Abstract
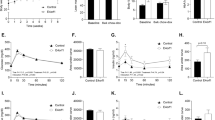
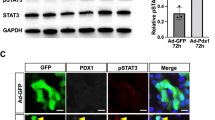
Insulin gene expression is restricted to islet β cells of the mammalian pancreas through specific control mechanisms mediated in part by specific transcription factors1,2. The protein encoded by the pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 (PDX-1) is central in regulating pancreatic development and islet cell function3. PDX-1 regulates insulin gene expression and is involved in islet cell-specific expression of various genes4,5,6,7. Involvement of PDX-1 in islet-cell differentiation and function has been demonstrated mainly by ‘loss-of-function’ studies8,9,10,11. We used a ‘gain-of-function’ approach to test whether PDX-1 could endow a non-islet tissue with pancreatic β-cell characteristics in vivo. Recombinant-adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of PDX-1 to the livers of BALB/C and C57BL/6 mice activated expression of the endogenous, otherwise silent, genes for mouse insulin 1 and 2 and prohormone convertase 1/3 (PC 1/3). Expression of PDX-1 resulted in a substantial increase in hepatic immunoreactive insulin content and an increase of 300% in plasma immunoreactive insulin levels, compared with that in mice treated with control adenovirus. Hepatic immunoreactive insulin induced by PDX-1 was processed to mature mouse insulin 1 and 2 and was biologically active; it ameliorated hyperglycemia in diabetic mice treated with streptozotocin. These data indicate the capacity of PDX-1 to reprogram extrapancreatic tissue towards a β-cell phenotype, may provide a valuable approach for generating ‘self’ surrogate β cells, suitable for replacing impaired islet-cell function in diabetics.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sander, M. & German, M.S. The β-cell transcription factors and development of the pancreas. J. Mol. Med. 75, 327–340 (1997).
Edlund, T., Walker, M.D., Barr, P.J. & Rutter, W.J. Cell specific expression of the rat insulin gene. Science 230, 912–916 (1985).
Stoffers, D.A., Thomas, M.K. & Habener, J.F. The homeodomain protein IDX-1. Trends Endocrinol. & Metab. 8, 145–151 (1997).
Watada, H. et al. The human glucokinase gene β-cell-type promoter. An essential role of insulin promoter factor 1/PDX-1 in its activation in HIT-T15 cells . Diabetes 45, 1478–1488 (1996).
Miller, C.P., McGehee, R. & Habener, J.F. A new homeodomain transcription factor expressed in rat pancreatic islets and duodenum stimulates somatostatin gene expression in pancreatic islets. EMBO J. 13, 1145– 1156 (1994).
Waeber, G., Thompson, N., Nicod, P. & Bonny, C. Transcriptional activation of the GLUT2 gene by the IPF-1/STF-1/IDX-1 homeobox factor. Mol. Endocrinol. 10, 1327–1333 (1996).
Marshak, S., Totary, H., Cerasi, E. & Melloul, D. Purification of the β-cell glucose-sensitive factor that transactivates the insulin gene differentially in normal and transformed islet cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 15057–15062 (1996).
Jonsson, J., Carlsson, L., Edlund, T. & Edlund, H. Insulin-promoter-factor-1 is required for pancreas development in mice. Nature 371, 606–609 (1994).
Offield, M.F. et al. PDX-1 is required for pancreatic outgrowth and differentiation of the rostral duodenum. Development 122, 983–995 (1996).
Edlund, H. Transcribing a pancreas. Diabetes 47, 1817 –1823 (1998).
Stoffers, D.A., Zinkin, N.T., Stanojevic, V., Clarke, W.L. & Habener, J.F. Pancreas agenesis attributable to a single nucleotide deletion in the human IPF-1 gene coding sequence. Nature Genet. 15, 106–110 (1997).
Seijffers, R. et al. Increase in PDX-1 levels supresses insulin gene expression in RIN-38 cells. Endocrinology 140, 3311 –3317 (1999).
Steiner, D.F., Chan, S.J., Welsh, M.J. & Kwok, S.C.M. Structure and evolution of the insulin gene. Annu. Rev. Genet. 19 , 463–484 (1985).
Siegfried, Z. & Cedar, H. DNA methylation: a molecular lock . Curr. Biol. 7, R305–R307 (1998).
Van-Holde, K.E. Chromatin structure and regulation of gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 26073 (1997).
Vollenweider, F., Irminger, J.C., Gross, D.J., Villa-Komaroff, L. & Halban, P.A. Processing of proinsulin by transfected hepatoma (FAO) cells. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14629–14636 (1992).
Steiner, D.F., Smeekens, S.P., Ohagi, S. & Chan, S.J. The new enzymology of precursor processing endopeptidases. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 23435–23438 ( 1992).
O'Doherty, R.M., Lehman, D.L., Telemaque-Potts, S. & Newgard, C.B. Metabolic impact of glucokinase overexpression in liver: lowering of blood glucose in fed rats is accompanied by hyperlipidemia. Diabetes 48, 2022–2027 ( 1999).
Emens, L.A., Landers, D.W. & Moss, L.G. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 α is expressed in a hamster insulinoma line and transactivates the rat insulin I gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 7300– 7304 (1992).
Lekstrom-Himes, J. & Xanthopoulos, K.G. Biological role of the CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein family of transcription factors . J.Biol. Chem. 273, 28545– 28548 (1998).
Weintraub, H., et al. Activation of muscle-specific genes in pigment, nerve, fat, liver, and fibroblast cell lines by forced expression of MyoD. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 5434– 5438 (1989).
Heller, R.S., Stoffer, D.A., Hussain, M.A., Miller, C.P. & Habener, J.F. Misexpression of IDX-1 by Hoxa-4 promoter associated with agenesis of the cecum. Gastroenterology 115, 381–3871 ( 1998).
Alison, M. Liver stem cells: a two compartment system. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 10, 710–716 ( 1998).
Thorgeirsson, S.S. Hepatic stem cells in liver regeneration. FASEB J. 10, 1249–1256 (1996).
Gross, D.J., Leibowitz, G., Cerasi, E. & Kaiser, N. Increased susceptibility of islets from diabetes-prone Psammomys obesus to the deleterious effects of chronic glucose exposure. Endocrinology 137, 5610–5615 ( 1996).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Gal, Y. Cohen, Y. Ariav, P. Keren, A. Shaish, M. Tal and D. Castel for technical support; M.D. Walker and C.B. Newgard for critically reviewing the manuscript; R. Skutelsky and H. Halkin for editing the manuscript; and B. Goldman for support. The study was partially supported by a grant from Israel Ministry of Health-Mendel Chodowski-Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferber, S., Halkin, A., Cohen, H. et al. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox gene 1 induces expression of insulin genes in liver and ameliorates streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Nat Med 6, 568–572 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/75050
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/75050
This article is cited by
-
Progress and application of adipose-derived stem cells in the treatment of diabetes and its complications
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2024)
-
A guide from the stomach to β cells
Nature Cell Biology (2023)
-
Transgenic mice for in vivo epigenome editing with CRISPR-based systems
Nature Methods (2021)
-
Emerging routes to the generation of functional β-cells for diabetes mellitus cell therapy
Nature Reviews Endocrinology (2020)
-
The role of the vasculature niche on insulin-producing cells generated by transdifferentiation of adult human liver cells
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2019)