Abstract
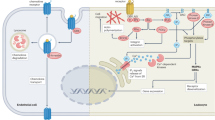
Since their discovery 13 years ago, chemokines have emerged as the most important regulators of leukocyte trafficking. On target cells, chemokines bind to seven-transmembrane-domain receptors that are coupled to heterotrimeric Gi proteins. The common response of all cells to chemokine stimulation is chemotaxis. In addition, leukocyte activation triggers diverse signal transduction cascades; which cascade is triggered depends on the chemokine and receptor engaged. The selective activation of distinct pathways suggests that the receptors couple not only to G proteins but also to additional downstream effectors. This review discusses recent advances in the elucidation of the signal transduction that occurs in proximity to receptors and that leads to the early biochemical events in leukocyte activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy, P. M. et al. International union of pharmacology. XXII. Nomenclature for chemokine receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 52, 145–176 (2000).
Thelen, M. et al. Mechanism of neutrophil activation by NAF, a novel monocyte-derived peptide agonist. FASEB J. 2, 2702–2706 (1988).
Boulay, F., Tardif, M., Brouchon, L. & Vignais, P. The human N-formylpeptide receptor. Characterization of two cDNA isolates and evidence for a new subfamily of G- protein-coupled receptors. Biochemistry 29, 11123–11133 (1990).
Holmes, W. E., Lee, J., Kuang, W.-J., Rice, G. C. & Wood, W. I. Structure and functional expression of a human interleukin-8 receptor. Science 253, 1278–1280 (1991).
Murphy, P. M. & Tiffany, H. L. Cloning of complementary DNA encoding a functional human interleukin-8 receptor. Science 253, 1280–1283 (1991).
Palczewski, K. et al. Crystal structure of rhodopsin: A G protein-coupled receptor. Science 289, 739–745 (2000).
Berger, E. A., Murphy, P. M. & Farber, J. M. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 657–700 (1999).
Amara, A. et al. HIV coreceptor downregulation as antiviral principle: SDF-1α-dependent internalization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 contributes to inhibition of HIV replication. J. Exp. Med. 186, 139–146 (1997).
Kuhmann, S. E., Platt, E. J., Kozak, S. L. & Kabat, D. Cooperation of multiple CCR5 coreceptors is required for infections by human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J. Virol. 74, 7005–7015 (2000).
Ugolini, S. et al. HIV-1 gp120 induces an association between CD4 and the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J. Immunol. 159, 3000–3008 (1997).
Davis, C. B. et al. Signal transduction due to HIV-1 envelope interactions with chemokine receptors CXCR4 or CCR5. J. Exp. Med. 186, 1793–1798 (1997).
Cicala, C. et al. Induction of phosphorylation and intracellular association of CC chemokine receptor 5 and focal adhesion kinase in primary human CD4+ T cells by macrophage-tropic HIV envelope. J. Immunol. 163, 420–426 (1999).
Bacon, K. B., Premack, B. A., Gardner, P. & Schall, T. J. Activation of dual T cell signaling pathways by the chemokine RANTES. Science 269, 1727–1730 (1995).
Wu, D., LaRosa, G. J. & Simon, M. I. G protein-coupled signal transduction pathways for interleukin-8. Science 261, 101–103 (1993).
Jones, S. A., Wolf, M., Qin, S., Mackay, C. R. & Baggiolini, M. Different functions for the interleukin 8 receptors (IL-8R) of human neutrophil leukocytes: NADPH oxidase and phospholipase D are activated through IL-8R1 but not IL-8R2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 6682–6686 (1996).
Fanning, A. S. & Anderson, J. M. PDZ domains: fundamental building blocks in the organization of protein complexes at the plasma membrane. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 767–772 (1999).
Hall, R. A. et al. The β2-adrenergic receptor interacts with the Na+/H+- exchanger regulatory factor to control Na+/H+ exchange. Nature 392, 626–630 (1998).
Cao, T. T., Deacon, H. W., Reczek, D., Bretscher, A. & von Zastrow, M. A kinase-regulated PDZ-domain interaction controls endocytic sorting of the β2-adrenergic receptor. Nature 401, 286–290 (1999).
Vicente-Manzanares, M. et al. The chemokine SDF-1α triggers a chemotactic response and induces cell polarization in human B lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 28, 2197–2207 (1998).
Nieto, M. et al. Polarization of chemokine receptors to the leading edge during lymphocyte chemotaxis. J. Exp. Med. 186, 153–158 (1997).
Servant, G., Weiner, O. D., Neptune, E. R., Sedat, J. W. & Bourne, H. R. Dynamics of a chemoattractant receptor in living neutrophils during chemotaxis. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 1163–1178 (1999).
Xiao, Z., Zhang, N., Murphy, D. B. & Devreotes, P. N. Dynamic distribution of chemoattractant receptors in living cells during chemotaxis and persistent stimulation. J. Cell Biol. 139, 365–374 (1997).
Parent, C. A., Blacklock, B. J., Froehlich, W. M., Murphy, D. B. & Devreotes, P. N. G protein signaling events are activated at the leading edge of chemotactic cells. Cell 95, 81–91 (1998).
Meili, R. et al. Chemoattractant-mediated transient activation and membrane localization of Akt/PKB is required for efficient chemotaxis to cAMP in Dictyostelium. EMBO J. 18, 2092–2105 (1999).
Servant, G. et al. Polarization of chemoattractant receptor signaling during neutrophil chemotaxis. Science 287, 1037–1040 (2000).
Meinhardt, H. Orientation of chemotactic cells and growth cones: models and mechanisms. J. Cell Sci. 112, 2867–2874 (1999).
Neptune, E. R., Iiri, T. & Bourne, H. R. Gαi is not required for chemotaxis mediated by Gi-coupled receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 2824–2828 (1999).
Neptune, E. R. & Bourne, H. R. Receptors induce chemotaxis by releasing the βγ subunit of Gi, not by activating Gq or Gs . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 14489–14494 (1997).
Jin, T., Zhang, N., Long, Y., Parent, C. A. & Devreotes, P. N. Localization of the G protein βγ complex in living cells during chemotaxis. Science 287, 1034–1036 (2000).
Baggiolini, M., Dewald, B. & Moser, B. Human chemokines: An update. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 15, 675–705 (1997).
Rhee, S. G. & Bae, Y. S. Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C isozymes. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 15045–15048 (1997).
Sankaran, B., Osterhout, J., Wu, D. Q. & Smrcka, A. V. Identification of a structural element in phospholipase C β2 that interacts with G protein βγ subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7148–7154 (1998).
Barr, A. J., Ali, H., Haribabu, B., Snyderman, R. & Smrcka, A. V. Identification of a region at the N-terminus of phospholipase C-β3 that interacts with G protein βγ subunits. Biochemistry 39, 1800–1806 (2000).
Li, Z. et al. Roles of PLC-β2 and -β3 and PI3Kγ in chemoattractant-mediated signal transduction. Science 287, 1046–1049 (2000).
Mandeville, J. T. & Maxfield, F. R. Effects of buffering intracellular free calcium on neutrophil migration through three-dimensional matrices. J. Cell Physiol. 171, 168–178 (1997).
Orsini, M. J., Parent, J. L., Mundell, S. J., Benovic, J. L. & Marchese, A. Trafficking of the HIV coreceptor CXCR4. Role of arrestins and identification of residues in the c-terminal tail that mediate receptor internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 31076–31086 (1999).
Signoret, N. et al. Phorbol esters and SDF-1 induce rapid endocytosis and down modulation of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J. Cell Biol. 139, 651–664 (1997).
Richardson, R. M. et al. Regulation of human interleukin-8 receptor A: Identification of a phosphorylation site involved in modulating receptor functions. Biochemistry 34, 14193–14201 (1995).
Stephens, L. et al. A novel phosphoinositide 3 kinase activity in myeloid-derived cells is activated by G protein βγ subunits. Cell 77, 83–93 (1994).
Stoyanov, B. et al. Cloning and characterization of a G protein-activated human phosphoinositide-3 kinase. Science 269, 690–693 (1995).
Stephens, L. E. et al. The Gβγ-sensitivity of a PI3K is dependent upon a tightly-associated adaptor, p101. Cell 89, 105–114 (1997).
Ward, S. G., Bacon, K. & Westwick, J. Chemokines and T lymphocytes: more than an attraction. Immunity 9, 1–11 (1998).
Tilton, B. et al. Signal transduction by CXC chemokine receptor 4. Stromal cell-derived factor 1 stimulates prolonged protein kinase b and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 activation in t lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 192, 313–324 (2000).
Sasaki, T. et al. Function of PI3Kγ in thymocyte development, T cell activation, and neutrophil migration. Science 287, 1040–1046 (2000).
Hirsch, E. et al. Central role for G protein-coupled phosphoinositide 3-kinase γ in inflammation. Science 287, 1049–1053 (2000).
Fruman, D. A. et al. Impaired B cell development and proliferation in absence of phosphoinositide 3-kinase p85α. Science 283, 393–397 (1999).
Bottomley, M. J., Salim, K. & Panayotou, G. Phospholipid-binding protein domains. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1436, 165–183 (1998).
Burgering, B. M. T. & Coffer, P. J. Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature 376, 599–602 (1995).
Didichenko, S. A., Tilton, B., Hemmings, B. A., Ballmer-Hofer, K. & Thelen, M. Constitutive activation of protein kinase B and phosphorylation of p47phox by membrane-targeted phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Curr. Biol. 6, 1271–1278 (1996).
Hemmings, B. A. Update: Signal transduction - PtdIns(3,4,5)P3 gets its message across. Science 277, 534–534 (1997).
Chan, T. O., Rittenhouse, S. E. & Tsichlis, P. N. AKT/PKB and other D3 phosphoinositide-regulated kinases: kinase activation by phosphoinositide-dependent phosphorylation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 68, 965–1014 (1999).
Frech, M. et al. High affinity binding of inositol phosphates and phosphoinositides to the pleckstin homology domain of RAC/protein kinase B and their influence on kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 8474–8481 (1997).
Klippel, A., Kavanaugh, W. M., Pot, D. & Williams, L. T. A specific product of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase directly activates the protein kinase Akt through its pleckstrin homology domain. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 338–344 (1997).
Toker, A. & Newton, A. C. Cellular signaling: pivoting around PDK-1. Cell 103, 185–188 (2000).
Alessi, D. R. et al. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr. Biol. 7, 261–269 (1997).
Tilton, B., Andjelkovic, M., Didichenko, S. A., Hemmings, B. A. & Thelen, M. G-protein-coupled receptors and Fcγ-receptors mediate activation of Akt protein kinase B in human phagocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 28096–28101 (1997).
Thelen, M., Uguccioni, M. & Bösiger, J. PI 3-kinase-dependent and independent chemotaxis of human neutrophil leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 217, 1255–1262 (1995).
Wymann, M. P. et al. Oscillatory motion in human neutrophils responding to chemotactic stimuli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 147, 361–368 (1987).
Knall, C. et al. Interleukin-8 regulation of the Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in human neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 2832–2838 (1996).
Huang, R. Y., Lian, J. P., Robinson, D. & Badwey, J. A. Neutrophils stimulated with a variety of chemoattractants exhibit rapid activation of p21-activated kinases (Paks): Separate signals are required for activation and inactivation of Paks. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 7130–7138 (1998).
Jones, S. A., Moser, B. & Thelen, M. A comparison of post-receptor signal transduction events in Jurkat cells transfected with either IL-8R1 or IL-8R2: Chemokine mediated activation of p42/p44 MAP-kinase (ERK- 2). FEBS Lett. 364, 211–214 (1995).
Lopez-Ilasaca, M., Crespo, P., Pellici, P. G., Gutkind, J. S. & Wetzker, R. Linkage of G protein-coupled receptors to the MAPK signaling pathway through PI3-kinase γ. Science 275, 394–397 (1997).
Bondeva, T. et al. Bifurcation of lipid and protein kinase signals of PI3Kγ to the protein kinases PKB and MAPK. Science 282, 293–296 (1998).
Ma, Y. C., Huang, J., Ali, S., Lowry, W. & Huang, X. Y. Src tyrosine kinase is a novel direct effector of G proteins. Cell 102, 635–646 (2000).
Kehrl, J. H. Heterotrimeric G protein signaling: Roles in immune function and fine-tuning by RGS proteins. Immunity 8, 1–10 (1998).
Thomas, S. M. & Brugge, J. S. Cellular functions regulated by Src family kinases. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 13, 513–609 (1997).
Sicheri, F. & Kuriyan, J. Structures of Src-family tyrosine kinases. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 7, 777–785 (1997).
Dikic, I., Dikic, I. & Schlessinger, J. Identification of a new Pyk2 isoform implicated in chemokine and antigen receptor signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 14301–14308 (1998).
Ganju, R. K. et al. The α-chemokine, stromal cell-derived factor-1α, binds to the transmembrane G-protein-coupled CXCR-4 receptor and activates multiple signal transduction pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 23169–23175 (1998).
Wang, J. F., Park, I. W. & Groopman, J. E. Stromal cell-derived factor-1α stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of multiple focal adhesion proteins and induces migration of hematopoietic progenitor cells: roles of phosphoinositide-3 kinase and protein kinase C. Blood 95, 2505–2513 (2000).
Bacon, K. B., Szabo, M. C., Yssel, H., Bolen, J. B. & Schall, T. J. RANTES induces tyrosine kinase activity of stably complexed p125FAK and ZAP-70 in human T cells. J. Exp. Med. 184, 873–882 (1996).
Bauer, P. H. et al. Interactions of phosducin with the subunits of G-proteins - Binding to the α as well as the β γ subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 9465–9471 (1998).
De Vries, L., Zheng, B., Fischer, T., Elenko, E. & Farquhar, M. G. The regulator of G protein signaling family. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 40, 235–271 (2000).
Bowman, E. P. et al. Regulation of chemotactic and proadhesive responses to chemoattractant receptors by RGS (Regulator of G-protein Signaling) family members. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 28040–28048 (1998).
Reif, K. & Cyster, J. G. RGS molecule expression in murine B lymphocytes and ability to down-regulate chemotaxis to lymphoid chemokines. J Immunol. 164, 4720–4729 (2000).
Pitcher, J. A., Freedman, N. J. & Lefkowitz, R. J. G protein-coupled receptor kinases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 653–692 (1998).
Zlotnik, A., Morales, J. & Hedrick, J. A. Recent advances in chemokines and chemokine receptors. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 19, 1–47 (1999).
Oppermann, M., Mack, M., Proudfoot, A. E. & Olbrich, H. Differential effects of CC chemokines on CC chemokine receptor 5 (CCR5) phosphorylation and identification of phosphorylation sites on the CCR5 carboxyl terminus. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8875–8885 (1999).
Aragay, A. M. et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1-induced CCR2B receptor desensitization mediated by the G protein-coupled receptor kinase 2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2985–2990 (1998).
Grimm, M. C. et al. Opiates transdeactivate chemokine receptors: δ and μ opiate receptor-mediated heterologous desensitization. J. Exp. Med. 188, 317–325 (1998).
Haribabu, B. et al. Regulation of human chemokine receptors CXCR4 - Role of phosphorylation in desensitization and internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 28726–28731 (1997).
Luttrell, L. M., Daaka, Y. & Lefkowitz, R. J. Regulation of tyrosine kinase cascades by G-protein-coupled receptors. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol 11, 177–183 (1999).
AbdAlla, S., Zaki, E., Lother, H. & Quitterer, U. Involvement of the amino terminus of the B(2) receptor in agonist- induced receptor dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 26079–26084 (1999).
AbdAlla, S., Lother, H. & Quitterer, U. AT1-receptor heterodimers show enhanced G-protein activation and altered receptor sequestration. Nature 407, 94–98 (2000).
Overton, M. C. & Blumer, K. J. G-protein-coupled receptors function as oligomers in vivo. Curr. Biol. 10, 341–344 (2000).
Vila-Coro, A. J. et al. HIV-1 infection through the CCR5 receptor is blocked by receptor dimerization. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3388–3393 (2000).
Herbert, T. E. et al. A peptide derived from a β2-adrenergic receptor transmembrane domain inhibits both receptor dimerization and activation. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 16384–16392 (1996).
Rodriguez-Frade, J. M. et al. The chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 induces functional responses through dimerization of its receptor CCR2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 3628–3633 (1999).
Vila-Coro, A. J. et al. The chemokine SDF-1α triggers CXCR4 receptor dimerization and activates the JAK/STAT pathway. FASEB J. 13, 1699–1710 (1999).
Feniger-Barish, R. et al. GCP-2-induced internalization of IL-8 receptors: hierarchical relationships between GCP-2 and other ELR(+)-CXC chemokines and mechanisms regulating CXCR2 internalization and recycling. Blood 95, 1551–1559 (2000).
Giannini, E. & Boulay, F. Phosphorylation, dephosphorylation, and recycling of the C5a receptor in differentiated HL60 cells. J. Immunol. 154, 4055–4064 (1995).
Ali, H., Richardson, R. M., Haribabu, B. & Snyderman, R. Chemoattractant receptor cross-desensitization. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 6027–6030 (1999).
Richardson, R. M., Ali, H., Pridgen, B. C., Haribabu, B. & Snyderman, R. Multiple signaling pathways of human interleukin-8 receptor A - Independent regulation by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 10690–10695 (1998).
Ali, H. et al. Differential regulation of formyl peptide and platelet-activating factor receptors - Role of phospholipase Cβ3 phosphorylation by protein kinase A. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 11012–11016 (1998).
Shen, W. et al. Down-regulation of the chemokine receptor CCR5 by activation of chemotactic formyl peptide receptor in human monocytes. Blood 96, 2887–2894 (2000).
Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 103, 211–225 (2000).
Jordan, B. A. & Devi, L. A. G-protein-coupled receptor heterodimerization modulates receptor function. Nature 399, 697–700 (1999).
Ilangumaran, S., He, H. T. & Hoessli, D. C. Microdomains in lymphocyte signalling: beyond GPI-anchored proteins. Immunol. Today 21, 2–7 (2000).
Nanki, T. & Lipsky, P. E. Cutting edge: stromal cell-derived factor-1 is a costimulator for CD4+ T cell activation. J. Immunol. 164, 5010–5014 (2000).
Jordan, J. D., Landau, E. M. & Iyengar, R. Signaling networks: the origins of cellular multitasking. Cell 103, 193–200 (2000).
Davis, R. J. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 103, 239–252 (2000).
Ptasznik, A. et al. A tyrosine kinase signaling pathway accounts for the majority of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate formation in chemoattractant-stimulated human neutrophils. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 25204–25207 (1996).
Mellado, M. et al. The chemokine monocyte chemotactic protein 1 triggers Janus kinase 2 activation and tyrosine phosphorylation of the CCR2B receptor. J. Immunol. 161, 805–813 (1998).
Luttrell, L. M. et al. β-arrestin-dependent formation of β2 adrenergic receptor Src protein kinase complexes. Science 283, 655–661 (1999).
Acknowledgements
The author thanks B. Dewald for critical reading and comments. Supported by the Swiss Science Foundation (NFP-38) and the Helmut Horten Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thelen, M. Dancing to the tune of chemokines. Nat Immunol 2, 129–134 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/84224
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/84224