Abstract
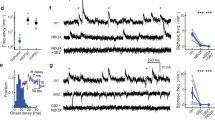
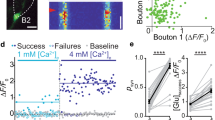
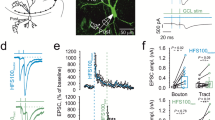
Metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) found on synaptic terminals throughout the brain are thought to be important in modulating neurotransmission1,2. Activation of mGluRs by synaptically released glutamate depresses glutamate release from excitatory terminals3,4,5 but the physiological role of mGluRs on inhibitory terminals is unclear. We have investigated activation of mGluRs on inhibitory terminals within the cerebellar glomerulus, a structure in which GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)-releasing inhibitory terminals and glutamatergic excitatory terminals are in close apposition and make axo-dendritic synapses onto granule cells6. Here we show that ‘spillover’ of glutamate, which is released from excitatory mossy fibres, inhibits GABA release from Golgi cell terminals by activating presynaptic mGluRs under physiological conditions. The magnitude of the depression of the inhibitory postsynaptic current is dependent on the frequency of mossy fibre stimulation, reaching 50% at 100 Hz. Furthermore, the duration of inhibitory postsynaptic current depression mirrors the time course of mossy fibre activity. Our results establish that mGluRs on inhibitory interneuron axons7 sense the activity of neighbouring excitatory synapses. This heterosynaptic mechanism is likely to boost the efficacy of active excitatory fibres by locally reducing the level of inhibition.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nakanishi, S. Metabotropic glutamate receptors: synaptic transmission, modulation and plasticity. Neuron 13, 1031–1037 (1994).
Conn, P. J. & Pin, J.-P. Pharmacology and functions of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 37, 205–237 (1997).
Scanziani, M., Salin, P. A., Vogt, K. E., Malenka, R. C. & Nicoll, R. A. Use-dependent increases in glutamate concentration activate presynaptic metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nature 385, 630–634 ( 1997).
von Gersdorff, H., Schneggenburger, R., Wiess, S. & Neher, E. Presynaptic depression at a calyx synapse: the small contribution of metabotropic glutamate receptors. J. Neurosci. 17, 8137 –8146 (1997).
Vogt, K. E. & Nicoll, R. A. Glutamate and γ-aminobutyric acid mediate a heterosynaptic depression at mossy fiber synapses in the hippocampus. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 96, 1118– 1122 (1999).
Jakab, R. L. & Hámori, J. Quantitative morphology and synaptology of cerebellar glomeruli in the rat. Anat. Embryol. 179, 81–88 ( 1988).
Ohishi, H. et al. Immunohistochemical localization of metabotropic glutamate receptors, mGluR2 and mGluR3, in rat cerebellar cortex. Neuron 13, 55–66 (1994).
Baude, A. et al. The metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR1α) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron 11, 771– 787 (1993).
Neki, A. et al. Metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR2 and mGluR5 are expressed in two non-overlapping populations of Golgi cells in the rat cerebellum. Neuroscience 75, 815–826 (1996).
Jaarsma, D., Dino, M. R., Ohishi, H., Shigemoto, R. & Mugnaini, E. Metabotropic glutamate receptors are associated with non-synaptic appendages of unipolar brush cells in rat cerebellar cortex and cochlear nuclear complex. J. Neurocytol. 27, 303–327 (1998).
Knoflach, F. & Kemp, J. A. Metabotropic glutamate group II receptors activate a G protein-coupled inwardly rectifying K+ current in neurones of the rat cerebellum. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 509, 347–354 ( 1998).
Vetter, P., Garthwaite, J. & Batchelor, A. M. Regulation of synaptic transmission in the mossy fibre-granule cell pathway of rat cerebellum by metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropharmacology 38, 805– 815 (1999).
van Kan, P. L., Gibson, A. R. & Houk, J. C. Movement-related inputs to intermediate cerebellum of monkeys. J. Neurophysiol. 69, 74– 94 (1993).
Silver, R. A., Momiyama, A. & Cull-Candy, S. G. Locus of frequency-dependent depression identified with multiple-probability fluctuation analysis at rat climbing fibre-Purkinje cell synapses. J. Physiol. (Lond) 510, 881 –902 (1998).
Clements J. D. & Silver, R. A. Unveiling synaptic plasticity: a new graphical and analytical approach. Trends Neurosci. 23, 105–113 (2000).
Llano, I. & Marty, A. Presynaptic metabotropic glutamatergic regulation of inhibitory synapses in rat cerebellar slices. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 486, 163–176 (1995).
Poncer, J. C., Shinozaki, H. & Miles, R. Dual modulation of synaptic inhibition by distinct metabotropic glutamate receptors in the rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 485, 121–134 ( 1995).
Silver, R. A., Cull-Candy, S. G. & Takahashi, T. Non-NMDA glutamate receptor occupancy and open probability at a rat cerebellar synapse with single and multiple release sites. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 494, 231–250 (1996).
Tia, S., Wang, J. F., Kotchabhakdi, N. & Vicini, S. Developmental changes of inhibitory synaptic currents in cerebellar granule neurons: role of GABAA receptor α6 subunit. J. Neurosci. 16, 3630–3640 (1996).
Brickley, S. G., Cull-Candy, S. G. & Farrant, M. Development of a tonic form of synaptic inhibition in rat cerebellar granule cells resulting from persistent activation of GABA A receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 497, 753–759 (1996).
Wall. M. J. & Usowicz, M. M. Development of action potential-dependent and independent spontaneous GABAA receptor-mediated currents in granule cells of postnatal rat cerebellum. Eur. J. Neurosci. 9, 533–548 (1997).
Rossi, D. J. & Hamann, M. Spillover-mediated transmission at inhibitory synapses promoted by high affinity α6 subunit GABAA receptors and glomerular geometry. Neuron 20 , 783–795 (1998).
Eccles, J. C., Ito, M. & Szentagothai, J. in The Cerebellum as a Neuronal Machine (Springer, Germany, 1967).
Barbour, B. & Häusser, M. Intersynaptic diffusion of neurotransmitter. Trends Neurosci. 20, 377 –384 (1997).
Hamori, J. & Somogyi, J. Differentiation of cerebellar mossy fiber synapses in the rat: a quantitative electron microscope study. J. Comp. Neurol. 220, 365–377 (1983).
Hayashi, Y., Momiyama, A., Takahashi, T, Ohishi, H., Ogawa-Meguro, R., Shigemoto, R., Mizuno, N. & Nakanishi, S. Role of a metabotropic glutamate receptor in synaptic modulation in the accessory olfactory bulb. Nature 366, 687–690 ( 1993).
Glitsch, M., Llano, I. & Marty, A. Morishita Glutamate as a candidate retrograde messenger at interneurone-Purkinje cell synapses of rat cerebellum. J. Physiol. (Lond) 497, 531–537 ( 1996).
Morishita, W., Kirov, S. A. & Alger, B. E. Evidence for metabotropic glutamate receptor activation in the induction of depolarization-induced suppression of inhibition in hippocampal CA1. J. Neurosci. 18, 4870– 4882 (1998).
Marr, D. A theory of cerebellar cortex. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 202, 437–470 (1969).
Ito, M. in The Cerebellum and Neural Control. (Raven, New York, 1984).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by The Wellcome Trust, the European Union and the Medical Research Council (Research Studentship to S.J.M.). We thank A. Momiyama and T. Takahashi for helpful discussion, J. Clements for providing Axograph and D. Attwell, M. Farrant, M. Häusser, B. Katz and T. Takahashi for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, S., Silver, R. Glutamate spillover suppresses inhibition by activating presynaptic mGluRs . Nature 404, 498–502 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35006649
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35006649
This article is cited by
-
Astrocytes in cocaine addiction and beyond
Molecular Psychiatry (2022)
-
GABAB receptors constrain glutamate presynaptic release and postsynaptic actions in substantia gelatinosa of rat spinal cord
Brain Structure and Function (2022)
-
Synaptic organisation and behaviour-dependent activity of mGluR8a-innervated GABAergic trilaminar cells projecting from the hippocampus to the subiculum
Brain Structure and Function (2020)
-
Glutamate spillover in C. elegans triggers repetitive behavior through presynaptic activation of MGL-2/mGluR5
Nature Communications (2019)
-
The role of glutamate transporters in the pathophysiology of neuropsychiatric disorders
npj Schizophrenia (2017)