Abstract
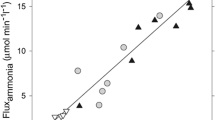
There is increasing evidence to suggest that hepatic encephalopathy in acute liver failure is the result of altered glutamatergic function. In particular, the high affinity uptake of glutamate is decreased in brain slices and synaptosomes from rats with acute liver failure as well as by exposure of cultured astrocytes to concentrations of ammonia equivalent to those reported in brain in acute liver failure. Both protein and gene expression of the recently cloned and sequenced astrocytic glutamate transporter GLT-1 are significantly reduced in the brains of rats with acute liver failure. Decreased expression of GLT-1 in brain in acute liver failure results in increased extracellular brain glutamate concentrations which correlates with arterial ammonia concentrations and with the appearance of severe encephalopathy and brain edema in these animals. Ammonia-induced reductions in expression of GLT-1 resulting in increased extracellular glutamate concentrations could explain some of the symptoms (hyperexcitability, cerebral edema) characteristic of hepatic encephalopathy in acute liver failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Record, C.O., Buxton, B., Chase, R., Curzon, G., Murray-Lyon, I.M., and Williams, R.1976.Plasma and brain amino acids in fulminant hepatic failure and their relationship to hepatic encephalopahy. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 6:387–394.
Lavoie, J., Giguere, J.F., Layrargues, G.P., and Butterworth, R.F.1987.Amino acid changes in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem. 9:692–697.
Swain, M., Bergeron, M., Audet, R., Blei, A.T., and Butterworth, R.F.1992.Monitoring of neurotransmitter amino acids by means an indwelling cisterna magna catheter:a comparison of two rodent models of fulminant hepatic failure. Hepatology 16:1028–1035.
Mans, A.M., De Joseph, M.R., and Hawkins, R.A.1994.Metabolic abnormalities and grade of encephalopathy in acute hepatic failure. J. Neurochem. 63:1829–183.
Bosnian, D.K., Deutz, N.E.P., Maas, M.A.W., van Eijk, H.M.H., Smit, J.J.H., de Haan, J.G., and Chamuleau, R.A.F.M.1992.Amino acid release from cerebral cortex in experimental acute liver failure, studied by in vivo microdialysis. J. Neurochem.59:591–599.
Michalak, A., Rose, C., Butterworth, J., and Butterworth, R.F. 1996.Neuroactive amino acids and glutamate (NMDA) receptors in frontal cortex of rats with experimental acute liver failure. Hepatology24:908–913.
De Kneght, R.J., Schalm, S.W., Van Der Rijt, C.C.D., Fekkes, D., Dalm, E., and Hekking-Weyma, I.1994.Extracellular brain glutamate during acute liver failure and during acute hyperammonemia stimulating acute liver failure:An experimental study based on in vivo brain dialysis. J. Hepatol. 20:19–26.
Oppong, K.N.W., Bartlett, K., Record, C.O., and Al Mardini, H. 1995.Synaptosomal glutamate transport in thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in the rat. Hepatology 22:53–558.
Moroni, F., Lombardi, G., Moneti, G., and Cortesini, C.1983.The release and the neosynthesis of glutamic acid are increased in experimental models of hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem.40:850–854.
Tossman, U., Delin, A., Eriksson, L.S., and Ungerstedt, U. 1987.Brain cortical amino acids measured by intracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats. Neurochem. Res. 12: 265–269.
Tossman, U., Eriksson, S., Delin, A., Hagenfeldt, L., Law, D., and Ungerstedt, U.1983.Brain amino acids measured by intracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats. J. Neurochem. 41:106–1051.
Raghavendra Rao, V.L., Audet, R.M., and Butterworth, R.F. 1995.Selective alterations of extracellular brain amino acids in relation to function in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy:results of an in vivo microdialysis study. J. Neurochem. 65:1221–1228.
Hamberger, A., Lindroth, B., and Nystrom, B.1982.Regulation of glutamate biosynthesis and release in vitro by low levels of ammonium ions. Brain Res. 237:339–350.
Butterworth, R.F. Girard, G., and Giguere, J.F.1988.Regional differences in the capacity for ammonia removal by brain following portacaval anastomosis. Neurochem. 51: 486–490.
Lockwood, A.H., Yap, E.W.H., and Wong, W.-H.1991.Cerebral ammonia metabolism in patients with severe liver disease and minimal hepatic encephalopathy. J. Cerebral Blood Flow Metab.11:337–341.
Hamberger, A., Hedquist, B., and Nystrom, B.1979.Ammonium ion inhibition of evoked release of endogenous glutamate from hippocampal slices. J. Neurochem. 33:1295–1302.
Erecinska, M., Pastuszko, A., Wilson, D.F., and Nelson, D. 1987.Ammonia-induced release of neurotransmitters from rat brain synaptosomes:Differences between the effects on amines and amino acids. J. Neurochem. 49:1258–1265.
Maddison J.E., Mickelthwaite, C., Watson, W.E.J., and Johnston, G.A.R.1996.Synaptosomal and brain slice cerebrocortical [3 H ]L-glutamate uptake in a rat model of chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Int. 28:89–93.
Michalak, A., Rose, C., and Butterworth, R.F.1998.Further evidence for decreased expression of glutamate and noradrenaline transporters in cortical and sub-cortical structures in acute liver failure. Hepatology, 28(4), pt.2, #688 (abstract).
Schmidt, W., Wolf, G., Grungreiff, K., Meier, M., and Reum, T. 1990.Hepatic encephalopathy influences high-affinity uptake of transmitter glutamate and aspartate into the hippocampal formation. Metab. Brain Dis. 5:19–31.
Bender, A.S., and Norenberg, M.D.1996.Effects of ammonia on L-glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 21:567–573.
Mena, E.E., and Cotman, C.W.1985.Pathologic concentrations of ammonium ions block L-glutamate uptake. Exp. Neurol. 89: 259–263.
Chaudhry, F.A., Lehre, K.P., van Lookeren Campagne, M., Ottersen, O.P., Danbolt, N.C., and Storm-Mathisen, J.1995.Glutamate transporters in glial plasma membranes:Highly differentiated localizations revealed by quantitative ultrastructural immunocytochemistry. Neuron, 1:711–720.
Rothstein, J.D., Martin, L., Levey, A.I., Dykes-Hoberg, M., Jin, L., Wu, D., Nash, N., and Kuncl, R.W.1994.Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron, 13: 713–725.
Robinson, M.B.1998.The family of sodium-dependent glutamate transporters:a focus on the GLT-1/EAAT2 subtype. Neurochem. Int.33:479–491, 1998.
Tanaka, K., Watase, K., Manabe, T., Yamada, K., Watanabe, M., Takahashi, K., Iwama, H., Nishikawa, T., Ichihara, N., Kikuchi, T., Okuyama, S., Kawashima, N., Hori, S., Takimoto, M., and Wada, K.1997.Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science 276: 1699–1702.
Knecht, K., Michalak, A., Rose, C, Rothstein, J.D., and Butterworth, R.F.1997.Decreased glutamate transporter (GLT-1) expression in frontal cortex of rats with acute liver failure. Neurosci. Left. 229:201–203.
Norenberg, M.D., Huo, Z., Neary, J.T., and Roig-Cantesano, A. 1997.The glial glutamate transporter in hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy:Relation to energy metabolism and glutamatergic neurotransmission.Glia21:124–133.
Chan, H., Desjardins, P., Hazell, A.S., and Butterworth, R.F. 1999.Effects of ammonia on glutamate (GLT-1 and GLAST) transporter expression in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 72, suppl., #S56A.
Gegelashvili, G., and Schousboe, A.1997.High affinity glutamate transporters:Regulation of expression and activity.Mol. Pharmacol. 52:6–15
Thorlin, T., Roginski, R.S., Choudhury, K., Nilsson, M., Ronnack, L., Hansson, E., and Eriksson, P.S.1998.Regulation of the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 by glutamate and 6-opioid receptor stimulation. FEBS Letters 425:43–459.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chan, H., Butterworth, R.F. Evidence for an Astrocytic Glutamate Transporter Deficit in Hepatic Encephalopathy. Neurochem Res 24, 1397–1401 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022532623281
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022532623281