Abstract
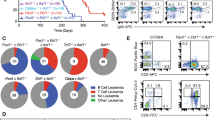
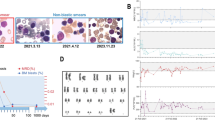
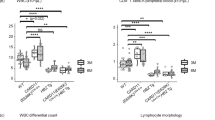
E2A-hepatic leukemia factor (HLF) is a chimeric protein found in B-lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) with t(17;19). To analyze the leukemogenic process and to create model mice for t(17;19)-positive leukemia, we generated inducible knock-in (iKI) mice for E2A-HLF. Despite the induced expression of E2A-HLF in the hematopoietic tissues, no disease was developed during the long observation period, indicating that additional gene alterations are required to develop leukemia. To elucidate this process, E2A-HLF iKI and control littermates were subjected to retroviral insertional mutagenesis. Virus infection induced acute leukemias in E2A-HLF iKI mice with higher morbidity and mortality than in control mice. Inverse PCR detected three common integration sites specific for E2A-HLF iKI leukemic mice, which induced overexpression of zinc-finger transcription factors: g rowth f actor i ndependent 1 (Gfi1), zinc-finger protein subfamily 1A1 isoform a (Zfp1a1, also known as Ikaros) and zinc-finger protein 521 (Zfp521). Interestingly, tumors with Zfp521 integration exclusively showed B-lineage ALL, which corresponds to the phenotype of human t(17;19)-positive leukemia. In addition, ZNF521 (human counterpart of Zfp521) was found to be overexpressed in human leukemic cell lines harboring t(17;19). Moreover, both iKI for E2A-HLF and transgenic for Zfp521 mice frequently developed B-lineage ALL. These results indicate that a set of transcription factors promote leukemic transformation of E2A-HLF-expressing hematopoietic progenitors and suggest that aberrant expression of Zfp521/ZNF521 may be clinically relevant to t(17;19)-positive B-lineage ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akagi K, Suzuki T, Stephens RM, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG . (2004). RTCGD: retroviral tagged cancer gene database. Nucleic Acids Res 32: (Database issue) D523–527.
Aspland SE, Bendall HH, Murre C . (2001). The role of E2A-PBX1 in leukemogenesis. Oncogene 20: 5708–5717.
Bain G, Engel I, Robanus Maandag EC, te Riele HP, Voland JR, Sharp LL et al. (1997). E2A deficiency leads to abnormalities in alphabeta T-cell development and to rapid development of T-cell lymphomas. Mol Cell Biol 17: 4782–4791.
Bain G, Maandag EC, Izon DJ, Amsen D, Kruisbeek AM, Weintraub BC et al. (1994). E2A proteins are required for proper B cell development and initiation of immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Cell 79: 885–892.
Beverly LJ, Capobianco AJ . (2003). Perturbation of Ikaros isoform selection by MLV integration is a cooperative event in Notch(IC)-induced T cell leukemogenesis. Cancer Cell 3: 551–564.
Bond HM, Mesuraca M, Amodio N, Mega T, Agosti V, Fanello D et al. (2008). Early hematopoietic zinc finger protein-zinc finger protein 521: a candidate regulator of diverse immature cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 40: 848–854.
Dang J, Inukai T, Kurosawa H, Goi K, Inaba T, Lenny NT et al. (2001). The E2A-HLF oncoprotein activates Groucho-related genes and suppresses Runx1. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5935–5945.
Gilks CB, Bear SE, Grimes HL, Tsichlis PN . (1993). Progression of interleukin-2 (IL-2)-dependent rat T cell lymphoma lines to IL-2-independent growth following activation of a gene (Gfi-1) encoding a novel zinc finger protein. Mol Cell Biol 13: 1759–1768.
Hentges KE, Weiser KC, Schountz T, Woodward LS, Morse HC, Justice MJ . (2005). Evi3, a zinc-finger protein related to EBFAZ, regulates EBF activity in B-cell leukemia. Oncogene 24: 1220–1230.
Higuchi M, O'Brien D, Kumaravelu P, Lenny N, Yeoh EJ, Downing JR . (2002). Expression of a conditional AML1-ETO oncogene bypasses embryonic lethality and establishes a murine model of human t(8;21) acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Cell 1: 63–74.
Honda H, Fujii T, Takatoku M, Mano H, Witte ON, Yazaki Y et al. (1995). Expression of p210bcr/abl by metallothionein promoter induced T-cell leukemia in transgenic mice. Blood 85: 2853–2861.
Honda H, Inaba T, Suzuki T, Oda H, Ebihara Y, Tsuiji K et al. (1999). Expression of E2A-HLF chimeric protein induced T-cell apoptosis, B-cell maturation arrest, and development of acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 93: 2780–2790.
Hunger SP . (1996). Chromosomal translocations involving the E2A gene in acute lymphoblastic leukemia: clinical features and molecular pathogenesis. Blood 87: 1211–1224.
Inaba T, Inukai T, Yoshihara T, Seyschab H, Ashmun RA, Canman CE et al. (1996). Reversal of apoptosis by the leukaemia-associated E2A-HLF chimaeric transcription factor. Nature 382: 541–544.
Inaba T, Roberts WM, Shapiro LH, Jolly KW, Raimondi SC, Smith SD et al. (1992). Fusion of the leucine zipper gene HLF to the E2A gene in human acute B-lineage leukemia. Science 257: 531–534.
Inukai T, Inaba T, Yoshihara T, Look AT . (1997). Cell transformation mediated by homodimeric E2A-HLF transcription factors. Mol Cell Biol 17: 1417–1424.
Inukai T, Inoue A, Kurosawa H, Goi K, Shinjyo T, Ozawa K et al. (1999). SLUG, a ces-1-related zinc finger transcription factor gene with antiapoptotic activity, is a downstream target of the E2A-HLF oncoprotein. Mol Cell 4: 343–352.
Jonkers J, Berns A . (1996). Retroviral insertional mutagenesis as a strategy to identify cancer genes. Biochem Biophys Acta 1287: 29–57.
Kuhn R, Schwenk F, Aguet M, Rajewsky K . (1995). Inducible gene targeting in mice. Science 269: 1427–1429.
Kurosawa H, Goi K, Inukai T, Inaba T, Chang KS, Shinjyo T et al. (1999). Two candidate downstream target genes for E2A-HLF. Blood 93: 321–332.
Lin H, Grosschedl R . (1995). Failure of B-cell differentiation in mice lacking the transcription factor EBF. Nature 376: 263–267.
Look AT . (1997). Oncogenic transcription factors in the human acute leukemias. Science 278: 1059–1064.
Matsunaga T, Inaba T, Matsui H, Okuya M, Miyajima A, Inukai T et al. (2003). Regulation of annexin II by cytokine-initiated signaling pathways and E2A-HLF oncoprotein. Blood 103: 3185–3191.
Mikkers H, Berns A . (2003). Retroviral insertional mutagenesis: tagging cancer pathways. Adv Cancer Res 88: 53–99.
Miyazaki K, Kawamoto T, Tanimoto K, Nishiyama M, Honda H, Kato Y . (2002). Identification of functional hypoxia response elements in the promoter region of the DEC1 and DEC2 genes. J Biol Chem 277: 47014–47021.
Miyazaki K, Yamasaki N, Oda H, Kuwata T, Kanno Y, Miyazaki M et al. (2009). Enhanced expression of p210BCR/ABL and aberrant expression of Zfp423/ZNF423 induce blast crisis of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 113: 4702–4710.
Mizuno T, Yamasaki N, Miyazaki K, Tazaki T, Koller R, Oda H et al. (2008). Overexpression/enhanced kinase activity of BCR/ABL and altered expression of Notch1 induced acute leukemia in p210BCR/ABL transgenic mice. Oncogene 27: 3465–3474.
Nakamura T . (2005). Retroviral insertional mutagenesis identifies oncogene cooperation. Cancer Sci 96: 7–12.
Nakayama H, Ishimaru F, Avitah N, Sezaki N, Fujii N, Nakase K et al. (1999). Decreases in Ikaros activity correlate with blast crisis in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Res 59: 3931–3934.
Rosenbaum H, Harris AW, Bath ML, McNeall J, Webb E, Adams JM et al. (1990). An E mu-v-abl transgene elicits plasmacytomas in concert with an activated myc gene. EMBOJ 9: 897–905.
Scheijen B, Jonkers J, Acton D, Berns A . (1997). Characterization of pal-1, a common proviral insertion site in murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas of c-myc and Pim-1 transgenic mice. J Virol 71: 9–16.
Seidel MG, Look AT . (2001). E2A-HLF usurps control of evolutionarily conserved survival pathways. Oncogene 20: 5718–5725.
Shinto Y, Morimoto M, Katsumata M, Uchida A, Aozasa K, Okamoto M et al. (1995). Moloneymurine leukemia virus infection accelerates lymphomagenesis in E mu-bcl-2 transgenic mice. Oncogene 11: 1729–1736.
Smith KS, Rhee JW, Cleary ML . (2002). Transformation of bone marrow B-cell progenitors by E2a-Hlf requires coexpression of Bcl-2. Mol Cell Biol 22: 7678–7687.
Smith KS, Rhee JW, Naumovski L, Cleary ML . (1999). Disrupted differentiation and oncogenic transformation of lymphoid progenitors in E2A-HLF transgenic mice. Mol Cell Biol 19: 4443–4451.
Wang J, Iwasaki H, Krivtsov A, Febbo PG, Thorner AR, Ernst P et al. (2005). Conditional MLL-CBP targets GMP and models therapy-related myeloproliferative disease. EMBOJ 24: 368–381.
Warming S, Liu P, Suzuki T, Akagi K, Lindtner S, Pavlakis GN et al. (2003). Evi3, a common retroviral integration site in murine B-cell lymphoma, encodes an EBFAZ-related Krüppel-like zinc finger protein. Blood 101: 1934–1940.
Wolff L, Garin MT, Koller R, Bies J, Liao W, Malumbres M et al. (2003a). Hypermethylation of the Ink4b locus in murine myeloid leukemia and increased susceptibility to leukemia in p15(Ink4b)-deficient mice. Oncogene 22: 9265–9274.
Wolff L, Koller R, Hu X, Anver MR . (2003b). A Moloney murine leukemia virus-based retrovirus with 4070A long terminal repeat sequences induces a high incidence of myeloid as well as lymphoid neoplasms. J Virol 77: 4965–4971.
Yamashita N, Osato M, Huang L, Yanagida M, Kogan SC, Iwasaki M et al. (2005). Haploinsufficiency of Runx1/AML1 promotes myeloid features and leukaemogenesis in BXH2 mice. Br J Haematol 131: 495–507.
Yoshihara T, Inaba T, Shapiro LH, Kato JY, Look AT . (1995). E2A-HLF-mediated cell transformation requires both the trans-activation domains of E2A and the leucine zipper dimerization domain of HLF. Mol Cell Biol 15: 3247–3255.
Zhuang Y, Soriano P, Weintraub H . (1994). The helix-loop-helix gene E2A is required for B cell formation. Cell 79: 875–884.
Zörnig M, Schmidt T, Karsunky H, Grzeschiczek A, Möröy T . (1996). Zinc finger protein GFI-1 cooperates with myc and pim-1 in T-cell lymphomagenesis by reducing the requirements for IL-2. Oncogene 12: 1789–1801.
Acknowledgements
We thank Yuki Sakai, Kayoko Hashimoto, Yuko Tsukawaki and Rika Tai, for the care of the mice and technical assistance, Dr Nobuaki Yoshida for E14 ES cells, Dr Søren Warming, Dr Neal G Copeland and Dr Nancy A Jenkins for mouse Zfp521 cDNA, Dr Koichi Ikuta for mouse TCRJβ probe, Dr Hirotaka Matsui for statistical analysis and Dr Takuro Nakamura for helpful discussion. This work was in part supported by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan, a grant-in-aid for Cancer Research from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (13-2), Takeda Science Foundation, Astellas Foundation for Research on Metabolic Disorders, the Japan Leukaemia Research Fund and Tsuchiya Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Authorship
Contribution: NY, Z-iH, TI and HH designed and performed the research and wrote the paper; HO centralized the pathological analysis; RK and LW generated the retrovirus; KM, MM and TS participated in the flow cytometric analysis; AN performed colony assays. All the authors checked the final version of the paper.
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamasaki, N., Miyazaki, K., Nagamachi, A. et al. Identification of Zfp521/ZNF521 as a cooperative gene for E2A-HLF to develop acute B-lineage leukemia. Oncogene 29, 1963–1975 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.475
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2009.475
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Direct reprogramming of fibroblasts into neural stem cells by single non-neural progenitor transcription factor Ptf1a
Nature Communications (2018)
-
ZNF521 Has an Inhibitory Effect on the Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports (2018)
-
ZFP521 contributes to pre-B-cell lymphomagenesis through modulation of the pre-B-cell receptor signaling pathway
Oncogene (2016)
-
Maintenance of the functional integrity of mouse hematopoiesis by EED and promotion of leukemogenesis by EED haploinsufficiency
Scientific Reports (2016)