Abstract
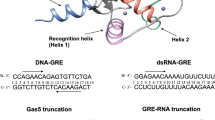
Regulatory factor X (RFX) proteins are transcriptional activators that recognize X-boxes (DNA of the sequence 5′-GTNRCC(0–3N)RGYAAC-3′, where N is any nucleotide, R is a purine and Y is a pyrimidine) using a highly conserved 76-residue DNA-binding domain (DBD). DNA-binding defects in the protein RFX5 cause bare lymphocyte syndrome or major histocompatibility antigen class II deficiency1. RFX1, -2 and -3 regulate expression of other medically important gene products (for example, interleukin-5 receptor α chain, IL-5Rα)2. Fusions of the ligand-binding domain of the oestrogen receptor with the DBD of RFX4 occur in some human breast tumours3. Here we present a 1.5 Å-resolution structure of two copies of the DBD of human RFX1 (hRFX1) binding cooperatively to a symmetrical X-box4,5. hRFX1 is an unusual member of the winged-helix subfamily of helix–turn–helix proteins6 because it uses a β-hairpin (or wing) to recognize DNA instead of the recognition helix typical of helix–turn–helix proteins. A new model for interactions between linker histones and DNA is proposed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mach, B., Steimle, V., Martinez-Soria, E. & Reith, W. Regulation of MHC class II genes: lessons from a disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 14, 301–331 (1996).
Iwama, A. et al. Dimeric RFX proteins contribute to the activity and lineage specificity of the interleukin-5 receptor alpha promoter through activation and repression domains. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 3940– 3950 (1999).
Dotzlaw, H., Alkhalaf, M. & Murphy, L. C. Characterization of estrogen receptor variant mRNAs from human breast cancers. Mol. Endocrinol. 6, 773–785 (1992).
Reith, W. et al. MHC class II regulatory factor RFX has a novel DNA-binding domain and a functionally independent dimerization domain. Genes Dev. 4, 1528–1540 ( 1990).
Cornille, F. et al. DNA binding properties of a chemically synthesized DNA binding domain of hRFX1. Nucleic Acids Res. 26, 2143–2149 (1998).
Clark, K. L., Halay, E. D., Lai, E. & Burley, S. K. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature 364, 412–420 ( 1993).
Lai, E., Clark, K. L., Burley, S. & James E. Darnell, J. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3/fork head or “winged helix” proteins: A family of transcription factors of diverse biological function. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 90, 10421–10423 (1993).
Emery, P. et al. A consensus motif in the RFX DNA binding domain and binding domain mutants with altered specificity. Mol. Cell Biol. 16 , 4486–4494 (1996).
Ostapchuk, P., Scheirle, G. & Hearing, P. Binding of nuclear factor EF-C to a functional domain of the hepatitis B virus enhancer region. Mol. Cell Biol. 9, 2787–2797 (1989).
Jin, C., Marsden, I., Chen, X. & Liao, X. Dynamic DNA contacts observed in the NMR structure of winged helix protein–DNA complex. J. Mol. Biol. 289, 683–690 (1999).
Zheng, N., Fraenkel, E., Pabo, C. O. & Pavletich, N. P. Structural basis of DNA recognition by the heterodimeric cell cycle transcription factor E2F-DP. Genes Dev. 13, 666– 674 (1999).
Janin, J. Principles of protein–protein recognition from structure to thermodynamics. Biochimie 77, 497–505 (1995).
Reith, W. et al. RFX1, a transactivator of hepatitis B virus enhancer I, belongs to a novel family of homodimeric and heterodimeric DNA-binding proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 14, 1230–1244 (1994).
Lavery, R. & Sklenar, H. The definition of generalized helicoidal parameters and of axis curvature for irregular nucleic acids. J. Biomol. Struct. Dynamics 6, 63– 91 (1988).
Klemm, J. D. & Pabo, C. O. Oct-1 POU domain-DNA interactions: cooperative binding of isolated subdomains and effects of covalent linkage. Genes Dev. 10, 27–36 (1996).
Ramakrishnan, V., Finch, J., Graziano, V. & Sweet, R. Crystal structure of the globular domain of histone H5 and its implications for nucleosome binding. Nature 362, 219–223 (1993).
Thomas, J. O. & Wilson, C. M. Selective radiolabelling and identification of a strong nucleosome binding site on the globular domain of histone H5. EMBO J. 5, 3531–3537 (1986).
Buckle, R. S., Maman, J. D. & Allan, J. Site-directed mutagenesis studies on the binding of the globular domain of linker histone H5 to the nucleosome. J. Mol. Biol. 223, 651–659 (1992).
Holm, L. & Sander, C. Families of structurally similar proteins, version 1. 0. J. Mol. Biol. 233, 123–138 (1993).
Goytisolo, F. A. et al. Identification of two DNA-binding sites on the globular domain of histone H5. EMBO J. 15, 3421– 3429 (1996).
Cirillo, L. A. et al. Binding of the winged-helix transcription factor HNF3 to a linker histone site on the nucleosome. EMBO J. 17, 244–254 (1998).
Zhou, Y. B., Gerchman, S. E., Ramakrishnan, V., Travers, A. & Muyldermans, S. Position and orientation of the globular domain of linker histone H5 on the nucleosome. Nature 395, 402–405 ( 1998).
Brunger, A. T. et al. Crystallography and NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 54, 905–921 ( 1998).
Laskowski, R. J., MacArthur, M. W., Moss, D. S. & Thornton, J. M. PROCHECK: a program to check stereochemical quality of protein structures. J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 283– 290 (1993).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K. & Honig, B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 11, 281–296 (1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Thiel and the MacCHESS staff, and Z. Dauter and K.R. Rajashankar and the NSLS X9B staff for help with X-ray data collection. We thank C. Lenoir for assistance in peptide synthesis, and J. Bonanno, K. L. Clark, J. E. Darnell, R. C. Deo, D. Jeruzalmi, J. Kuriyan, E. Lai, H. A. Lewis, S. K. Nair and G. A. Petsko for many useful discussions. S.K.B. is an Investigator in the Howard Hughes Medical Institute. This work was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gajiwala, K., Chen, H., Cornille, F. et al. Structure of the winged-helix protein hRFX1 reveals a new mode of DNA binding. Nature 403, 916–921 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/35002634
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/35002634