Abstract
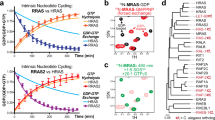
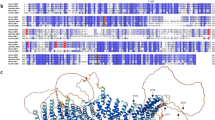
SMALL GTP-binding proteins of the ras superfamily are important for exocytosis from eukaryotic cells1–5. GTP-binding proteins can exist in two different conformations depending on whether they are bound to GDP or GTP, and are thought to function as molecular switches that regulate a variety of cellular processes1,3. The GTP–GDP cycle is controlled by accessory proteins that promote the exchange of bound GDP or the hydrolysis of GTP. The protein Sec4, a member of the Sec4/Yptl/Rab branch of the Ras superfamily, is involved in a late stage of the secretory pathway in yeast6. Here we report the isolation of a mammalian complementary DNA, mss4, encoding a GDP-releasing protein that enhances Sec4 function. The Mss4 protein also stimulates GDP release from Yptl and from the mammalian protein Rab3a, but not from Ras2. Mss4 shows sequence similarity to Dss4, a yeast protein with similar biochemical properties.7
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hall, A. Science 249, 635–640 (1990).
Balch, W. Trends biochem. Sci. 15, 473–477 (1990).
Bourne, H. R., Sanders, D. A. & McCormick, F. Nature 349, 117–127 (1991).
Pfeffer, S. Trends Cell Biol. 2, 41–45 (1992).
Bollag, G. & McCormick, F. A. Rev. Cell. Biol. 7, 601–632 (1991).
Salminen, A. & Novick, P. J. Cell 49, 527–538 (1987).
Moya, M., Roberts, D. & Novick, P. Nature 361, 460–463 (1993).
Vernet, T., Dignard, D. & Thomas, D. Gene 52, 225–233 (1987).
Novick, P. J., Field, C., & Schekman, R. Cell 21, 205–215 (1980).
Kyte, J. & Doolittle, R. F. J. molec. Biol. 157, 105–132 (1982).
Kabcenell, A. K., Goud, B., Northrup, J. & Novick, P. J. J. biol. Chem. 265, 9366–9372 (1990).
Jones, S., Vignais, M. & Broach, J. R. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 2641–2646 (1991).
Kaibuchi, K. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 2873–2880 (1991).
Burnstein, E. S. & Macara, I. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 1154–1158 (1992).
Chant, J., Corrado, K., Pringle, J. R. & Herskowitz, I. Cell 65, 1213–1224 (1991).
Powers, S., Gonzales, E., Christensen, T., Cubert, J. & Broek, D. Cell 65, 1225–1231 (1991).
Simon, M. A., Bowtell, D. D. L., Dodson, G. S., Laverty, T. R. & Rubin, G. M. Cell 67, 701–716 (1991).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. & Maniatis, T. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual 2nd edn (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Burgers, P. M. J. & Percival, K. J. Analyt. Biochem. 163, 391–397 (1987).
Ito, H., Fukada, Y., Murata, K. & Kimura, A. J. Bact. 153, 163–168 (1983).
Davis, L. G., Dibner, M. D. & Battey, J. F. Basic Methods in Molecular Biology (Elsevier, New York, 1986).
Smith, T. F. & Waterman, M. S. Adv. appl. Math. 2, 482–489 (1981).
Kellerman, O. K. & Ferenci, T. Meth. Enzym. 90, 459–463 (1982).
Marquart, D. W. J. Soc. ind. appl. Math. 11, 431–441 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burton, J., Roberts, D., Montaldi, M. et al. A mammalian guanine-nucleotide-releasing protein enhances function of yeast secretory protein Sec4. Nature 361, 464–467 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/361464a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/361464a0