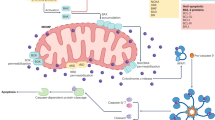
Abstract
There is widespread agreement that mitochondria have a function in apoptosis, but the mechanisms behind their involvement remain controversial. Here we suggest that opening of a multiprotein complex called the mitochondrial permeability transition pore complex is sufficient (and, usually, necessary) for triggering apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Green, D. R. & Reed, J. C. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281, 1309–1312 ( 1998).
Kroemer, G. & Reed, J. C. Mitochondrial control of cell death . Nature Med. 6, 513–519 (2000).
Budijardjo, I., Oliver, H., Lutter, M., Luo, X. & Wang, X. Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 15, 269–290 (1999).
Vander Heiden, M. G. & Thompson, C. B. Bcl-2 proteins: Inhibitors of apoptosis or regulators of mitochondrial homeostasis? Nature Cell Biol. 1, E209–E216 (1999).
Gross, A., McDonnell, J. M. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Bcl-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis . Genes Dev. 13, 1899–1911 (1999).
Crompton, M. The mitochondrial permeability transition pore and its role in cell death . Biochem. J. 341, 233– 249 (1999).
Woodfield, K., Ruck, A., Brdiczka, D. & Halestrap, A. P. Direct demonstration of a specific interaction between cyclophilin-D and the adenine nucleotide translocase confirms their role in the mitochondrial permeability transition . Biochem. J. 336, 287– 290 (1998).
Feldmann, G. et al. Opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore causes matrix expansion and outer membrane rupture in Fas-mediated hepatic apoptosis in mice. Hepatology 31, 674– 683 (2000).
Yin, X.-M. et al. Bid-deficient mice are resistant to Fas-induced hepatocellular apoptosis. Nature 400, 886– 891 (1999).
Eskes, R. et al. Bax-induced cytochrome c release from mitochondria is independent of the permeability transition pore but highly dependent on Mg2+ ions. J. Cell Biol. 143, 217– 224 (1998).
von Ahsen, O. et al. Preservation of mitochondrial structure and function after Bid- or Bax-mediated cytochrome c release. J. Cell Biol. 150, 1027–1036 ( 2000).
Eskes, R., Desagher, S., Antonsson, B. & Martinou, J. C. Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax into the outer mitochondrial membrane. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 929– 935 (2000).
Wei, M. C. et al. tBID, a membrane-targeted death ligand, oligomerizes BAK to release cytochrome c. Genes Dev. 14, 2060–2071 (2000).
Kroemer, G., Dallaporta, B. & Resche-Rigon, M. The mitochondrial death/life regulator in apoptosis and necrosis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 60, 619 –642 (1998).
Sullivan, P. G., Thompson, M. B. & Scheff, S. W. Cyclosporin A attenuates acute mitochondrial dysfunction following traumatic brain injury. Exp. Neurol. 160, 226–234 (1999).
Budd, S. L., Tenneti, L., Lishnak, T. & Lipton, S. A. Mitochondrial and extramitochondrial apoptotic signaling pathways in cerebrocortical neurons . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6161– 6166 (2000).
Tafain, M., Schneider, T. G., Pastorino, J. G. & Farber, J. L. Cytochrome c-dependent activation of caspase-3 by tumor necrosis factor requires induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition. Am. J. Pathol. 156, 2111–2121 (2000).
Jacotot, E. et al. The HIV-1 viral protein R induces apoptosis via a direct effect on the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J. Exp. Med. 191, 33–45 ( 2000).
Goldmacher, V. S. et al. A cytomegalovirus-encoded mitochondria-localized inhibitor of apoptosis structurally unrelated to Bcl-2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 12536–12541 (1999).
Rahmani, Z., Huh, K. W., Lasher, R. & Siddiqui, A. Hepatitis B virus X protein colocalizes to mitochondria with a human voltage-dependent anion channel, HVDAC3, and alters its transmembrane potential. J. Virol. 74, 2840–2846 ( 2000).
Massari, P., Ho, Y. & Wetzler, L. M. Neisseria meningitidis porin PorB interacts with mitochondria and protects cells from apoptosis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9070–9075 ( 2000).
Shimizu, S., Narita, M. & Tsujimoto, Y. Bcl-2 family proteins regulate the release of apoptogenic cytochrome c by the mitochondrial channel VDAC. Nature 399, 483–487 (1999).
Marzo, I. et al. Bax and adenine nucleotide translocator cooperate in the mitochondrial control of apoptosis. Science 281, 2027– 2031 (1998).
Kaukonen, J. et al. Role of adenine nucleotide translocator 1 in mtDNA maintenance . Science 289, 782–785 (2000).
Motoyama, S. et al. Bcl-2 is located predominantly in the inner membrane and crista of mitochondria in rat liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 249, 628–636 (1998).
Gotow, T. et al. Selective localization of Bcl-2 to the inner mitochondrial and smooth endoplasmic reticulum membranes in mammalian cells. Cell. Death Differ. 7, 666–674 (2000).
Costantini, P. et al. Oxidation of a critical thiol residue of the adenine nucleotide translocator enforces Bcl-2-independent permeability transition pore opening and apoptosis. Oncogene 19, 307– 314 (2000).
Brenner, C. et al. Bcl-2 and Bax regulate the channel activity of the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocator. Oncogene 19, 329–336 (2000).
Shimizu, S., Ide, T., Yanagida, T. & Tsujimoti, Y. Electrophysiological study of a novel large pore formed by Bax and the voltage-dependent anion channel that is permeable to cytochrome c. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 12321–12325 ( 2000).
Shimizu, S., Konishi, A., Kodama, T. & Tsujimoto, Y. BH4 domain of antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members closes voltage-dependent anion channel and inhibits apoptotic mitochondrial changes and cell death. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 3100–3105 (2000).
Jürgensmeier, J. M. et al. Bax directly induces release of cytochrome c from isolated mitochondria. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4997–5002 (1998).
Narita, M. et al. Bax interacts with the permeability transition pore to induce permeability transition and cytochrome c release in isolated mitochondria . Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 14681– 14686 (1998).
Pastorino, J. G. et al. Functional consequences of sustained or transient activation by Bax of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 31734–31739 ( 1999).
Vande Velde, C. et al. BIP3 and genetic control of necrosis-like cell death through the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 5454–5468 ( 2000).
Harris, M. H., Vander Heiden, M. G., Kron, S. J. & Thompson, C. B. Role of oxidative phosphorylation in Bax toxicity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 3590–3596 ( 2000).
Matsuyama, S., Xu, Q., Velours, J. & Reed, J. C. Mitochondrial F0F1-ATPase proton pump is required for function of proapoptotic protein Bax in yeast and mammalian cells. Mol. Cell 1, 327–336 ( 1998).
Basañez, G. et al. Bax, but not Bcl-xL, decreases the lifetime of planar phospholipid bilayer membranes at subnanomolar concentrations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 5492– 5497 (1999).
Kudla, G. et al. The destabilization of lipid membrane induced by the C-terminal fragment of caspase 8-cleaved Bid is inhibited by the N-terminal fragment . J. Biol. Chem. 275, 22713– 22718 (2000).
Schendel, S. L. et al. Ion channel activity of the BH3 only bcl-2 family member, BID. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21932– 21936 (1999).
Saito, M., Korsmeyer, S. J. & Schlesinger, P. H. Bax-dependent transport of cytochrome c reconstituted in pure liposomes. Nature Cell Biol. 2, 553–555 (2000).
Shimizu, S. & Tsujimoto, Y. Proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family members induce cytochrome c release, but not mitochondrial membrane potential loss, and do not directly modulate voltage-dependent anion channel activity. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 577–582 (2000).
Acknowledgements
The authors' work is supported by a special grant from the Ligue Nationale contre le Cancer, as well as grants from ANRS, FRM and EC (to G.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Related links
Related links
DATABASE LINKS
ENCYCLOPEDIA OF LIFE SCIENCES
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zamzami, N., Kroemer, G. The mitochondrion in apoptosis: how Pandora's box opens. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2, 67–71 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/35048073
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35048073