Abstract
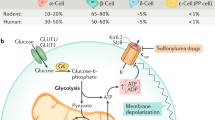
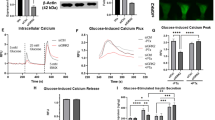
Diabetes, a disease in which carbohydrate and lipid metabolism are regulated improperly by insulin, is a serious worldwide health issue1,2. Insulin is secreted from pancreatic β cells in response to elevated plasma glucose, with various factors modifying its secretion3. Free fatty acids (FFAs) provide an important energy source as nutrients, and they also act as signalling molecules in various cellular processes, including insulin secretion4,5. Although FFAs are thought to promote insulin secretion in an acute phase, this mechanism is not clearly understood6. Here we show that a G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR40, which is abundantly expressed in the pancreas, functions as a receptor for long-chain FFAs. Furthermore, we show that long-chain FFAs amplify glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells by activating GPR40. Our results indicate that GPR40 agonists and/or antagonists show potential for the development of new anti-diabetic drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gadsby, R. Epidemiology of diabetes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 54, 1165–1172 (2002)
Jovanovic, L. & Gondos, B. Type 2 diabetes: The epidemic of the new millennium. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 29, 33–42 (1999)
Henquin, J. C. Triggering and amplifying pathways of regulation of insulin secretion by glucose. Diabetes 49, 1751–1760 (2000)
Nunez, E. A. Biological complexity is under the ‘strange attraction’ of non-esterified fatty acids. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fatty Acids 57, 107–110 (1997)
Haber, E. P. et al. Pleiotropic effects of fatty acids on pancreatic β-cells. J. Cell Physiol. 194, 1–12 (2003)
Dobbins, R. L. et al. A fatty acid-dependent step is critically important for both glucose-and non-glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. J. Clin. Invest. 101, 2370–2376 (1998)
Sawzdargo, M. et al. A cluster of four novel human G protein-coupled receptor genes occurring in close proximity to CD22 gene on chromosome 19q13.1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 239, 543–547 (1997)
Fujii, R. et al. Identification of neuromedin U as the cognate ligand of the orphan G protein-coupled receptor FM-3. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21068–21074 (2000)
Wank, S. A. et al. Purification, molecular cloning, and functional expression of the cholecystokinin receptor from rat pancreas. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 3125–3129 (1992)
Lankat-Buttgereit, B., Goke, R., Fehmann, H. C., Richter, G. & Goke, B. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding for the GLP-1 receptor expressed in rat lung. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. 102, 341–347 (1994)
Aguilar-Bryan, L. et al. Cloning of the beta cell high-affinity sulfonylurea receptor: a regulator of insulin secretion. Science 268, 423–426 (1995)
Braun, T., Schofield, P. R., Shivers, B. D., Pritchett, D. B. & Seeburg, P. H. A novel subtype of muscarinic receptor identified by homology screening. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 149, 125–132 (1987)
Bruno, J. F., Xu, Y., Song, J. & Berelowitz, M. Tissue distribution of somatostatin receptor subtype messenger ribonucleic acid in the rat. Endocrinology 133, 2561–2567 (1993)
Miyazaki, J. et al. Establishment of a pancreatic beta cell line that retains glucose-inducible insulin secretion: special reference to expression of glucose transporter isoforms. Endocrinology 127, 126–132 (1990)
Hinuma, S. et al. A prolactin-releasing peptide in the brain. Nature 393, 272–276 (1998)
Hinuma, S., Onda, H. & Fujino, M. The quest for novel bioactive peptides utilizing orphan seven-transmembrane-domain receptors. J. Mol. Med. 77, 495–504 (1999)
Briscoe, C. P. et al. The orphan G protein-coupled receptor GPR40 is activated by medium and long-chain fatty acids. J. Biol. Chem. published online, 19 December 2002 (doi:211495200)
Spector, A. A. & Hoak, J. C. Fatty acids, platelets, and microcirculatory obstruction. Science 190, 490–492 (1975)
Stein, D. T. et al. Essentiality of circulating fatty acids for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in the fasted rat. J. Clin. Invest. 97, 2728–2735 (1996)
Bergman, R. N. & Ader, M. Free fatty acids and pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 11, 351–356 (2000)
Newgard, C. B. & McGarry, J. D. Metabolic coupling factors in pancreatic β-cell signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 64, 689–719 (1995)
Ashcroft, F. M. et al. Stimulus-secretion coupling in pancreatic beta cells. J. Cell Biochem. 55, 54–65 (1994)
Wolheim, C. B. & Biden, T. J. Signal transduction in insulin secretion: comparison between fuel stimuli and receptor agonists. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 488, 317–333 (1986)
Gutkind, J. S. Cell growth control by G protein-coupled receptors: from signal transduction to signal integration. Oncogene 17, 1331–1342 (1998)
Lacy, P. E. & Kostianovsky, M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes 16, 35–39 (1967)
Kawamata, Y. et al. A G protein-coupled receptor responsive to bile acids. J. Biol. Chem. published online, 10 January 2003 (doi:209706200)
Acknowledgements
We thank Y. Sumino, T. Soda, K. Kato, H. Odaka, F. Itoh, M. Kajino, K. Fukatsu and N. Suzuki for their discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Itoh, Y., Kawamata, Y., Harada, M. et al. Free fatty acids regulate insulin secretion from pancreatic β cells through GPR40. Nature 422, 173–176 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01478
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01478
This article is cited by
-
A nutrient responsive lipase mediates gut-brain communication to regulate insulin secretion in Drosophila
Nature Communications (2024)
-
GPCRs involved in metabolic diseases: pharmacotherapeutic development updates
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica (2024)
-
Taurine promotes insulin synthesis by enhancing Isl-1 expression through miR-7a/RAF1/ERK1/2 pathway
In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology - Animal (2024)
-
Targeting of G-protein coupled receptor 40 alleviates airway hyperresponsiveness through RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway in obese asthmatic mice
Respiratory Research (2023)
-
Liver-derived metabolites as signaling molecules in fatty liver disease
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)