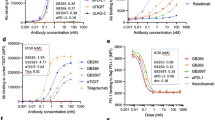
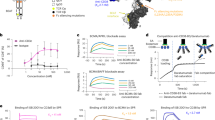
Abstract
Inhibitory receptors have been proposed to modulate the in vivo cytotoxic response against tumor targets for both spontaneous and antibody-dependent pathways1. Using a variety of syngenic and xenograft models, we demonstrate here that the inhibitory FcγRIIB molecule is a potent regulator of antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity in vivo, modulating the activity of FcγRIII on effector cells. Although many mechanisms have been proposed to account for the anti-tumor activities of therapeutic antibodies, including extended half-life, blockade of signaling pathways, activation of apoptosis and effector-cell-mediated cytotoxicity, we show here that engagement of Fcγ receptors on effector cells is a dominant component of the in vivo activity of antibodies against tumors. Mouse monoclonal antibodies, as well as the humanized, clinically effective therapeutic agents trastuzumab (Herceptin®) and rituximab (Rituxan®), engaged both activation (FcγRIII) and inhibitory (FcγRIIB) antibody receptors on myeloid cells, thus modulating their cytotoxic potential. Mice deficient in FcγRIIB showed much more antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity; in contrast, mice deficient in activating Fc receptors as well as antibodies engineered to disrupt Fc binding to those receptors were unable to arrest tumor growth in vivo. These results demonstrate that Fc-receptor-dependent mechanisms contribute substantially to the action of cytotoxic antibodies against tumors and indicate that an optimal antibody against tumors would bind preferentially to activation Fc receptors and minimally to the inhibitory partner FcγRIIB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bolland, S. & Ravetch, J.V. Inhibitory pathways triggered by ITIM-containing receptors. Adv. Immunol. 72, 149–177 (1999).
Clynes, R.A., Tekechi, Y., Moroi, Y., Houghton, A. & Ravetch, J.V. Fc receptors are required in passive and active immunity to melanoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 652 (1998).
Hudziak, R. et al. p185HER2 monoclonal antibody has antiproliferative effects in vitro and sensitizes human breast tumor cells to tumor necrosis factor Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 1165 ( 1989);
Taji, H. et al. Growth inhibition of CD20 positive B lymphoma cell lines by IDEC-C2B8 anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 89, 748 (1998).
Masui, H., Moroyama, T. & Mendelsohn, J. Mechanism of antitumor activity in mice for anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies with different isotypes Cancer Res. 46, 5592 (1986);
Waldmann, T.A. Lymphokine receptors: a target for immunotherapy of lymphomas. Ann. Oncol. Supp. 13, 5, 1– 45 (1994).
Tutt, A.L. et al. Monoclonal antibody therapy of a B cell lymphoma: signaling activity on tumor cells appears more important than recruitment of effectors. J. Immunol. 161, 3176 (1998).
Pegram, M.D. et al. Phase II study of receptor enhanced chemosensitivity using recombinant humanized anti-p185HER2/neu monoclonal antibody plus cisplatin in patients with HER2.neu overexpressing metastatic breast cancer refractory to chemotherapy treatment J. Clin. Oncol. 16, 2659 (1998)
Carter, P.L. et al. Humanization of an anti-p185HER2 antibody for human cancer treatment, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 4285 (1992).
Leget, G.A. & Czuczman, M.S. Use of Rituximab, the new FDA-approved antibody. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 10, 548– 551 (1998)
Kopreski, M., Lipton, A., Harvey, H.A. & Kumar, R. Growth inhibition of breast cancer cell lines by combinations of anti-p185 monoclonal antibody and cytokines. Anticancer Res. 16, 433– 436 (1996).
Lewis, G.D. et al. Differential responses of human tumor cell lines to anti-p185HER2 monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 37, 255–263 (1993).
Shan, D., Ledbetter, J.A. & Press, O.W. Apoptosis of malignant human B cells by ligation of CD20 with monoclonal antibodies. Blood 91, 1644–1652 (1998).
Takai, T., Li., M., Sylvestre, D., Clynes, R. & Ravetch, J.V. FcR γ chain deletion results in pleiotropic effector cell defects. Cell 76, 519– 529 (1994).
Takai, T., Ono, M, Hikida, M., Ohmori, H. & Ravetch, J.V. Augmented humoral and anaphylactic responses in Fc_RIIB deficient mice. Nature 379, 346– 349 (1996).
Funakoshi, S., Longo, D.L. & Murphy, W.J. Differential in vitro and in vivo antitumor effects mediated by anti-CD40 and anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies against human B-cell lymphomas. J. Immunother. 19, 93–101 (1996).
Fan, Z., Masui, H., Altas, I. & Mendelsohn, J. Blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor function by bivalent and monovalent fragments of 225 anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies Cancer Res. 53, 4322–4328 (1993)
Baselga, J., Norton, L., Albanell, J., Kim, Y.M. & Mendelsohn, J. Recombinant humanized anti-HER2 antibody (Herceptin) enhances the anti-tumor activity of paclitaxel and doxorubicin against HER2/neu overexpressing human breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Res. 58, 2825–2831 (1998).
Liu, J., Lester, P., Builder, S. & Shine, J. Characterization of complex formation by humanized anti-IgE monoclonal antibody and monoclonal human IgE. Biochemistry 34, 10474– 10482 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. White for his technical expertise, C. Ritter for her administrative assistance and R. Steinman and M. Nussenzweig for their comments on the manuscript. These studies were supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health, Cancer Research Institute and Genentech.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clynes, R., Towers, T., Presta, L. et al. Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytoxicity against tumor targets. Nat Med 6, 443–446 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/74704
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/74704
This article is cited by
-
Cuproptosis-related genes predict prognosis and trastuzumab therapeutic response in HER2-positive breast cancer
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Steroid Premedication and Monoclonal Antibody Therapy: Should We Reconsider?
Current Treatment Options in Oncology (2024)
-
Advances in antibody-based therapy in oncology
Nature Cancer (2023)
-
Alterations in immune cell phenotype and cytotoxic capacity in HER2+ breast cancer patients receiving HER2-targeted neo-adjuvant therapy
British Journal of Cancer (2023)
-
Effect of posttranslational modifications and subclass on IgG activity: from immunity to immunotherapy
Nature Immunology (2023)