Abstract
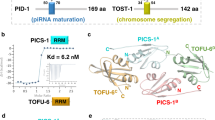
THE NIMA kinase is essential for progression through mitosis in Aspergillus nidulans1–6, and there is evidence for a similar pathway in other eukaryotic cells5–8. Here we describe the human protein Pinl, a peptidyl–prolyl cis/trans isomerase (PPIase) that interacts with NIMA. PPIases are important in protein folding, assembly and/or transport9–13, but none has so far been shown to be required for cell viability9–11. Pinl is nuclear PPIase containing a WW protein interaction domain, and is structurally and functionally related to Essl/Ptfl, an essential protein in budding yeast14,15. PPIase activity is necessary for Essl/Pinl function in yeast. Depletion of Pinl/Essl from yeast or HeLa cells induces mitotic arrest, whereas HeLa cells overexpressing Pinl arrest in the G2 phase of the cell cycle. Pinl is thus an essential PPIase that regulates mitosis presumably by interacting with NIMA and attenuating its mitosis-promoting activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Osmani, S. A., Pu, R. T. & Morris, N. R. Cell 53, 237–244 (1988).
Osmani, A. H., McGuire, S. L. & Osmani, S. A. Cell 67, 283–291 (1991).
Lu, K. P. & Means, A. R. EMBO J. 13, 2103–2113 (1994).
Pu, R. T. & Osmani, S. A. EMBO J. 14, 995–1003 (1995).
Lu, K. P. & Hunter, T. in Progress in Cell Cycle Research Vol. 1 (eds Meijer, L., Guidet, S. & Tung, H. Y. L.) 187–205 (Plenum, New York, 1996).
Fry, A. M. & Nigg, E. A. Curr. Biol. 5, 1122–1125 (1995).
Lu, K. P. & Hunter, T. Cell 81, 413–424 (1995).
O'Connell, M. J., Norbury, C. & Nurse, P. EMBO J. 13, 4926–4937 (1994).
Schreiber, S. L. Science 251, 283–287 (1991).
Heitman, J., Mowa, N. R. & Hall, M. N. New Biol. 4, 448–460 (1992).
Fischer, G. Angew. Chem. int. Edn. engl. 63, 67–118 (1994).
Rahfeld, J. U. et al. FEBS Lett. 343, 65–69 (1994).
Rudd, K. E. et al. Trends biochem. Sci. 20, 12–14 (1995).
Hanes, S. D., Shank, P. R. & Bostian, K. A. Yeast 5, 55–72 (1989).
Hani, J., Stumpf, G. & Domdey, H. FEBS Lett. 365, 198–202 (1995).
Sudol, M. et al. FEBS Lett. 369, 67–71 (1995).
Chen, H. I. & Sudol, M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 92, 7819–7823 (1995).
Davis, E. S. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 11169–11173 (1992).
Fu, X. D. & Maniatis, T. Nature 343, 437–441 (1990).
Spector, D. L. A. Rev. Cell Biol. 9, 265–315 (1993).
Fu, X. D. RNA 1, 663–680 (1995).
Takeuchi, M. & Yanagida, M. Molec. Biol. Cell 4, 247–260 (1993).
Gui, J. F., Lane, W. S. & Fu, X. D. Nature 369, 678–682 (1994).
Maleszka, R. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 93, 447–451 (1996).
Harper, J. W. et al. Cell 75, 805–816 (1993).
Hannon, G. J., Demetrick, D. & Beach, D. Genes Dev. 7, 2378–2391 (1993).
Heitman, J. et al. Methods 5, 176–187 (1993).
Louvion, J. F., Havaux, C. B. & Picard, D. Gene 131, 129–134 (1993).
Roberts, C. J. et al. Meth. Enzym. 194, 644–661 (1991).
Lu, K. P., Osmani, S. A. & Means, A. R. J. biol. Chem. 268, 8769–8776 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ping Lu, K., Hanes, S. & Hunter, T. A human peptidyl–prolyl isomerase essential for regulation of mitosis. Nature 380, 544–547 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/380544a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/380544a0
This article is cited by
-
Expression and significance of pin1 in the wound healing
Archives of Dermatological Research (2024)
-
Long-term normalization of calcineurin activity in model mice rescues Pin1 and attenuates Alzheimer’s phenotypes without blocking peripheral T cell IL-2 response
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2023)
-
Cancer and Alzheimer’s Inverse Correlation: an Immunogenetic Analysis
Molecular Neurobiology (2023)
-
Spinal Cord Injury Causes Prominent Tau Pathology Associated with Brain Post-Injury Sequela
Molecular Neurobiology (2022)
-
Genome-wide characterization of peptidyl-prolyl cis–trans isomerases in Penicillium and their regulation by salt stress in a halotolerant P. oxalicum
Scientific Reports (2021)