Abstract
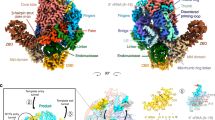
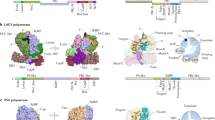
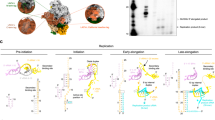
Various classes of nucleotidyl polymerases with different transcriptional roles contain a conserved core structure. Less is known, however, about the distinguishing features of these enzymes, particularly those of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase class. The 1.9 Å resolution crystal structure of hepatitis C virus (HCV) nonstructural protein 5B (NS5B) presented here provides the first complete and detailed view of an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase. While canonical polymerase features exist in the structure, NS5B adopts a unique shape due to extensive interactions between the fingers and thumb polymerase subdomains that serve to encircle the enzyme active site. Several insertions in the fingers subdomain account for intersubdomain linkages that include two extended loops and a pair of antiparallel α-helices. The HCV NS5B apoenzyme structure reported here can accommodate a template:primer duplex without global conformational changes, supporting the hypothesis that this structure is essentially preserved during the reaction pathway. This NS5B template:primer model also allows identification of a new structural motif involved in stabilizing the nascent base pair.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
World Health Organization. Weekly Epidemiological Record 72, 341–344 (1997).
Rice, C.M. In Fields virology 3rd edn (eds Fields, B.N., Knipe, D.N. & Howley, P.M.) 931–959 (Lippincott–Raven Publishers, Philadelphia; 1996).
Takamizawa, A. et al. J. Virol. 65, 1105–1113 (1991).
Hwang, S.B., Park, K.-J., Kim, Y.-S., Sung, Y.C. & Lai, M.M.C. Virology 227, 439–446 (1997).
Yamashita, T. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 15479–15486 (1998).
Poch, O., Sauvaget, I., Delarue, M. & Tordo, N. EMBO J. 8, 3867–3874 (1989).
Behrens, S.E., Tomei, L. & De Francesco, R. EMBO J. 15, 12–22 (1996).
Lohmann, V., Korner, F., Herian, U. & Bartenschlager, R. J. Virol. 71, 8416–8428 (1997).
Ferrari, E. et al. J. Virol. 73, 1649–1654 (1999).
Ishido, S., Fujita, T. & Hotta, H. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 244, 35–40 (1998).
Joyce, C.M. & Steitz, T.A. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 63, 777–822 (1994).
Sousa, R. Trends Biochem. Sci. 21, 186–190 (1996).
Doublié, S., Sawaya, M.R. & Ellenberger, T. Structure 7, R31–R35 (1999).
Jäger, J., Smerdon, S.J., Wang, J., Boisvert, D.C. & Steitz, T.A. Structure 2, 869–876 (1994).
Li, Y., Korolev, S. & Waksman, G. EMBO J. 17, 7514–7525 (1998).
Hansen, J.L., Long, A.M. & Schultz, S.C. Structure 5, 1109–1122 (1997).
Huang, H., Chopra, R., Verdine, G.L. & Harrison, S.C. Science 282, 1669–1675 (1998).
Ollis, D.L., Brick, P., Hamlin, R., Xuong, N.G. & Steitz, T.A. Nature 313, 762–766 (1985).
Kornberg, A. DNA replication. (Freeman, San Francisco; 1980).
Johnson, M.S., McClure, M.A., Feng, D.F., Gray, J. & Doolittle, R.F. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 7648–7652 (1986).
Jeruzalmi, D. & Steitz, T.A. EMBO J. 17, 4101–4113 (1998).
Beese, L.S. & Steitz, T.A. EMBO J. 10, 25–33 (1991).
Gao, G., Orlova, M., Georgiadis, M.M., Hendrickson, W.A. & Goff, S.P. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 407–411 (1997).
Jacobo-Molina, A. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 6320–6324 (1993).
Wang, J. et al. Cell 89, 1087–1099 (1997).
Doublié, S., Tabor, S., Long, A.M., Richardson, C.C. & Ellenberger, T. Nature 391, 251–258 (1998).
Kiefer, J.R., Mao, C., Braman, J.C. & Beese, L.S. Nature 391, 304–307 (1998).
Lohmann, V., Roos, A., Korner, F., Koch, J.O. & Bartenschlager, R. Virology 249, 108–118 (1998).
Doublié, S. Methods Enzymol. 276, 523–530 (1997).
Hendrickson, W.A. & Ogata, C.M. Methods Enzymol. 276, 494–523 (1997).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Methods Enzymol. 276, 307–326 (1997).
Bailey, S. Acta Crystallogr. D 50, 760–763 (1994).
Miller, R., Gallo, S.M., Khalak, H.G. & Weeks, C.M. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 27, 613–621 (1994).
de La Fortelle, E. & Bricogne, G. Methods Enzymol. 276, 472–494 (1996).
Jones, T.A., Zou, J.Y., Cowan, S.W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Brünger, A.T. X-PLOR: a system for X-ray crystallography and NMR. (Yale University Press, New Haven, Connecticut; 1992).
Kleywegt, G.J. & Brünger, A.T. Structure 4, 897–904 (1996).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K.A. & Honig, B. Proteins 11, 281–296 (1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Fischmann, A. Hruza, P. Reichert and the IMCA-CAT staff for assistance with crystallization and synchrotron data collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lesburg, C., Cable, M., Ferrari, E. et al. Crystal structure of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from hepatitis C virus reveals a fully encircled active site. Nat Struct Mol Biol 6, 937–943 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/13305
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/13305
This article is cited by
-
Analysis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-dependent RNA polymerase as a potential therapeutic drug target using a computational approach
Journal of Translational Medicine (2020)
-
Stringent control of the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase translocation revealed by multiple intermediate structures
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Cryo-EM structure of the respiratory syncytial virus RNA polymerase
Nature Communications (2020)
-
Dissection of two drug-targeted regions of Hepatitis C virus subtype 4a infecting Egyptian patients
Virus Genes (2020)