Abstract
Background: The prognostic value of the metabolic status of cerebral gliomas determined by positron emission tomography with [18F]-fluoro-deoxy-D-glucose (FDG-PET) has been established in populations with a mixture of grades 2, 3 and 4 gliomas, but remains uncertain when only malignant gliomas are considered (grade 3 and 4).
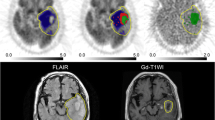
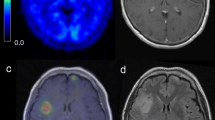
Methods: FDG-PET performed in 30 patients with anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III) and 61 patients with glioblastoma (grade 4) were classified according to a metabolic grading. The uptake of FDG was lower in the tumor compared to white matter (WM) in grade 1 (4 glioblastoma, 4 anaplastic astrocytoma), it was intermediate between WM and cortex in grade 2 (20 glioblastoma, 22 anaplastic astrocytoma), and it was superior to cortex in grade 3 (38 glioblastoma, 4 anaplastic astrocytoma).
Results: Kaplan–Meier survival curves were similar in patient with grades 1 and 2, but were significantly worse (p = 0.007) in grade 3. In multivariate analysis considering age, pathological grade (anaplastic astrocytoma versus glioblastoma), and metabolic grades, the metabolic grade did not appear to be an independent prognostic factor. When anaplastic astrocytomas and glioblastomas were considered separately, metabolic grade is of predictive value only in the group of glioblastomas.
Conclusion: In malignant gliomas, metabolic grading determined by FDG-PET was not superior to the pathological grading for survival prediction. Still, it remains of predictive value when applied to malignant gliomas histologically classified as glioblastoma.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Keles GE, Anderson B, Berger M: The effect of extent of resection on the time to progression in patients with glioblastoma multiforme of the cerebral hemisphere. Surg Neurol 52: 371-379, 1999
De Witte O, Levivier M, Violon P, Salmon I, Damhaut P, Wikler D, Hildebrand J, Brotchi J, Goldman S: Prognostic value of positron emission tomography with [18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose in the low-grade glioma. Neurosurgery 39: 470-476, 1996
Di Chiro G, DeLaPaz RL, Brooks RA, Sokoloff L, Kornblith PL, Smith BH: Glucose utilization of cerebral gliomas measured by [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose and positron emission tomography. Neurology 32: 1323-1329, 1982
Patronas NJ, Di Chiro G, Kufta C, Bairamian D, Kornblith PL, Simon R, Larson SM: Prediction of survival in glioma patients by means of positron emission tomography. J Neurosurg 62: 816-822, 1985
De Witte O, Hildebrand J, Luxen A, Goldman S: Acute effect of carmustine on glucose metabolism in brain and glioblastoma. Cancer 74: 2836-2842, 1994
O'Neil A, Macapinlac H, DeAngelis L: Positron emission tomography hypermetabolism with cerebral radionecrosis (abstract). Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Brain Tumor Research and Therapy, 1995, p 23
Kleihues P, Burger PC, Scheithauer BW: The new WHO classification of brain tumours. Brain Pathol 3: 255-268, 1993
Kubota R, Yamada S, Kubota K, Ishiwata K, Tamahashi N: Intratumoral distribution of fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose in vivo: high accumulation in macrophages and granulation tissues studies by microautoradiography. J Nucl Med 33: 1972-1980, 1992
Levivier M, Goldman S, Bidaut L, Luxen A, Stanus E, Przedborski S, Baleriaux D, Hildebrand J, Brotchi J: Positron emission tomography-guided stereotaxic brain biopsy. Neurosurgery 31: 792-797, 1992
Hamacher K, Coenen HH, Stöcklin G: Efficient stereospecific synthesis of no-carrier-added 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose using aminopolyether supported nucleophilic substitution. J Nucl Med 27: 235-238, 1986
Di Chiro G, Brooks RA, Patronas NJ, Bairamian D, Kornblith PL, Smith BH, Mansi L, Barker J: Issues in the in vivo measurement of glucose metabolism of human central nervous system tumors. Ann Neurol, 15(suppl): S138-S146, 1984
Alavi JB, Alavi A, Chawluk J, Kushner M, Powe J, Hickey W, Reivich M: Positron emission tomography in patients with glioma. Cancer 62: 1074-1078, 1988
Di Chiro G: Positron emission tomography using [18F]Fluorodeoxyglucose in brain tumors: a powerful diagnostic and prognostic tool. Invest Radiol 22: 360-371, 1986
De Kim C, Alavi JB, Alavi A, Reivich M: New grading system of cerebral gliomas using positron emission tomography with F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose. J Neuro-Oncol 10: 85-91, 1996
Goldman S, Levivier M, Pirotte B, Brucher JM, Wikler D, Damhaut P, Stanus E, Brotchi J, Hildebrand J: Regional glucose metabolism and histopathology of gliomas. Cancer 78, 1098-1106, 1996
Kubota R, Kubota K, Yamada S, Tada M, Tamahashi N: Active and passive mechanism of [fluorine-18]fluorodeoxyglucose uptake by proliferating and prenecrotic cancer cells in vivo: a microautoradiography study. J Nucl Med 35: 1067-1075, 1994
De Witte O, Levivier M, Violon P, Brotchi J, Goldman S: Quantitative imaging study of extent of surgical resection and prognosis of malignant astocytomas. Neurosurgery, 43: 398-399, 1998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
De Witte, O., Lefranc, F., Levivier, M. et al. FDG-PET as a Prognostic Factor in High-grade Astrocytoma. J Neurooncol 49, 157–163 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026518002800
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026518002800