Abstract
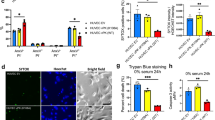
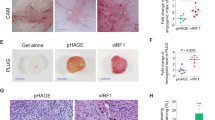
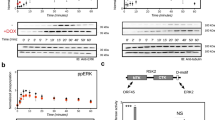
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV8) is a γ-2 herpesvirus1,2,3,4,5 that is implicated in the pathogenesis of Kaposi's sarcoma1,5 and of primary effusion B-cell lymphomas (PELs)6. KSHV infects malignant and progenitor cells of Kaposi's sarcoma7 and PEL2,6,8, it encodes putative oncogenes4,5,9 and genes that may cause Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis by stimulating angiogenesis4,5,9,10. The G-protein-coupled receptor encoded by an open reading frame (ORF 74) of KSHV9 is expressed in Kaposi's sarcoma lesions and in PEL9,11 and stimulates signalling pathways linked to cell proliferation12 in a constitutive (agonist-independent) way12. Here we show that signalling by this KSHV G-protein-coupled receptor leads to cell transformation and tumorigenicity, and induces a switch to an angiogenic phenotype13 mediated by vascular endothelial growth factor14, an angiogenesis13,14 and Kaposi's-spindle-cell growth factor15,16,17. We find that this receptor can activate two protein kinases, JNK/SAPK and p38MAPK, by triggering signalling cascades like those induced by inflammatory cytokines18 that are angiogenesis activators19 and mitogens for Kaposi's sarcoma cells10 and B cells. We conclude that the KSHV G-protein-coupled receptor is a viral oncogene that can exploit cell signalling pathways to induce transformation and angiogenesis in KSHV-mediated oncogenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang, Y. et al. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposis's sarcoma. Science 266, 1865– 1869 (1994).
Mesri, E. A. et al. Human herpesvirus-8/Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a new transmissible virus that infects B-cells. J. Exp. Med. 183, 2385–2390 ( 1996).
Renne, R. et al. Lytic growth of Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus (HHV-8) in culture. Nature Med. 2, 342– 346 (1996).
Russo, J. L. et al. Nucelotide sequence of the Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus (HHV8). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 14862 –14867 (1997).
Boshoff, C. & Weiss, R. A. Kaposis sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 10, 26– 31 (1997).
Cesarman, E., Chang, Y., Moore, P. S., Said, J. W. & Knowles, D. M. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences are present in AIDS-related body cavity B-cell lymphomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 332, 1186–1191 (1995).
Boshoff, C. et al. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infects endothelial and spindle cells. Nature Med. 1, 1274– 1278 (1995).
Arvanitakis, L. et al. Establishment and characterization of a body cavity-based lymphoma cell line (BC-3) harboring Kapos's Sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) in the absence of EBV. Blood 86, 2708–2714 ((1996)).
Cesarman, E. et al. Kaposis sarcoma-associated herpesvirus contains G protein-coupled receptor and cyclin D homologs which are expressed in Kaposis sarcoma and malignant lymphoma. J. Virol. 70, 8218– 8223 (1996).
Ensoli, B., Barillari, G. & Gallo, R. C. Cytokines and growth factors in the pathogenesis of AIDS-associated Kaposi's Sarcoma. Immunol. Rev. 127, 147–155 (1992).
Guo, H. G. et al. Characterization of a chemokine receptor-related gene in human herpesvirus 8 and its expression in Kaposi's sarcoma. Virology 228, 371–378 ( 1997).
Arvanitakis, L., Geras Raaka, E., Varma, A., Gershengorn, M. & Cesarman, E. Human herpesvirus KSHV encodes a constitutively active G-protein coupled receptor linked to cell proliferation. Nature 385, 347– 350 (1997).
Hanahan, D. & Folkman, J. Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86, 356–364 (1996).
Ferrara, N. Vascular endothelial growth factor. Eur. J. Cancer 14, 2413–2422 (1996).
Masood, R. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor is an autocrine growth factor in AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 979–984 (1997).
Nakamura, S., Murakamimori, K., Rao, N., Weich, H. A. & Rajeev, B. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potent angiogenic factor in aids-associated kaposis-sarcoma-derived spindle cells. J. Immunol. 158, 4992– 5001 (1997).
Cornali, E. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor regulates angiogenesis and vascular permeability in kaposis sarcoma. Am. J. Pathol. 149, 1851–1869 (1996).
Kyriakis, J. M. & Avruch, J. Sounding the alarm—Protein kinase cascades activated by stress and inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 24313–24316 ( 1996).
Samaniego, F., Markham, P. D., Gallo, R. C. & Ensoli, B. Inflammatory cytokines induce AIDS-Kaposi's sarcoma-derived spindle cells to produce and release basic fibroblast growth factor and enhance Kaposi's sarcoma-like lesion formation in nude mice. J. Immunol. 154, 3582–3592 (1994).
Gutkind, S., Novotny, E. A., Brann, M. R. & Robbins, K. C. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors as agonist dependent oncogenes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 4703– 4707 (1991).
Van Sande, J. et al. Genetic basis of endocrine disease: Somatic and germline mutations of the TSH receptor gene in thyroid diseases. J. Clin. Endocr. Metab. 80, 2577–2585 ( 1995).
Premont, R. T., Inglese, J. & Lefkowitz, R. J. Protein kinases that phosphorylate activated G-protein coupled receptors. FASEB J. 9, 175–182 (1995).
Geras Raaka, E. et al. Inhibitionof constitutive signalling of Kaposi's sarcoma associated herpesvirus G protein coupled receptor by protein kinases in mammalian cells in culture. J. Exp. Med.(submitted).
Koch, A. E. et al. Interleukin-8 as a macrophage mediator of angiogenesis. Science 258, 1798–1801 ( 1992).
Kolch, W., Martiny-Baron, G., Kieser, A. & Marme, D. Regulation of the expression of the VEGF/VPS and its receptors: role in rumor angiogenesis. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 36, 139–155 (1995).
Goto, F., Goto, K., Weindel, K. & Folkman, J. Synergistic effects of vascular endothelial growth factor and basic fibroblast growth factor on the proliferation and cord formation of bovine capillary endothelial cells within collagen gels. Lab. Invest. 69, 508 –517 (1993).
Montesano, R., Pepper, M. S. & Orci, L. Paracrine induction of angiogenesis in vitro by Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 105, 1013–1024 (1993).
Rickinson, A. B. & Kieff, E. in Fields Virology 3rd edn (eds Fields, B. N., Knipe, D. M. & Howley, P. M.) 2397–2446 (Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, ( 1996)).
Mesri, E. A., Federoff, H. J. & Brownlee, M. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor from a defective herpes simplex virus type 1 amplicon vector induces angiogenesis in mice. Circ. Res. 76, 161– 167 (1995).
Coso, O. A. et al. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell 81 , 1137–1146 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank G. Lam for HUVECs, R. Nador and O. Flore for sharing data and for comments, and A. Chadburn for help with histopathological characterization. Plasmids encoding GRK-2 and GRK-5 were a gift from R. J. Lefkowitz. This work was supported by NIH grants from NIAID to E.A.M., from NCI to E.C., and from NIDDK to M.C.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bais, C., Santomasso, B., Coso, O. et al. G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator. Nature 391, 86–89 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/34193
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/34193
This article is cited by
-
Viruses exploit growth factor mechanisms to achieve augmented pathogenicity and promote tumorigenesis
Archives of Microbiology (2024)
-
Application of the CDK9 inhibitor FIT-039 for the treatment of KSHV-associated malignancy
BMC Cancer (2023)
-
Molecular insight into isoform specific inhibition of PI3K-α and PKC-η with dietary agents through an ensemble pharmacophore and docking studies
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Cell Type-Specific Interferon-γ-mediated Antagonism of KSHV Lytic Replication
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Kaposi sarcoma
Nature Reviews Disease Primers (2019)