Abstract
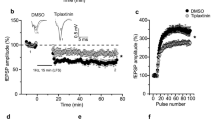
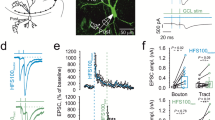
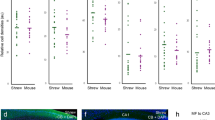
Repetitive activation of excitatory synapses in the central nervous system results in a long-lasting increase in synaptic transmission called long-term potentiation (LTP). It is generally believed that this synaptic plasticity may underlie certain forms of learning and memory. LTP at most synapses involves the activation of the NMDA (N-methyl-d-aspartate) subtype of glutamate receptor, but LTP at hippocampal mossy fibre synapses is independent of NMDA receptors and has a component that is induced and expressed presynaptically1. It appears to be triggered by a rise in presynaptic Ca2+(refs 2, 3), and requires the activation of protein kinase A4,5,6, which leads to an increased release of glutamate3,7,8,9,10. Agreat deal is known about the biochemical steps involved in the vesicular release of transmitter11,12,13, but none of these steps has been directly implicated in long-term synaptic plasticity. Here we show that, although a variety of short-term plasticities are normal, LTP at mossy fibre synapses is abolished in mice lacking the synaptic vesicle protein Rab3A.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicoll, R. A. & Malenka, R. C. Contrasting properties of two forms of long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 377, 115–118 (1995).
Castillo, P. E., Weisskopf, M. G. & Nicoll, R. A. The role of Ca2+ channels in hippocampal mossy fiber synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation. Neuron 12, 261–269 (1994).
Tong, G., Malenka, R. C. & Nicoll, R. A. Long-term potentiation in cultures of single hippocampal granule cells: A presynaptic form of plasticity. Neuron 16, 1147–1157 (1996).
Weisskopf, M. G., Castillo, P. E., Zalutsky, R. A. & Nicoll, R. A. Mediation of hippocampal mossy fiber long-term potentiation by cyclic AMP. Science 265, 1878–1882 (1994).
Huang, Y-Y., Li, X.-C. & Kandel, E. cAMP contributes to mossy fiber LTP by initiating both a covalently mediated early phase and macromolecular synthesis-dependent late phase. Cell 79, 69–79 (1994).
Huang, Y. Y.et al. Agenetic test of the effects of mutations in PKA on mossy fiber LTP and its relation to spatial and contextual learning. Cell 83, 1211–1222 (1995).
Zalutsky, R. A. & Nicoll, R. A. Comparison of two forms of long-term potentiation in single hippocampal neurons. Science 248, 1619–1624 (1990).
Weisskopf, M. G. & Nicoll, R. A. Presynaptic changes during mossy fiber LTP revealed by NMDA receptor-mediated synaptic responses. Nature 376, 256–259 (1995.).
López-García, J. C., Arancio, O., Kandel, E. R. & Baranes, D. Apresynaptic locus for long-term potentiation of elementary synaptic transmission at mossy fiber synapses in culture. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4712–4717 (1996).
Xiang, Z., Greenwood, A. C., Kairiss, E. W. & Brown, T. H. Quantal mechanism of long-term potentiation in hippocampal mossy-fiber synapses. J. Neurophysiol. 71, 2552–2556 (1994).
Ferro-Novick, S. & Jahn, R. Vesicle fusion from yeast to man. Nature 370, 191–193 (1994).
Bennett, M. K. & Scheller, R. H. Amolecular description of synaptic vesicle membrane trafficking. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 63, 63–100 (1994).
Südhof, T. C. The synaptic vesicle cycle: a cascade of protein–protein interactions. Nature 375, 645–653 (1995).
DeCamilli, P., Benfenati, F., Valtorta, F. & Greengard, P. The synapsins. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 6, 433–460 (1990).
Spillane, D. M., Rosahl, T. W., Südhof, T. C. & Malenka, R. C. Long-term potentiation in mice lacking synapsins. Neuropharmacology 34, 1573–1579 (1995).
Fykse, E. M., Li, C. & Südhof, T. C. Phosphorylation of rabphilin-3A by Ca2+/calmodulin- and cAMP-dependent protein kinases in vitro. J. Neurosci. 15, 2385–2395 (1995).
Wang, Y., Okamoto, M., Schmitz, F., Hofmann, K. & Südhof, T. C. Rim is a putative Rab3 effector in regulating synaptic-vesicle fusion. Nature 387, 000–000 (1997).
Geppert, M.et al. The role of Rab3A in neurotransmitter release. Nature 369, 493–497 (1994).
Rosahl, T. W.et al. Essential functions of synapsins I and II in synaptic vesicle regulation. Nature 375, 488–493 (1995).
Fykse, E. M.et al. Relative properties and localizations of synaptic vesicle protein isoforms: the case of the synaptophysins. J. Neurosci. 13, 4997–5007 (1993).
Kamiya, H., Shinozaki, H. & Yamamoto, C. Activation of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 2/3 suppresses transmission at rat hippocampal mossy fibre synapses. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 493, 447–455 (1996).
Yokoi, M.et al. Impairment of hippocampal mossy fiber LTD in mice lacking mGluR2. Science 273, 645–647 (1996).
Zucker, R. S. Short-term synaptic plasticity. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 12, 13–31 (1989).
Geppert, M., Goda, Y., Stevens, C. F. & Südhof, T. C. Rab3A regulates a late step in synaptic vesicle fusion. Nature 387, 810–814 (1997).
Regehr, W. G., Delaney, K. R. & Tank, D. W. The role of presynaptic calcium in short-term enhancement at the hippocampal mossy fiber synapse. J. Neurosci. 14, 523–537 (1994).
Salin, P. A., Scanziani, M., Malenka, R. C. & Nicoll, R. A. Distinct short-term plasticity at two excitatory synapses in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 13304–13309 (1996).
Seamon, K. B. & Daly, J. W. Forskolin: Its biological and chemical properties. Adv. Cyclic Nucleot. Prot. Phosphoryl. Res. 20, 1–150 (1986).
Dixon, D. & Atwood, L. Adenylate cyclase system is essential for long-term facilitation at the crayfish neuromuscular junction. J. Neurosci. 9, 4246–4252 (1989).
Schacher, S., Castellucci, V. F. & Kandel, E. R. cAMP evokes long-term facilitation in Aplysia sensory neurons that requires new protein synthesis. Science 240, 1667–1669 (1988).
Li, C.et al. Synaptic targeting of rabphilin-3A, a synaptic vesicle Ca2+/phospholipid-binding protein, depends on rab3A/3C. Neuron 13, 885–898 (1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank H. Czerwonka for secretarial assistance. R.A.N. is a member of the Keck Center for Integrative Neuroscience and the Silvio Conte Center for Neuroscience Research. R.C.M. is a member of the Center for Neurobiology and Psychiatry, and the Center for the Neurobiology of Addiction. R.A.N. and R.C.M. are supported by grants from the NIH. T.C.S. was supported by grants from the HFJP and the W.M. Keck Foundation. R.J. was supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from DFG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castillo, P., Janz, R., Sdhof, T. et al. Rab3A is essential for mossy fibre long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 388, 590–593 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/41574
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/41574