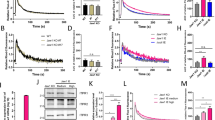
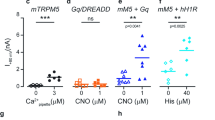
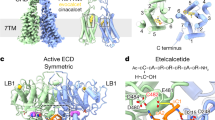
Abstract
Calcium plays a critical part in the regulation of cell growth, and growth factors stimulate calcium entry into cells through calcium-permeable channels. However, the molecular nature and regulation of calcium-permeable channels are still unclear at present. Here we report the molecular characterization of a calcium-permeable cation channel that is regulated by insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I). This channel, which we name growth-factor-regulated channel (GRC), belongs to the TRP-channel family and localizes mainly to intracellular pools under basal conditions. Upon stimulation of cells by IGF-I, GRC translocates to the plasma membrane. Thus, IGF-I augments calcium entry through GRC by regulating trafficking of the channel.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on SpringerLink
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lu, K. P. & Means, A. Regulation of the cell cycle by calcium and calmodulin. Endocrine Rev. 14, 40–58 (1993).
Lovisolo, D., Distasi, C., Antoniotti, S. & Munaron, L. Mitogens and calcium channel. News Physiol. Sci. 12, 279–285 (1997).
LeRoith, D., Werner, H., Beitner-Johnson, D. & Roberts, C. T. Molecular and cellular aspects of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor. Endocrine Rev. 16, 143–163 (1995).
Kojima, I., Matsunaga, H., Kurokawa, K., Ogata, E. & Nishimoto, I. Calcium influx: an intracellular message of the mitogenic action of insulin-like growth factor-I. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 16561–16567 (1988).
Kojima, I., Mogami, H. & Ogata, E. Role of calcium entry and protein kinase C in the progression activity of insulin-like growth factor-I. J.Biol. Chem. 268, 1003–1006 (1993).
Tedder, T. F., Forsgre, A., Boyd, A. W., Nadler, L. M. & Schlossman, S. F. Antibodies reactive with the B1 molecule inhibit cell cycle progression but not activation of human B lymphocytes. Eur. J. Immunol. 16, 881–887 (1986).
Tedder, T. F. & Engel, P. D20: a regulator of cell-cycle progression of B lymphocytes. Immunol. Today 15, 450–454 (1994).
Bubien, J. K., Zhou, L. J., Bell, P. D., Frizzell, R. A. & Tedder, T. F. Transfection of the CD20 cell surface molecule into ectopic cell types generates a Ca2+ conductance found constitutively in B lymphocytes. J. Cell Biol. 121, 1121–1132 (1993).
Kanzaki, M., Nie, L., Shibata, H. & Kojima, I. Activation of calcium-permeable cation channel CD20 by insulin-like growth factor-I in Balb/c 3T3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 4964–4969 (1997).
Caterina, M. J. et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 389, 816–824 (1997).
Kyte, J. & Doolittle, R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 157, 105–132 (1982).
Saitou, N. & Nei, M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol. Evol. 4, 406-425 (1987).
Thompson, J. D., Higgins, D. G. & Gibson, T. J. CLUSTAL W: improving the sensitivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4673–4680 (1994).
Okada, T., Sakuma, L., Fukui, Y., Hazeki, O. & Ui, M. Blockage of chemotactic peptide-induced stimulation of neutrophils by wortmannin as a result of selective inhibition of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. J.Biol.Chem. 269, 3563–3567 (1994).
Vlahos, C. J., Matter, W. F., Hui, Y. & Brown, R. F. A specific inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J. Biol. Chem. 269, 5241–5248 (1994).
Caterina, M. J., Rosen, T. A., Tominaga, M., Brake, A. J. & Julius, D. A capsaicin-receptor homologue with a high threshold for noxious heat. Nature 398, 436–441 (1999).
Hara, K. et al. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activity is required for insulin-stimulated glucose transport but not for RAS activation in CHO cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 7415–7419 (1994).
Miyazaki, J. et al. Establishment of a pancreatic β-cell line that retains glucose-inducible insulin secretion. Endocrinol. 127, 126–132 (1990).
Holman, G. D. & Kasuga, M. From receptor to transport: insulin signalling to glucose transport. Diabetologia 40, 991–1003 (1997).
Marks, M. S., Ohno, H., Kirchhausen, T. & Bonifacino, J. S. Protein sorting by tyrosine-based signals. Trends Cell Biol. 7, 124–128 (1997).
Shibata, H., Suzuki, Y., Omata, W., Tanaka, S. & Kojima, I. Dissection of GLUT4 recycling pathway into exocytosis and endocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 11489–11495 (1995).
Kanzaki, M., Shibata, H., Mogami, H. & Kojima, I. Expression of calcium-permeable cation channel CD20 accelerates cell-cycle progression in Balb/c 3T3 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 13099–13104 (1995).
Laemmli, U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685 (1970).
Matsumoto, B. Cell biological applications of confocal microscopy. Methods Cell Biol. 38, 20–35 (1993).
Hamil, O. P., Marty, M., Neher, E., Sackman, B. & Sigworth, F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 391, (1981).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Area from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan. We thank J. Takeda and K. Takata for discussions.
Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to I.K. The cDNA sequence for mouse GRC has been deposited at GenBank under accession number AB021665.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kanzaki, M., Zhang*, YQ., Mashima*, H. et al. Translocation of a calcium-permeable cation channel induced by insulin-like growth factor-I. Nat Cell Biol 1, 165–170 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/11086
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/11086