Abstract
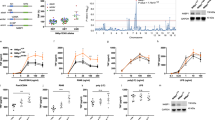
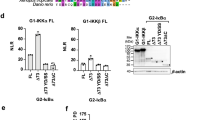
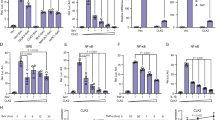
Pro-inflammatory cytokines activate the transcription factor NF-κB by stimulating the activity of a protein kinase that phosphorylates IκB, an inhibitor of NF-κB1,2,3,4,5, at sites that trigger its ubiquitination and degradation. This results in the nuclear translocation of freed NF-κB dimers and the activation of transcription of target genes6,7. Many of these target genes code for immunoregulatory proteins8,9. A large, cytokine-responsive IκB kinase (IKK) complex has been purified and the genes encoding two of its subunits have been cloned1,2,5. These subunits, IKK-α and IKK-β, are protein kinases whose function is needed for NF-κB activation by pro-inflammatory stimuli. Here, by using a monoclonal antibody against IKK-α, we purify the IKK complex to homogeneity from human cell lines. We find that IKK is composed of similar amounts of IKK-α, IKK-β and two other polypeptides, for which we obtained partial sequences. These polypeptides are differentially processed forms of a third subunit, IKK-γ. Molecular cloning and sequencing indicate that IKK-γ is composed of several potential coiled-coil motifs. IKK-γ interacts preferentially with IKK-β and is required for the activation of the IKK complex. An IKK-γ carboxy-terminal truncation mutant that still binds IKK-β blocks the activation of IKK and NF-κB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
DiDonato, J. A., Hayakawa, M., Rothwarf, D. M., Zandi, E. & Karin, M. Acytokine-responsive IκB kinase that activates the transcription factor NF-κB. Nature 388, 548–554 (1997).
Mercurio, F.et al. IKK-1 and IKK-2: cytokine-activated IκB kinases essential for NF-κB activation. Science 278, 860–866 (1997).
Régnier, C. H.et al. Identification and characterization of an IκB kinase. Cell 90, 373–383 (1997).
Woronicz, J. D., Gao, X., Cao, Z., Rothe, M. & Goeddel, D. V. IκB kinase-beta; NF-κB activation and complex formation with IκB kinase-alpha and NIK. Science 278, 866–869 (1997).
Zandi, E., Rothwarf, D., Delhase, M., Hayakawa, M. & Karin, M. The IκB kinase complex (IKK) contains two kinase subunits, IKKalpha and IKKbeta, necessary for NF-κB activation. Cell 91, 243–252 (1997).
Verma, I. M., Stevenson, J. K., Schwarz, E. M., Van Antwerp, D. & Miyamoto, S. Rel/NF-κB/IκB family: intimate tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 9, 2723–2735 (1995).
Baeuerle, P. A. & Baltimore, D. NF-κ B: ten years after. Cell 87, 13–20 (1996).
Baeuerle, P. A. & Henkel, T. Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 12, 141–179 (1994).
Barnes, P. J. & Karin, M. Nuclear factor-κB—a pivotal transcription factor in chronic inflammatory diseases. New Engl. J. Med. 336, 1066–1071 (1997).
Ling, L., Cao, Z. & Goeddel, D. V. NF-κB-inducing kinase activates IKK-alpha by phosphorylation of Ser-176. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2791–2797 (1998).
Nakano, H.et al. Differential regulation of IkB kinase α and β by two upstream kinases, NF-κB-inducing kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase/ERK kinase kinase-1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 3537–3542 (1998).
Karin, M. & Delhase, M. JNK or IKK, AP-1 or NF-κB, which are the targets for MEKK1 action? Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 9067–9069 (1998).
Berger, B.et al. Predicting coiled coils by use of pairwise residue correlations. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8259–8263 (1995).
Rost, B. PHD: predicting one-dimensional protein structure by profile based neural network. Methods Enzymol. 266, 525–539 (1996).
Frishman, D. & Argos, P. Incorporation of non-local interactions in protein secondary structure prediction from the amino acid sequence. Protein Eng. 9, 133–142 (1996).
Zandi, E., Chen, Y. & Karin, M. Direct phosphorylation of IκB by IKKα and IKKβ: discrimination between free and NF-κB-bound substrate. Science 281, 1360–1363 (1998).
Yamaoka, S.et al. Complementation cloning of NEMO, a component of the IκB kinase complex essential for NF-κB activation. Cell 93, 1231–1240 (1998).
DiDonato, J. A., Mercurio, F. & Karin, M. Phosphorylation of IκBα precedes but is not sufficient for its dissociation from NF-κB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 1302–1322 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Thannhauser for help with peptide sequencing, A. Israel for the NEMO antibody and sharing of unpublished information, F. Mercurio for the IKK-β antibody, G. Cadwell and J.Lewis for technical assistance and B. Thompson for manuscript preparation. D.M.R., E.Z. and G.N. were supported for postdoctoral fellowships by the NIH, the Leukemia Society of America and the Damon–Runyon Walter–Winchell Cancer Research Fund, respectively. This work was supported by grants from the NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothwarf, D., Zandi, E., Natoli, G. et al. IKK-γ is an essential regulatory subunit of the IκB kinase complex. Nature 395, 297–300 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/26261
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/26261