. F., Simecek, S. & Sturek, M. Cytochrome P450 mono-oxygenase-regulated signalling of Ca2+ entry in human and bovine endothelial cells. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 482, 259–274 (1995)
Wilson, R. I. & Nicoll, R. A. Endocannabinoid signaling in the brain. Science 296, 678–682 (2002)
Suh, S. H. et al. Characterisation of explanted endothelial cells from mouse aorta: electrophysiology and Ca2+ signalling. Pflügers Arch. 438, 612–620 (1999)
Freichel, M. et al. Lack of an endothelial store-operated Ca2+ current impairs agonist-dependent vasorelaxation in TRP4-/- mice. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 121–127 (2001)
Grainger, J. & Boachie Ansah, G. Anandamide-induced relaxation of sheep coronary arteries: The role of the vascular endothelium, arachidonic acid metabolites and potassium channels. Br. J. Pharmacol. 134, 1003–1012 (2001)
Williams, D. A. & Fay, F. S. Intracellular calibration of the fluorescent calcium indicator Fura-2. Cell Calcium 11, 75–83 (1990)
Acknowledgements
We thank V. Flockerzi and C. D. Benham for comments, and V. Flockerzi and U. Wissenbach for providing the mTRP12 clone (mTRPV4). This work was supported by the Belgian Federal Government, the Flemish Government and the Onderzoeksraad KU Leuven (Interuniversity Poles of Attraction Program, IUAP). T.V. is a postdoctoral Fellow of the Fund for Scientific Research–Flanders (Belgium) (FWO–Vlaanderen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, H., Vriens, J., Prenen, J. et al. Anandamide and arachidonic acid use epoxyeicosatrienoic acids to activate TRPV4 channels. Nature 424, 434–438 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01807
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01807
This article is cited by
-
Integrating transcriptomics and metabolomics to elucidate the mechanism by which taurine protects against DOX-induced depression
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Aortic smooth muscle TRPV4 channels regulate vasoconstriction in high salt-induced hypertension
Hypertension Research (2023)
-
Acute and long-term effects of cannabinoids on hypertension and kidney injury
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The endocannabinoid anandamide is an airway relaxant in health and disease
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Excessive dietary linoleic acid promotes plasma accumulation of pronociceptive fatty acyl lipid mediators
Scientific Reports (2022)