Abstract
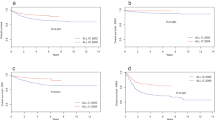
Long term follow-up of 378 children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) treated at a single centre showed that at six years from diagnosis 202 (53%) were alive, of whom 140 (37%) remained in first remission. Only three children had a first relapse after six years. Children who survived six years despite a single extramedullary relapse in the testis or CNS were likely to remain in second remission but patients with previous marrow or with multiple relapses continued at risk for up to ten years from diagnosis. Presenting factors influencing event-free survival were: leucocyte count, age and sex. After allowing for these factors morphological (FAB) subtype and liver enlargement retained their prognostic significance. Immunological type of ALL was not of independent prognostic significance, except for the small number of patients with B-ALL. Most factors lost their significance after 2-4 years. It is concluded that patients alive 6 years from diagnosis without relapse or even with a single extramedullary relapse of ALL, have a high chance of prolonged survival and cure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chessells, J., Hardisty, R. & Richards, S. Long survival in childhood lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Cancer 55, 315–319 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1987.62
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1987.62
This article is cited by
-
Reappearance of acute lymphoblastic leukemia 34 years after initial diagnosis: a case report and study of the origin of the reappeared blasts
International Journal of Hematology (2013)