Abstract
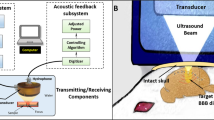
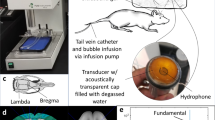
Transcranial pulsed ultrasound with microbubbles has been shown to temporally open the blood–brain barrier (BBB) to allow therapeutic agents to penetrate into the CNS for improved therapeutic efficacy. Recent studies have shown the feasibility of using passive cavitation detection (PCD) for monitoring or real-time control of the BBB opening in a focused ultrasound device. Planar ultrasound has unique advantages including the capability to create larger BBB openings in a single exposure, simple operation, and reduced reliance on medical imaging for sonication guidance. This study proposes a novel planar ultrasound apparatus design that can provide real-time analysis for ultrasound BBB opening monitoring. In-vitro tube phantom experiments were conducted to characterize the dependence of the energy spectrum density (ESD) change with microbubble infusion. In-vivo experiments characterized the dependence of ESD change on BBB opening. We showed that the proposed configuration provide superior ESD detection than traditional water-immersed PCD arrangement and can well correlated with the cavitation activity either in the in vitro or in vivo measurement. The ESD response corresponds well to the occurrence of BBB-opening. In animal groups which demonstrated successful BBB-opening, the peak ESD was significantly higher (12.22 ± 7.019 and 14.763 ± 11.812 dB in 0.332 and 0.463-MPa exposure). The 5-dB ESD level was found to be a valid threshold level to discriminate between the BBB-intact and BBB-opened groups to provide both high detection sensitivity (100%) and specificity (88%). These results may facilitate the design of a planar ultrasound treatment apparatus for BBB opening and drug delivery to the brain.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hynynen, K., McDannold, N., Sheikov, N. A., Jolesz, F. A., & Vykhodtseva, N. (2005). Local and reversible blood-brain barrier disruption by noninvasive focused ultrasound at frequencies suitable for trans-skull sonications. Neuroimage, 24(1), 12–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.06.046.
Hynynen, K., McDannold, N., Vykhodtseva, N., & Jolesz, F. A. (2001). Noninvasive MR imaging-guided focal opening of the blood-brain barrier in rabbits. Radiology, 220(3), 640–646.
Kinoshita, M., McDannold, N., Jolesz, F. A., & Hynynen, K. (2006). Targeted delivery of antibodies through the blood-brain barrier by MRI-guided focused ultrasound. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 340(4), 1085–1090. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.12.112.
Kinoshita, M., McDannold, N., Jolesz, F. A., & Hynynen, K. (2006). Noninvasive localized delivery of Herceptin to the mouse brain by MRI-guided focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier disruption. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 103(31), 11719–11723. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0604318103.
Hynynen, K., McDannold, N., Vykhodtseva, N., Raymond, S., Weissleder, R., Jolesz, F. A., et al. (2006). Focal disruption of the blood-brain barrier due to 260-kHz ultrasound bursts: A method for molecular imaging and targeted drug delivery. Journal of Neurosurgery, 105(3), 445–454. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.2006.105.3.445.
McDannold, N., Clement, G. T., Black, P., Jolesz, F., & Hynynen, K. (2010). Transcranial magnetic resonance imaging- guided focused ultrasound surgery of brain tumors: Initial findings in 3 patients. Neurosurgery, 66(2), 323–332. https://doi.org/10.1227/01.neu.0000360379.95800.2f.
Treat, L. H., McDannold, N., Vykhodtseva, N., Zhang, Y., Tam, K., & Hynynen, K. (2007). Targeted delivery of doxorubicin to the rat brain at therapeutic levels using MRI-guided focused ultrasound. International Journal of Cancer, 121(4), 901–907. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.22732.
Liu, H. L., Hua, M. Y., Chen, P. Y., Chu, P. C., Pan, C. H., Yang, H. W., et al. (2010). Blood-brain barrier disruption with focused ultrasound enhances delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs for glioblastoma treatment. Radiology, 255(2), 415–425. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10090699.
Chen, P. Y., Liu, H. L., Hua, M. Y., Yang, H. W., Huang, C. Y., Chu, P. C., et al. (2010). Novel magnetic/ultrasound focusing system enhances nanoparticle drug delivery for glioma treatment. Neuro Oncology, 12(10), 1050–1060. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/noq054.
Liu, H. L., Hua, M. Y., Yang, H. W., Huang, C. Y., Chu, P. C., Wu, J. S., et al. (2010). Magnetic resonance monitoring of focused ultrasound/magnetic nanoparticle targeting delivery of therapeutic agents to the brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 107(34), 15205–15210. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1003388107.
Fan, C. H., Ting, C. Y., Lin, C. Y., Chan, H. L., Chang, Y. C., Chen, Y. Y., et al. (2016). Noninvasive, targeted, and non-viral ultrasound-mediated GDNF-plasmid delivery for treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Scientific Reports, 6, 19579. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep19579.
Lin, C. Y., Hsieh, H. Y., Chen, C. M., Wu, S. R., Tsai, C. H., Huang, C. Y., et al. (2016). Non-invasive, neuron-specific gene therapy by focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening in Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Journal of Controlled Release, 235, 72–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.05.052.
McDannold, N., Vykhodtseva, N., & Hynynen, K. (2006). Targeted disruption of the blood-brain barrier with focused ultrasound: Association with cavitation activity. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 51(4), 793–807. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/51/4/003.
Tung, Y. S., Vlachos, F., Choi, J. J., Deffieux, T., Selert, K., & Konofagou, E. E. (2010). In vivo transcranial cavitation threshold detection during ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening in mice. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 55(20), 6141–6155. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/55/20/007.
O’Reilly, M. A., & Hynynen, K. (2010). A PVDF receiver for ultrasound monitoring of transcranial focused ultrasound therapy. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 57(9), 2286–2294. https://doi.org/10.1109/TBME.2010.2050483.
O’Reilly, M. A., & Hynynen, K. (2012). Blood-brain barrier: Real-time feedback-controlled focused ultrasound disruption by using an acoustic emissions-based controller. Radiology, 263(1), 96–106. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.11111417.
Arvanitis, C. D., Livingstone, M. S., Vykhodtseva, N., & McDannold, N. (2012). Controlled ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier disruption using passive acoustic emissions monitoring. PLoS ONE, 7(9), e45783. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0045783.
Huang, Y., Alkins, R., Schwartz, M. L., & Hynynen, K. (2017). Opening the blood-brain barrier with MR imaging-guided focused ultrasound: Preclinical testing on a trans-human skull porcine model. Radiology, 282(1), 123–130. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016152154.
Huang, Y., & Hynynen, K. (2011). MR-guided focused ultrasound for brain ablation and blood-brain barrier disruption. Methods in Molecular Biology, 711, 579–593. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-61737-992-5_30.
Xia, J., Tsui, P. H., & Liu, H. L. (2016). Low-pressure burst-mode focused ultrasound wave reconstruction and mapping for blood-brain barrier opening: A preclinical examination. Scientific Reports, 6, 27939. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27939.
Fan, C. H., Lin, W. H., Ting, C. Y., Chai, W. Y., Yen, T. C., Liu, H. L., et al. (2014). Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging for the detection of focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening. Theranostics, 4(10), 1014–1025. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.9575.
Wei, K. C., Tsai, H. C., Lu, Y. J., Yang, H. W., Hua, M. Y., Wu, M. F., et al. (2013). Neuronavigation-guided focused ultrasound-induced blood-brain barrier opening: A preliminary study in swine. AJNR. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 34(1), 115–120. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3150.
Van Ruijssevelt, L., Smirnov, P., Yudina, A., Bouchaud, V., Voisin, P., & Moonen, C. (2013). Observations on the viability of C6-glioma cells after sonoporation with low-intensity ultrasound and microbubbles. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control, 60(1), 34–45. https://doi.org/10.1109/TUFFC.2013.2535.
Pan, H., Zhou, Y., Sieling, F., Shi, J., Cui, J., & Deng, C. (2004). Sonoporation of cells for drug and gene delivery. Conference of the Proceedings of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, 5, 3531–3534. https://doi.org/10.1109/IEMBS.2004.1403993.
Feril, L. B., Jr. (2009). Ultrasound-mediated gene transfection. Methods in Molecular Biology, 542, 179–194. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-59745-561-9_10.
Taniyama, Y., Tachibana, K., Hiraoka, K., Aoki, M., Yamamoto, S., Matsumoto, K., et al. (2002). Development of safe and efficient novel nonviral gene transfer using ultrasound: Enhancement of transfection efficiency of naked plasmid DNA in skeletal muscle. Gene Therapy, 9(6), 372–380. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301678.
Beccaria, K., Canney, M., Goldwirt, L., Fernandez, C., Adam, C., Piquet, J., et al. (2013). Opening of the blood-brain barrier with an unfocused ultrasound device in rabbits. Journal of Neurosurgery, 119(4), 887–898. https://doi.org/10.3171/2013.5.JNS122374.
Goldwirt, L., Canney, M., Horodyckid, C., Poupon, J., Mourah, S., Vignot, A., et al. (2016). Enhanced brain distribution of carboplatin in a primate model after blood-brain barrier disruption using an implantable ultrasound device. Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology, 77(1), 211–216. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-015-2930-5.
Carpentier, A., Canney, M., Vignot, A., Reina, V., Beccaria, K., Horodyckid, C., et al. (2016). Clinical trial of blood-brain barrier disruption by pulsed ultrasound. Science Translational Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf6086.
Blackstock, D. T. (2000). Fundamentals of physical acoustics. New York: Wiley.
Tsai, C. H., Zhang, J. W., Liao, Y. Y., & Liu, H. L. (2016). Real-time monitoring of focused ultrasound blood-brain barrier opening via subharmonic acoustic emission detection: Implementation of confocal dual-frequency piezoelectric transducers. Physics in Medicine & Biology, 61(7), 2926–2946. https://doi.org/10.1088/0031-9155/61/7/2926.
White, P. J. (2006). Transcranial focused ultrasound surgery. Topics in Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 17(3), 165–172. https://doi.org/10.1097/RMR.0b013e31803774a3.
Sun, J., & Hynynen, K. (1998). Focusing of therapeutic ultrasound through a human skull: A numerical study. Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 104(3 Pt 1), 1705–1715.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan, under Grants Nos. 105-2221-E-182-022, 106-2221-E-182-002, 105-2923-B-002-001-MY3, Taiwan, French National Research Agency ANR-MOST project under Grant No. ANR-15-CE19-0003, and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan, under Grants Nos. CIRPD2E0051-53, CMRPD2D0111-13. We also thank the facility support from Center for Advanced Molecular Imaging and Translation, Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, CH., Chen, KT., Lin, YX. et al. Acoustic Emission-Feedback Planar Ultrasound System for Localized Blood–Brain Barrier Opening Monitoring. J. Med. Biol. Eng. 39, 277–286 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-018-0406-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40846-018-0406-x