Abstract
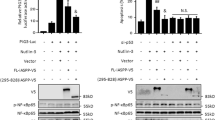
The tumour suppressor p53 inhibits cell growth through activation of cell-cycle arrest and apoptosis1, and most cancers have either mutation within the p53 gene or defects in the ability to induce p53. Activation or re-introduction of p53 induces apoptosis in many tumour cells and may provide effective cancer therapy2. One of the key proteins that modulates the apoptotic response is NF-κB, a transcription factor that can protect or contribute to apoptosis3. Here we show that induction of p53 causes an activation of NF-κB that correlates with the ability of p53 to induce apoptosis. Inhibition or loss of NF-κB activity abrogated p53-induced apoptosis, indicating that NF-κB is essential in p53-mediated cell death. Activation of NF-κB by p53 was distinct from that mediated by tumour-necrosis factor-α and involved MEK1 and the activation of pp90rsk. Inhibition of MEK1 blocked activation of NF-κB by p53 and completely abrogated p53-induced cell death. We conclude that inhibition of NF-κB in tumours that retain wild-type p53 may diminish, rather than augment, a therapeutic response.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sionov,R. V. & Haupt,Y. The cellular response to p53: the decision between life and death. Oncogene 18, 6145 –6157 (1999).
Lane,D. P. Exploiting the p53 pathway for cancer diagnosis and therapy. Br. J. Cancer 80, 1–5 ( 1999).
Foo,S. Y. & Nolan,G. P. NF-kappaB to the rescue: RELs, apoptosis and cellular transformation. Trends Genet. 15, 229–235 (1999).
Karin,M. The beginning of the end: IκB kinase (IKK) and NFκB activation. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 27339–27342 (1999).
Ghoda,L., Lin,X. & Greene,W. C. The 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase (pp90rsk) phosphorylated the N-terminal regulatory domain of IκBα and stimulates its degradation in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 272 , 21281–21288 (1997).
Schouten,G. J. et al. IκBα is a target for the mitogen-activated 90 kDa ribosonal S6 kinse. EMBO J. 16, 3133-3144 (1997).
Chen,X., Ko,L. J., Jayaraman,L. & Prives,C. p53 levels, functional domains, and DNA damage determine the extent of the apoptotic response of tumor cells. Genes Dev. 10, 2438– 2451 (1996).
Kessis,T. D. et al. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 expression disrupts the p53-mediated cellular response to DNA damage. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 3988–3992 (1993).
Ryan,K. M. & Vousden,K. H. Characterization of structural p53 mutants which show selective defects in apoptosis, but not cell cycle arrest. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 3692– 3698 (1998).
Ashkenazi,A. & Dixit,V. M. Death receptors: signalling and modulation. Science 281, 1305– 1308 (1998).
Zhou,Q. et al. Interaction of the baculovirus anti-apoptotic protein p35 with caspases. Specificity, kinetics, and characterization of the caspase/p35 complex. Biochemistry 37, 10757–10765 (1998).
Adams,J. M. & Cory,S. The Bcl-2 protein family: arbiters of cell survival. Science 281, 1322– 1326 (1998).
Chiou,S. K., Rao,L. & White,E. Bcl-2 blocks p53-dependent apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2556–2563 (1994).
Brown,K., Gerstberger,S., Carlson,L., Franzoso,G. & Siebenlist,U. Control of IκBα proteolysis by site-specific, signal-induced phosphorylation. Science 267, 1485–1491 (1995).
Whiteside,S. T. et al. N- and C-terminal sequences control degradation of MAD3/Ikappa B alpha in response to inducers of NF-kappa B activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 5339–5345 ( 1995).
Hickman,E. S., Bates,S. & Vousden,K. H. Perturbation of the p53 response by human papillomavirus type16 E7. J. Virol. 71, 3710– 3718 (1997).
Wu,H. & Lozano,G. NF-kappaB activation of p53. A potential mechanism for suppressing cell growth in response to stress. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 20067–20074 (1994).
Kirch,H. C., Flaswinkel,S., Rumpf,H., Brockmann,D. & Esche, H. Expression of human p53 requires synergistic activation of transcription from the p53 promoter by AP-1, NF-kappaB and Myc/Max. Oncogene 18, 2728–2738 ( 1999).
Webster,G. A. & Perkins,N. D. Transcriptional cross talk between NF-kappaB and p53. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 3485–3495 (1999).
Beg,A. A., Sha,W. C., Bronson,R. T., Ghosh,S. & Baltimore, D. Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-kappa B. Nature 376, 167–170 (1995).
Lowe,S. W., Ruley,H. E., Jacks,T. & Housman,D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell 74, 957–967 ( 1993).
Shao,R. et al. E1A sensitizes cells to tumor necrosis factor-induced apoptosis through inhibition of IκB kinases and nuclear factor κB activities. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 21495– 21498 (1999).
Samuelson,A. V. & Lowe,S. W. Selective induction of p53 and chemosensitivity in RB-deficient cells by E1A mutants unable to binf the RB-related proteins. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 12094–12099 (1997).
Malinin,N. L., Boldin,M. P., B., Kovalenko,A. V. & Wallach, D. MAP3K-related kinase involved in NF-kappaB induction by TNF, CD95 and IL-1. Nature 385, 540– 544 (1997).
Dudley,D. T., Pang,L., Decker,S. J., Bridges,A. J. & Saltiel, A. R. A synthetic inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7686–7689 (1995).
Phillips,A. C., Ernst,M. K., Bates,S., Rice,N. R. & Vousden, K. H. E2F-1 potentiates cell death by blocking anti-apoptotic signalling pathways. Mol. Cell 4, 771– 781 (1999).
Waddick,K. G. & Uckun,F. M. Innovative treatment programs against cancer II. Nuclear factor-kappa (NF-kappaB) as a molecular target. Biochem. Pharmacol. 57, 9–17 (1999).
Song,H. Y., Regnier,C. H., Kirschning, C. J., Goeddel,D. V. & Rothe,M. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-mediated kinase cascades: birfurcation of nuclear factor-kappa and c-jun N-terminal kinase (JNK/SAPK) pathways at TNF receptor-associated factor 2. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 9792– 9796 (1999).
Phillips,A. C., Bates,S., Ryan,K. M., Helin,K. & Vousden,K. H. Induction of DNA synthesis and apoptosis are separable functions of E2F-1. Genes Dev. 11, 1853– 1863 (1997).
Ernst,M. K., Dunn,L. L. & Rice,N. R. The PEST-like sequence of I kappa B alpha is responsible for inibition of DNA binding bit not for cytoplasmic retention of c-Rel or RelA homodimers. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 872 –882 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to A. Phillips, M. Dobrovolskaia and D. Woods for helpful discussion. We thank C. Rosen, G. Nunez, A. Israel and E. Harlow for plasmids, and D. Baltimore for the p65-deficient MEFs. We are also indebted to S. Lowe for providing us with E1A-expressing retroviruses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ryan, K., Ernst, M., Rice, N. et al. Role of NF-κB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature 404, 892–897 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35009130
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35009130