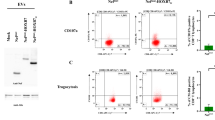
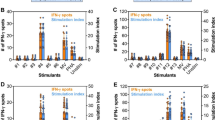
Abstract
Vaccination with idiotypic protein protects against B-cell lymphoma, mainly through anti-idiotypic antibody. For use in patients, DNA vaccines containing single-chain Fv derived from tumor provide a convenient alternative vaccine delivery system. However, single-chain Fv sequence alone induces low anti-idiotypic response and poor protection against lymphoma. Fusion of the gene encoding fragment C of tetanus toxin to single-chain Fv substantially promotes the anti-idiotypic response and induces strong protection against B-cell lymphoma. The same fusion design also induces protective immunity against a surface Ig-negative myeloma. These findings indicate that fusion to a pathogen sequence allows a tumor antigen to engage diverse immune mechanisms that suppress growth. This fusion design has the added advantage of overcoming potential tolerance to tumor that may exist in patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisen, H.N., Sakato, N. & Hall, S.J. Myeloma proteins as tumor-specific antigens. Transplant. Proc. 7, 209–214(1975).
George, A.J.T. & Stevenson, F.K. Prospect for the treatment of B cell tumors using idiotypic vaccination. Int. Rev. Immunol. 4,271–310(1989).
Kaminski, M.S., Kitamura, K., Maloney, D.G. & Levy, R. Idiotypic vaccination against a murine B cell lymphoma: inhibition of tumor immunity by free idiotypic protein. J. Immunol. 138, 1289–1296(1987).
Hsu, F.J. et al. Tumor-specific idiotype vaccines in the treatment of patients with B-cell lymphoma-long term results of a clinical trial. Blood 89, 3129–3135( 1997).
Hsu, F.J. et al. Vaccination of patients with B-cell lymphoma using autologous antigen-pulsed dendritic cells. Nature Med. 2, 52–58 (1996).
Davis, H.L. & Whalen, R.G. in Molecular and Cell Biology of Human Gene Therapeutics (ed. Dickson, G.) 368 (Chapman & Hall, London, 1995).
Conry, R.M., LoBuglio, A.F. & Curiel, D.T. Polynucleotide-mediated immunization therapy of cancer. Semin. Oncol. 23, 135– 147(1996).
Stevenson, F.K. et al. Idiotypic DNA vaccines against B-cell lymphoma. Immunol. Rev. 145, 211–228(1995).
Syrenglas, A.D., Chen, T.T. & Levy, R. DNA immunization induces protective immunity against B cell lymphoma. Nature Med. 2, 1038– 1041(1996).
Kumar, A., Arora R., Kaur, P., Chauhan, V.S. & Sharma, P. "Universal" T helper cell determinants enhance immunogenicity of a Plasmodium falciparum merozoite surface antigen peptide. J. Immunol. 148, 1499–1505(1992).
Spellerberg, M.B. et al. Promotion of anti-idiotypic antibody responses induced by single chain Fv genes by fusion to Tetanus Toxin Fragment C. J. Immunol. 159, 1885–1892( 1997).
Anderson, R. & Gao, X.-M., Papakonstantinopolou, A., Roberts, M. & Dougan, G. Immune response in mice following immunization with DNA encoding fragment C of tetanus toxin. Infect. Immun. 64, 3168–3173( 1996).
Manning, L.S. et al. A model of multiple myeloma: Culture of 5T33 murine myeloma cells and evaluation of tumorgenicity in the C57BL/KaLRij mouse. Br. J. Cancer 66, 1088–1093(1992).
Rammensee, H.-G., Rötzschke, O. & Falk, K. MHC Class I-restricted antigen processing-lessons from natural ligands. Chem. Immunol. 57, 113– 133(1993).
Bogen, B. Peripheral T cell tolerance as a tumor escape mechanism: deletion of CD4+ T cells specific for a monoclonal immunoglobulin idiotype secreted by a plasmacytoma. Eur. J. Imunol. 26, 2671 –2679(1996).
Dyke, R.J. et al. Idiotypic vaccination against B-cell lymphoma leads to dormant tumor. Cell. Immunol. 132, 70– 83(1991).
Scheuermann, R.H. & Uhr, J.W. Connections between signal transduction components and cellular responses initiated by antigen receptor on B lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 182, 903–906(1995).
Wilson, A., George, A.J.T., King, C.A. & Stevenson, F.K. Recognition of a B cell lymphoma by anti-idiotypic T cells. J. Immunol. 145, 3973–3943( 1990).
Hawkins, R.E., Russell, S.J., Hamblin, T. & Stevenson, F. Clinical protocol. A pilot study of idiotypic vacination for follicular B-cell lymphoma using a genetic approach. Hum. Gene Ther. 8, 1287–1299(1997).
Vollmers, H. P. et al. A rapid method for purification of monoclonal human IgM from mass culture. Hum. Antibod. Hybridomas 7, 37–41(1996).
Zhu, D. et al. Immunoglobulin VH gene sequence analysis of spontaneous immunoglobulin-secreting B-cell tumors with clinical features of human disease. Immunology 93, 162–170 (1998).
Huse, W.D. et al. Generation of a large combinational library of the immunoglobulin repertoire in phage lambda. Science 246, 1275–1281(1989).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Leukaemia Research Fund, Tenovus, and the Cancer Research Campaign, UK. We also thank the Kathy Giusti Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
King, C., Spellerberg, M., Zhu, D. et al. DNA vaccines with single-chain Fv fused to fragment C of tetanus toxin induce protective immunity against lymphoma and myeloma. Nat Med 4, 1281–1286 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/3266
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/3266