Abstract
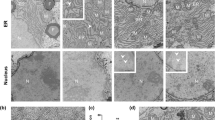
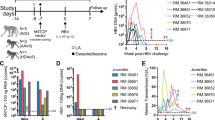
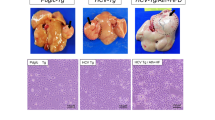
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) is the main cause of chronic hepatitis worldwide. Chronic hepatitis ultimately results in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma1,2 (HCC). However, the mechanism of hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic HCV infection is still unclear. The ability of the core protein of HCV to modulate gene transcription, cell proliferation and cell death3,4,5,6,7,8 may be involved in the pathogenesis of HCC. Here, we report the development of HCC in two independent lines of mice transgenic for the HCV core gene, which develop hepatic steatosis early in life as a histological feature characteristic of chronic hepatitis C ( ref. 9 ). After the age of 16 months, mice of both lines developed hepatic tumors that first appeared as adenomas containing fat droplets in the cytoplasm. Then HCC, a more poorly-differentiated neoplasia, developed from within the adenomas, presenting in a 'nodule-in-nodule' manner without cytoplasmic fat droplets; this closely resembled the histopathological characteristics of the early stage of HCC in patients with chronic hepatitis C (refs. 10,11 ). These results indicate that the HCV core protein has a chief role in the development of HCC, and that these transgenic mice provide good animal models for determining the molecular events in hepatocarcinogenesis with HCV infection.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saito, I. et al. Hepatitis C virus infection is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 6547–6549 (1990).
Simonetti, R.G. et al. Hepatitis C virus infection as a risk factor for hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. Ann. Intern. Med. 116, 97–102 (1992).
Ray, R.B., Lagging, L.M. Meyer, K. & Ray, R. Hepatitis C virus core protein cooperates ras and transforms primary rat embryo fibroblasts to tumorigenic phenotype. J. Virol. 70, 4438–4443 (1996).
Chang, J. et al. Hepatitis C virus core from two different genotypes has an oncogenic potential but is not sufficient for transforming primary rat embryo fibroblasts in cooperation with the H-ras oncogene. J. Virol. 72, 3060–3065 (1998).
Kim, D.W., Suzuki, R., Harada, T., Saito, I. & Miyamura, T. Trans-suppression of gene expression by hepatitis C viral core protein. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 47, 211–220 (1994).
Ray, R.B., Steele, R., Meyer, K. & Ray, R. Transcriptional repression of p53 promoter by hepatitis C virus core protein. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 10983–10986 ( 1997).
Ruggieri, A., Harada, T., Matsuura, Y. & Miyamura, T. Sensitization to Fas-mediated apoptosis by hepatitis C virus core protein. Virology 229, 68–76 ( 1997).
Ray, R.B., Meyer, K. & Ray, R. Suppression of apoptotic cell death by hepatitis C virus core protein. Virology 226, 176–182 ( 1996).
Moriya, K. et al. Hepatitis C virus core protein induces hepatic steatosis in transgenic mice. J. Gen. Virol. 78,1527 –1531 (1997).
Sugihara, S. et al. The morphologic transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 70, 1488–1492 (1992).
Nakashima, O., Sugihara, S., Kage, M. & Kojiro, M. Pathomorphologic characteristics of small hepatocellular carcinoma: a special reference to small hepatocellular carcinoma with distinct margins. Hepatology 22, 101–105 ( 1995).
Hino, O. & Kajino, K. Hepatitis virus-related hepatocarcinogenesis. Intervirology 37, 133– 135 (1994).
Bach, N., Thung, S.N. & Schaffner F. The histological features of chronic hepatitis C and autoimmune chronic hepatitis: a comparative analysis. Hepatology 15, 572– 577 (1992).
Frith, C.H. & Ward, J.M. A morphological classification of proliferative and neoplastic hepatic lesions in mice. J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. 3, 329–351 (1979).
Smith, G.S., Walford, R.L. & Mickey, M.R. Lifespan and incidence of cancer and other diseases in selected long-lived inbred mice and their F1 hybrids. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 50, 1195–1213 (1973).
Nakamura, K., Kuramoto, K., Shibasaki, K., Sumiya, S. & Ohtsubo, K. Age-related incidence of spontaneous tumors in SPF C57BL/6 and BDF1 mice. Exp. Anim. 41, 279–285 (1992).
Caporaso, N. et al. Hepatitis C virus infection is an additive risk factor for development of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 12, 367–371 (1991).
Koike, K. et al. Sialadenitis resembling Sjogren's syndrome in hepatitis C virus envelope gene transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 233–236 ( 1997).
Kawamura, T. et al. Transgenic expression of hepatitis C virus structural proteins in the mice. Hepatology 25, 1014– 1021 (1997).
Matsuda, J. et al. Transgenic mouse expressing a full-length hepatitis C virus cDNA. Jpn. J. Cancer Res. 89, 150– 158 (1998).
Pasquinelli, C. et al. Hepatitis C virus core and E2 protein expression in transgenic mice. Hepatology 25, 719– 727 (1997).
Moriya, K. et al. Subcellular localization of hepatitis C virus structural proteins in the liver of transgenic mice. Jpn. J. Med. Sci. Biol. 50, 169–177 (1997).
Paradis, V. et al. In situ detection of lipid peroxidation in chronic hepatitis C: correlation with pathological features. J. Clin. Pathol. 50, 401–406 ( 1997).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Suzuki for excellent electron microscopy and C. Ariga for technical assistance. This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture of Japan and grants from The Sankyo Foundation of Life Science and The Mochida Memorial Foundation for Medical and Pharmaceutical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moriya, K., Fujie, H., Shintani, Y. et al. The core protein of hepatitis C virus induces hepatocellular carcinoma in transgenic mice. Nat Med 4, 1065–1067 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/2053
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/2053
This article is cited by
-
Impact of eradication of hepatitis C virus on liver-related and -unrelated diseases: morbidity and mortality of chronic hepatitis C after SVR
Journal of Gastroenterology (2023)
-
Impact of Interferon-Free Direct-Acting Antivirals on the Incidence of Extrahepatic Malignancies in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C
Digestive Diseases and Sciences (2023)
-
A single mutation in the E2 glycoprotein of hepatitis C virus broadens the claudin specificity for its infection
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Hemojuvelin deficiency promotes liver mitochondrial dysfunction and predisposes mice to hepatocellular carcinoma
Communications Biology (2022)
-
The liver steatosis severity and lipid characteristics in primary biliary cholangitis
BMC Gastroenterology (2021)