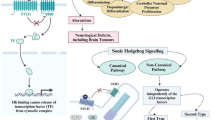
Abstract
The hedgehog pathway, for which sonic hedgehog (Shh) is the most prominent ligand, is highly conserved and is tightly associated with embryonic development in a number of species. This pathway is also tightly associated with the development of several types of cancer, including basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and acute promyelocytic leukemia, among many others. Inactivating mutations in Patched-1 (PTCH1), leading to ligand-independent pathway activation, are frequent in several cancer types, but most prominent in BCC. This has led to the development of several compounds targeting this pathway as a cancer therapeutic. These compounds target the inducers of this pathway in Smoothened (SMO) and the GLI transcription factors, although targeting SMO has had the most success. Despite the many attempts at targeting this pathway, only three US FDA-approved drugs for cancers affect the Shh pathway. Two of these compounds, vismodegib and sonidegib, target SMO to suppress signaling from either PTCH1 or SMO mutations that lead to upregulation of the pathway. The other approved compound is arsenic trioxide, which can suppress this pathway at the level of the GLI proteins, although current evidence suggests it also has other targets. This review focuses on the safety and tolerability of these clinically approved drugs targeting the Shh pathway, along with a discussion on other Shh pathway inhibitors being developed.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ingham PW, Nakano Y, Seger C. Mechanisms and functions of Hedgehog signalling across the metazoa. Nat Rev Genet. 2011;12(6):393–406.
Alman BA. The role of hedgehog signalling in skeletal health and disease. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2015;11(9):552–60.
Choudhry Z, Rikani AA, Choudhry AM, Tariq S, Zakaria F, Asghar MW, et al. Sonic hedgehog signalling pathway: a complex network. Ann Neurosci. 2014;21(1):28–31.
Carpenter RL, Lo HW. Identification, functional characterization, and pathobiological significance of GLI1 isoforms in human cancers. Vitam Horm. 2012;88:115–40.
Pathi S, Pagan-Westphal S, Baker DP, Garber EA, Rayhorn P, Bumcrot D, et al. Comparative biological responses to human Sonic, Indian, and Desert hedgehog. Mech Dev. 2001;106(1–2):107–17.
Porter JA, von Kessler DP, Ekker SC, Young KE, Lee JJ, Moses K, et al. The product of hedgehog autoproteolytic cleavage active in local and long-range signalling. Nature. 1995;374(6520):363–6.
Bailey JM, Mohr AM, Hollingsworth MA. Sonic hedgehog paracrine signaling regulates metastasis and lymphangiogenesis in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 2009;28(40):3513–25.
Yauch RL, Gould SE, Scales SJ, Tang T, Tian H, Ahn CP, et al. A paracrine requirement for hedgehog signalling in cancer. Nature. 2008;455(7211):406–10.
Gailani MR, Bale SJ, Leffell DJ, DiGiovanna JJ, Peck GL, Poliak S, et al. Developmental defects in Gorlin syndrome related to a putative tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 9. Cell. 1992;69(1):111–7.
Gailani MR, Stahle-Backdahl M, Leffell DJ, Glynn M, Zaphiropoulos PG, Pressman C, et al. The role of the human homologue of Drosophila patched in sporadic basal cell carcinomas. Nat Genet. 1996;14(1):78–81.
Hahn H, Wicking C, Zaphiropoulous PG, Gailani MR, Shanley S, Chidambaram A, et al. Mutations of the human homolog of Drosophila patched in the nevoid basal cell carcinoma syndrome. Cell. 1996;85(6):841–51.
Johnson RL, Rothman AL, Xie J, Goodrich LV, Bare JW, Bonifas JM, et al. Human homolog of patched, a candidate gene for the basal cell nevus syndrome. Science. 1996;272(5268):1668–71.
Northcott PA, Nakahara Y, Wu X, Feuk L, Ellison DW, Croul S, et al. Multiple recurrent genetic events converge on control of histone lysine methylation in medulloblastoma. Nat Genet. 2009;41(4):465–72.
Pietsch T, Waha A, Koch A, Kraus J, Albrecht S, Tonn J, et al. Medulloblastomas of the desmoplastic variant carry mutations of the human homologue of Drosophila patched. Cancer Res. 1997;57(11):2085–8.
Raffel C, Jenkins RB, Frederick L, Hebrink D, Alderete B, Fults DW, et al. Sporadic medulloblastomas contain PTCH mutations. Cancer Res. 1997;57(5):842–5.
Taylor MD, Liu L, Raffel C, Hui CC, Mainprize TG, Zhang X, et al. Mutations in SUFU predispose to medulloblastoma. Nat Genet. 2002;31(3):306–10.
Tostar U, Malm CJ, Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG, Toftgard R, Unden AB. Deregulation of the hedgehog signalling pathway: a possible role for the PTCH and SUFU genes in human rhabdomyoma and rhabdomyosarcoma development. J Pathol. 2006;208(1):17–25.
Xie J, Johnson RL, Zhang X, Bare JW, Waldman FM, Cogen PH, et al. Mutations of the PATCHED gene in several types of sporadic extracutaneous tumors. Cancer Res. 1997;57(12):2369–72.
Xie J, Murone M, Luoh SM, Ryan A, Gu Q, Zhang C, et al. Activating Smoothened mutations in sporadic basal-cell carcinoma. Nature. 1998;391(6662):90–2.
Bonilla X, Parmentier L, King B, Bezrukov F, Kaya G, Zoete V, et al. Genomic analysis identifies new drivers and progression pathways in skin basal cell carcinoma. Nat Genet. 2016;48(4):398–406.
Cohen MH, Hirschfeld S, Flamm Honig S, Ibrahim A, Johnson JR, O’Leary JJ, et al. Drug approval summaries: arsenic trioxide, tamoxifen citrate, anastrazole, paclitaxel, bexarotene. Oncologist. 2001;6(1):4–11.
Axelson M, Liu K, Jiang X, He K, Wang J, Zhao H, et al. U.S. Food and Drug Administration approval: vismodegib for recurrent, locally advanced, or metastatic basal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(9):2289–93.
Robarge KD, Brunton SA, Castanedo GM, Cui Y, Dina MS, Goldsmith R, et al. GDC-0449-a potent inhibitor of the hedgehog pathway. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009;19(19):5576–81.
Casey D, Demko S, Shord S, Zhao H, Chen H, He K, et al. FDA approval summary: sonidegib for locally advanced basal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2017;23(10):2377–81.
Pan S, Wu X, Jiang J, Gao W, Wan Y, Cheng D, et al. Discovery of NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective Smoothened antagonist. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2010;1(3):130–4.
Carpenter RL, Jiang Y, Jing Y, He J, Rojanasakul Y, Liu LZ, et al. Arsenite induces cell transformation by reactive oxygen species, AKT, ERK1/2, and p70S6K1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414(3):533–8.
IARC. Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic. IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog Risks Hum. 2004;84:1–477.
Beauchamp EM, Ringer L, Bulut G, Sajwan KP, Hall MD, Lee YC, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits human cancer cell growth and tumor development in mice by blocking Hedgehog/GLI pathway. J Clin Investig. 2011;121(1):148–60.
Chen GQ, Zhu J, Shi XG, Ni JH, Zhong HJ, Si GY, et al. In vitro studies on cellular and molecular mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia: As2O3 induces NB4 cell apoptosis with downregulation of Bcl-2 expression and modulation of PML-RAR alpha/PML proteins. Blood. 1996;88(3):1052–61.
Li X, Ding X, Adrian TE. Arsenic trioxide causes redistribution of cell cycle, caspase activation, and GADD expression in human colonic, breast, and pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Investig. 2004;22(3):389–400.
Wang C, Li B, Zhang H, Shi G, Li W, Jonas JB. Effect of arsenic trioxide on uveal melanoma cell proliferation in vitro. Ophthalmic Res. 2007;39(6):302–7.
Zhao S, Tsuchida T, Kawakami K, Shi C, Kawamoto K. Effect of As2O3 on cell cycle progression and cyclins D1 and B1 expression in two glioblastoma cell lines differing in p53 status. Int J Oncol. 2002;21(1):49–55.
Shen ZX, Chen GQ, Ni JH, Li XS, Xiong SM, Qiu QY, et al. Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): II. Clinical efficacy and pharmacokinetics in relapsed patients. Blood. 1997;89(9):3354–60.
Soignet SL, Maslak P, Wang ZG, Jhanwar S, Calleja E, Dardashti LJ, et al. Complete remission after treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide. N Engl J Med. 1998;339(19):1341–8.
Melnick A, Licht JD. Deconstructing a disease: RARalpha, its fusion partners, and their roles in the pathogenesis of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1999;93(10):3167–215.
Chen GQ, Shi XG, Tang W, Xiong SM, Zhu J, Cai X, et al. Use of arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL): I As2O3 exerts dose-dependent dual effects on APL cells. Blood. 1997;89(9):3345–53.
Ghavamzadeh A, Alimoghaddam K, Ghaffari SH, Rostami S, Jahani M, Hosseini R, et al. Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide without ATRA and/or chemotherapy. Ann Oncol. 2006;17(1):131–4.
Lallemand-Breitenbach V, Guillemin MC, Janin A, Daniel MT, Degos L, Kogan SC, et al. Retinoic acid and arsenic synergize to eradicate leukemic cells in a mouse model of acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Exp Med. 1999;189(7):1043–52.
Mathews V, George B, Lakshmi KM, Viswabandya A, Bajel A, Balasubramanian P, et al. Single-agent arsenic trioxide in the treatment of newly diagnosed acute promyelocytic leukemia: durable remissions with minimal toxicity. Blood. 2006;107(7):2627–32.
Kim J, Lee JJ, Kim J, Gardner D, Beachy PA. Arsenic antagonizes the Hedgehog pathway by preventing ciliary accumulation and reducing stability of the Gli2 transcriptional effector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(30):13432–7.
Han JB, Sang F, Chang JJ, Hua YQ, Shi WD, Tang LH, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits viability of pancreatic cancer stem cells in culture and in a xenograft model via binding to SHH-Gli. OncoTargets Ther. 2013;6:1129–38.
Ally MS, Ransohoff K, Sarin K, Atwood SX, Rezaee M, Bailey-Healy I, et al. Effects of combined treatment with arsenic trioxide and itraconazole in patients with refractory metastatic basal cell carcinoma. JAMA Dermatol. 2016;152(4):452–6.
Cai X, Yu K, Zhang L, Li Y, Li Q, Yang Z, et al. Synergistic inhibition of colon carcinoma cell growth by Hedgehog-Gli1 inhibitor arsenic trioxide and phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor LY294002. OncoTargets Ther. 2015;8:877–83.
Chang KJ, Yang MH, Zheng JC, Li B, Nie W. Arsenic trioxide inhibits cancer stem-like cells via down-regulation of Gli1 in lung cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(2):1133–43.
Kerl K, Moreno N, Holsten T, Ahlfeld J, Mertins J, Hotfilder M, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits tumor cell growth in malignant rhabdoid tumors in vitro and in vivo by targeting overexpressed Gli1. Int J Cancer. 2014;135(4):989–95.
Meister MT, Boedicker C, Graab U, Hugle M, Hahn H, Klingebiel T, et al. Arsenic trioxide induces Noxa-dependent apoptosis in rhabdomyosarcoma cells and synergizes with antimicrotubule drugs. Cancer Lett. 2016;381(2):287–95.
Nakamura S, Nagano S, Nagao H, Ishidou Y, Yokouchi M, Abematsu M, et al. Arsenic trioxide prevents osteosarcoma growth by inhibition of GLI transcription via DNA damage accumulation. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e69466.
Neumann JE, Wefers AK, Lambo S, Bianchi E, Bockstaller M, Dorostkar MM, et al. A mouse model for embryonal tumors with multilayered rosettes uncovers the therapeutic potential of Sonic-hedgehog inhibitors. Nat Med. 2017;23(10):1191–202.
Tang CM, Lee TE, Syed SA, Burgoyne AM, Leonard SY, Gao F, et al. Hedgehog pathway dysregulation contributes to the pathogenesis of human gastrointestinal stromal tumors via GLI-mediated activation of KIT expression. Oncotarget. 2016;7(48):78226–41.
Yang D, Cao F, Ye X, Zhao H, Liu X, Li Y, et al. Arsenic trioxide inhibits the Hedgehog pathway which is aberrantly activated in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Acta Haematol. 2013;130(4):260–7.
Zhang KZ, Zhang QB, Zhang QB, Sun HC, Ao JY, Chai ZT, et al. Arsenic trioxide induces differentiation of CD133+ hepatocellular carcinoma cells and prolongs posthepatectomy survival by targeting GLI1 expression in a mouse model. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7:28.
Mathews V, Chendamarai E, George B, Viswabandya A, Srivastava A. Treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia with single-agent arsenic trioxide. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2011;3(1):e2011056.
Barbey JT, Pezzullo JC, Soignet SL. Effect of arsenic trioxide on QT interval in patients with advanced malignancies. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21(19):3609–15.
Hai JJ, Gill H, Tse HF, Kumana CR, Kwong YL, Siu CW. Torsade de Pointes during oral arsenic trioxide therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia in a patient with heart failure. Ann Hematol. 2015;94(3):501–3.
Naito K, Kobayashi M, Sahara N, Shigeno K, Nakamura S, Shinjo K, et al. Two cases of acute promyelocytic leukemia complicated by torsade de pointes during arsenic trioxide therapy. Int J Hematol. 2006;83(4):318–23.
Yamazaki K, Terada H, Satoh H, Naito K, Takeshita A, Uehara A, et al. Arrhythmogenic effects of arsenic trioxide in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia and an electrophysiological study in isolated guinea pig papillary muscles. Circ J. 2006;70(11):1407–14.
Roboz GJ, Ritchie EK, Carlin RF, Samuel M, Gale L, Provenzano-Gober JL, et al. Prevalence, management, and clinical consequences of QT interval prolongation during treatment with arsenic trioxide. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(33):3723–8.
Vargas-Bermudez A, Cardenal F, Porta-Sales J. Opioids for the management of dyspnea in cancer patients: evidence of the last 15 years: a systematic review. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2015;29(4):341–52.
Akare UR, Bandaru S, Shaheen U, Singh PK, Tiwari G, Singare P, et al. Molecular docking approaches in identification of high affinity inhibitors of human SMO receptor. Bioinformation. 2014;10(12):737–42.
Karlou M, Lu JF, Wu G, Maity S, Tzelepi V, Navone NM, et al. Hedgehog signaling inhibition by the small molecule smoothened inhibitor GDC-0449 in the bone forming prostate cancer xenograft MDA PCa 118b. Prostate. 2012;72(15):1638–47.
Katagiri S, Tauchi T, Okabe S, Minami Y, Kimura S, Maekawa T, et al. Combination of ponatinib with Hedgehog antagonist vismodegib for therapy-resistant BCR-ABL1-positive leukemia. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(6):1422–32.
Mimeault M, Rachagani S, Muniyan S, Seshacharyulu P, Johansson SL, Datta K, et al. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling improves the anti-carcinogenic effects of docetaxel in prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(6):3887–903.
Nachtergaele S, Whalen DM, Mydock LK, Zhao Z, Malinauskas T, Krishnan K, et al. Structure and function of the smoothened extracellular domain in vertebrate Hedgehog signaling. eLife. 2013;2:e01340.
Razumilava N, Gradilone SA, Smoot RL, Mertens JC, Bronk SF, Sirica AE, et al. Non-canonical Hedgehog signaling contributes to chemotaxis in cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2014;60(3):599–605.
Rominger CM, Bee WL, Copeland RA, Davenport EA, Gilmartin A, Gontarek R, et al. Evidence for allosteric interactions of antagonist binding to the smoothened receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2009;329(3):995–1005.
Singh BN, Fu J, Srivastava RK, Shankar S. Hedgehog signaling antagonist GDC-0449 (Vismodegib) inhibits pancreatic cancer stem cell characteristics: molecular mechanisms. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27306.
Tian F, Mysliwietz J, Ellwart J, Gamarra F, Huber RM, Bergner A. Effects of the Hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449 on lung cancer cell lines are mediated by side populations. Clin Exp Med. 2012;12(1):25–30.
Tian F, Schrodl K, Kiefl R, Huber RM, Bergner A. The hedgehog pathway inhibitor GDC-0449 alters intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and inhibits cell growth in cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(1):89–94.
Wang C, Wu H, Evron T, Vardy E, Han GW, Huang XP, et al. Structural basis for Smoothened receptor modulation and chemoresistance to anticancer drugs. Nat Commun. 2014;5:4355.
Wang C, Wu H, Katritch V, Han GW, Huang XP, Liu W, et al. Structure of the human smoothened receptor bound to an antitumour agent. Nature. 2013;497(7449):338–43.
Wong H, Alicke B, West KA, Pacheco P, La H, Januario T, et al. Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic analysis of vismodegib in preclinical models of mutational and ligand-dependent Hedgehog pathway activation. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(14):4682–92.
Yauch RL, Dijkgraaf GJ, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn CP, Holcomb T, et al. Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science. 2009;326(5952):572–4.
Zuo M, Rashid A, Churi C, Vauthey JN, Chang P, Li Y, et al. Novel therapeutic strategy targeting the Hedgehog signalling and mTOR pathways in biliary tract cancer. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(6):1042–51.
Proctor AE, Thompson LA, O’Bryant CL. Vismodegib: an inhibitor of the Hedgehog signaling pathway in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. Ann Pharmacother. 2014;48(1):99–106.
LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, Reddy JC, Tibes R, Weiss GJ, Borad MJ, et al. Phase I trial of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with refractory, locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(8):2502–11.
Von Hoff DD, LoRusso PM, Rudin CM, Reddy JC, Yauch RL, Tibes R, et al. Inhibition of the hedgehog pathway in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(12):1164–72.
Sekulic A, Migden MR, Oro AE, Dirix L, Lewis KD, Hainsworth JD, et al. Efficacy and safety of vismodegib in advanced basal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(23):2171–9.
McCusker M, Basset-Seguin N, Dummer R, Lewis K, Schadendorf D, Sekulic A, et al. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma: prognosis dependent on anatomic site and spread of disease. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(4):774–83.
Sekulic A, Migden MR, Basset-Seguin N, Garbe C, Gesierich A, Lao CD, et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of vismodegib in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma: final update of the pivotal ERIVANCE BCC study. BMC Cancer. 2017;17(1):332.
Danial C, Lingala B, Balise R, Oro AE, Reddy S, Colevas A, et al. Markedly improved overall survival in 10 consecutive patients with metastatic basal cell carcinoma. Br J Dermatol. 2013;169(3):673–6.
von Domarus H, Stevens PJ. Metastatic basal cell carcinoma. Report of five cases and review of 170 cases in the literature. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1984;10(6):1043–60.
Lear JT, Migden MR, Lewis KD, Chang ALS, Guminski A, Gutzmer R, et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of sonidegib in patients with locally advanced and metastatic basal cell carcinoma: 30-month analysis of the randomized phase 2 BOLT study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32(3):372–81.
Raszewski RL, Guyuron B. Long-term survival following nodal metastases from basal cell carcinoma. Ann Plast Surg. 1990;24(2):170–5.
Sharpe HJ, Wang W, Hannoush RN, de Sauvage FJ. Regulation of the oncoprotein Smoothened by small molecules. Nat Chem Biol. 2015;11(4):246–55.
Graham RA, Lum BL, Cheeti S, Jin JY, Jorga K, Von Hoff DD, et al. Pharmacokinetics of hedgehog pathway inhibitor vismodegib (GDC-0449) in patients with locally advanced or metastatic solid tumors: the role of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein binding. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17(8):2512–20.
Wong H, Chen JZ, Chou B, Halladay JS, Kenny JR, La H, et al. Preclinical assessment of the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of GDC-0449 (2-chloro-N-(4-chloro-3-(pyridin-2-yl)phenyl)-4-(methylsulfonyl)benzamide), an orally bioavailable systemic Hedgehog signalling pathway inhibitor. Xenobiotica. 2009;39(11):850–61.
Ding X, Chou B, Graham RA, Cheeti S, Percey S, Matassa LC, et al. Determination of GDC-0449, a small-molecule inhibitor of the Hedgehog signaling pathway, in human plasma by solid phase extraction-liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2010;878(9–10):785–90.
Tang JY, So PL, Epstein EH Jr. Novel Hedgehog pathway targets against basal cell carcinoma. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2007;224(3):257–64.
Graham RA, Chang I, Jin JY, Wang B, Dufek MB, Ayache JA, et al. Daily dosing of vismodegib to steady state does not prolong the QTc interval in healthy volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013;61(1):83–9.
Apalla Z, Papageorgiou C, Lallas A, Sotiriou E, Lazaridou E, Vakirlis E, et al. Spotlight on vismodegib in the treatment of basal cell carcinoma: an evidence-based review of its place in therapy. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2017;10:171–7.
Jacobsen AA, Kydd AR, Strasswimmer J. Practical management of the adverse effects of Hedgehog pathway inhibitor therapy for basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76(4):767–8.
Lacouture ME, Dreno B, Ascierto PA, Dummer R, Basset-Seguin N, Fife K, et al. Characterization and management of Hedgehog pathway inhibitor-related adverse events in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma. Oncologist. 2016;21(10):1218–29.
Macdonald JB, Macdonald B, Golitz LE, LoRusso P, Sekulic A. Cutaneous adverse effects of targeted therapies: Part II: Inhibitors of intracellular molecular signaling pathways. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015;72(2):221–36 (quiz 37–8).
Malhi V, Colburn D, Williams SJ, Hop CE, Dresser MJ, Chandra P, et al. A clinical drug-drug interaction study to evaluate the effect of a proton-pump inhibitor, a combined P-glycoprotein/cytochrome 450 enzyme (CYP)3A4 inhibitor, and a CYP2C9 inhibitor on the pharmacokinetics of vismodegib. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016;78(1):41–9.
Ventarola DJ, Silverstein DI. Vismodegib-associated hepatotoxicity: a potential side effect detected in postmarketing surveillance. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;71(2):397–8.
Basset-Seguin N, Hauschild A, Grob JJ, Kunstfeld R, Dreno B, Mortier L, et al. Vismodegib in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma (STEVIE): a pre-planned interim analysis of an international, open-label trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(6):729–36.
Blotta S, Jakubikova J, Calimeri T, Roccaro AM, Amodio N, Azab AK, et al. Canonical and noncanonical Hedgehog pathway in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Blood. 2012;120(25):5002–13.
Chaudary N, Pintilie M, Hedley D, Hill RP, Milosevic M, Mackay H. Hedgehog inhibition enhances efficacy of radiation and cisplatin in orthotopic cervical cancer xenografts. Br J Cancer. 2017;116(1):50–7.
D’Amato C, Rosa R, Marciano R, D’Amato V, Formisano L, Nappi L, et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signalling by NVP-LDE225 (Erismodegib) interferes with growth and invasion of human renal cell carcinoma cells. Br J Cancer. 2014;111(6):1168–79.
Fan YH, Ding J, Nguyen S, Liu XJ, Xu G, Zhou HY, et al. Aberrant hedgehog signaling is responsible for the highly invasive behavior of a subpopulation of hepatoma cells. Oncogene. 2016;35(1):116–24.
Fendrich V, Wiese D, Waldmann J, Lauth M, Heverhagen AE, Rehm J, et al. Hedgehog inhibition with the orally bioavailable Smo antagonist LDE225 represses tumor growth and prolongs survival in a transgenic mouse model of islet cell neoplasms. Ann Surg. 2011;254(5):818–23 (discussion 23).
Fu J, Rodova M, Nanta R, Meeker D, Van Veldhuizen PJ, Srivastava RK, et al. NPV-LDE-225 (Erismodegib) inhibits epithelial mesenchymal transition and self-renewal of glioblastoma initiating cells by regulating miR-21, miR-128, and miR-200. Neuro-oncology. 2013;15(6):691–706.
Gorojankina T, Hoch L, Faure H, Roudaut H, Traiffort E, Schoenfelder A, et al. Discovery, molecular and pharmacological characterization of GSA-10, a novel small-molecule positive modulator of Smoothened. Mol Pharmacol. 2013;83(5):1020–9.
Irvine DA, Zhang B, Kinstrie R, Tarafdar A, Morrison H, Campbell VL, et al. Deregulated hedgehog pathway signaling is inhibited by the smoothened antagonist LDE225 (Sonidegib) in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukaemia. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25476.
Jalili A, Mertz KD, Romanov J, Wagner C, Kalthoff F, Stuetz A, et al. NVP-LDE225, a potent and selective SMOOTHENED antagonist reduces melanoma growth in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 2013;8(7):e69064.
Kool M, Jones DT, Jager N, Northcott PA, Pugh TJ, Hovestadt V, et al. Genome sequencing of SHH medulloblastoma predicts genotype-related response to smoothened inhibition. Cancer Cell. 2014;25(3):393–405.
Li X, Chen F, Zhu Q, Ding B, Zhong Q, Huang K, et al. Gli-1/PI3K/AKT/NF-kB pathway mediates resistance to radiation and is a target for reversion of responses in refractory acute myeloid leukemia cells. Oncotarget. 2016;7(22):33004–15.
Sabbatino F, Wang Y, Wang X, Flaherty KT, Yu L, Pepin D, et al. PDGFRalpha up-regulation mediated by sonic hedgehog pathway activation leads to BRAF inhibitor resistance in melanoma cells with BRAF mutation. Oncotarget. 2014;5(7):1926–41.
Sirkisoon SR, Carpenter RL, Rimkus T, Anderson A, Harrison A, Lange AM, et al. Interaction between STAT3 and GLI1/tGLI1 oncogenic transcription factors promotes the aggressiveness of triple-negative breast cancers and HER2-enriched breast cancer. Oncogene. 2018;37(19):2502–14.
Steg AD, Katre AA, Bevis KS, Ziebarth A, Dobbin ZC, Shah MM, et al. Smoothened antagonists reverse taxane resistance in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012;11(7):1587–97.
Teichman J, Dodbiba L, Thai H, Fleet A, Morey T, Liu L, et al. Hedgehog inhibition mediates radiation sensitivity in mouse xenograft models of human esophageal adenocarcinoma. PLoS One. 2018;13(5):e0194809.
Skvara H, Kalthoff F, Meingassner JG, Wolff-Winiski B, Aschauer H, Kelleher JF, et al. Topical treatment of Basal cell carcinomas in nevoid Basal cell carcinoma syndrome with a smoothened inhibitor. J Investig Dermatol. 2011;131(8):1735–44.
Rodon J, Tawbi HA, Thomas AL, Stoller RG, Turtschi CP, Baselga J, et al. A phase I, multicenter, open-label, first-in-human, dose-escalation study of the oral smoothened inhibitor Sonidegib (LDE225) in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(7):1900–9.
Migden MR, Guminski A, Gutzmer R, Dirix L, Lewis KD, Combemale P, et al. Treatment with two different doses of sonidegib in patients with locally advanced or metastatic basal cell carcinoma (BOLT): a multicentre, randomised, double-blind phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16(6):716–28.
Dummer R, Guminski A, Gutzmer R, Dirix L, Lewis KD, Combemale P, et al. The 12-month analysis from Basal Cell Carcinoma Outcomes with LDE225 Treatment (BOLT): a phase II, randomized, double-blind study of sonidegib in patients with advanced basal cell carcinoma. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016;75(1):113–25.e5.
Danial C, Sarin KY, Oro AE, Chang AL. An investigator-initiated open-label trial of sonidegib in advanced basal cell carcinoma patients resistant to vismodegib. Clin Cancer Res. 2016;22(6):1325–9.
Einolf HJ, Zhou J, Won C, Wang L, Rebello S. A physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling approach to predict drug–drug interactions of sonidegib (LDE225) with perpetrators of CYP3A in cancer patients. Drug Metab Dispos. 2017;45(4):361–74.
Goel V, Hurh E, Stein A, Nedelman J, Zhou J, Chiparus O, et al. Population pharmacokinetics of sonidegib (LDE225), an oral inhibitor of hedgehog pathway signaling, in healthy subjects and in patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2016;77(4):745–55.
Jain S, Song R, Xie J. Sonidegib: mechanism of action, pharmacology, and clinical utility for advanced basal cell carcinomas. OncoTargets Ther. 2017;10:1645–53.
Quinlan M, Zhou J, Hurh E, Sellami D. Exposure-QT analysis for sonidegib (LDE225), an oral inhibitor of the hedgehog signaling pathway, for measures of the QT prolongation potential in healthy subjects and in patients with advanced solid tumors. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2016;72(12):1427–32.
Ericson J, Morton S, Kawakami A, Roelink H, Jessell TM. Two critical periods of Sonic Hedgehog signaling required for the specification of motor neuron identity. Cell. 1996;87(4):661–73.
Maun HR, Wen X, Lingel A, de Sauvage FJ, Lazarus RA, Scales SJ, et al. Hedgehog pathway antagonist 5E1 binds hedgehog at the pseudo-active site. J Biol Chem. 2010;285(34):26570–80.
Song Z, Yue W, Wei B, Wang N, Li T, Guan L, et al. Sonic hedgehog pathway is essential for maintenance of cancer stem-like cells in human gastric cancer. PLoS One. 2011;6(3):e17687.
O’Toole SA, Machalek DA, Shearer RF, Millar EK, Nair R, Schofield P, et al. Hedgehog overexpression is associated with stromal interactions and predicts for poor outcome in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2011;71(11):4002–14.
Coon V, Laukert T, Pedone CA, Laterra J, Kim KJ, Fults DW. Molecular therapy targeting Sonic hedgehog and hepatocyte growth factor signaling in a mouse model of medulloblastoma. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9(9):2627–36.
Stanton BZ, Peng LF, Maloof N, Nakai K, Wang X, Duffner JL, et al. A small molecule that binds Hedgehog and blocks its signaling in human cells. Nat Chem Biol. 2009;5(3):154–6.
Buglino JA, Resh MD. Hhat is a palmitoylacyltransferase with specificity for N-palmitoylation of Sonic Hedgehog. J Biol Chem. 2008;283(32):22076–88.
Mann RK, Beachy PA. Novel lipid modifications of secreted protein signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 2004;73:891–923.
Petrova E, Rios-Esteves J, Ouerfelli O, Glickman JF, Resh MD. Inhibitors of Hedgehog acyltransferase block Sonic Hedgehog signaling. Nat Chem Biol. 2013;9(4):247–9.
Matevossian A, Resh MD. Hedgehog acyltransferase as a target in estrogen receptor positive, HER2 amplified, and tamoxifen resistant breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:72.
Petrova E, Matevossian A, Resh MD. Hedgehog acyltransferase as a target in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2015;34(2):263–8.
Cooper MK, Porter JA, Young KE, Beachy PA. Teratogen-mediated inhibition of target tissue response to Shh signaling. Science. 1998;280(5369):1603–7.
Incardona JP, Gaffield W, Kapur RP, Roelink H. The teratogenic Veratrum alkaloid cyclopamine inhibits sonic hedgehog signal transduction. Development. 1998;125(18):3553–62.
Feldmann G, Dhara S, Fendrich V, Bedja D, Beaty R, Mullendore M, et al. Blockade of hedgehog signaling inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion and metastases: a new paradigm for combination therapy in solid cancers. Cancer Res. 2007;67(5):2187–96.
Karhadkar SS, Bova GS, Abdallah N, Dhara S, Gardner D, Maitra A, et al. Hedgehog signalling in prostate regeneration, neoplasia and metastasis. Nature. 2004;431(7009):707–12.
Sanchez P, Ruiz i Altaba A. In vivo inhibition of endogenous brain tumors through systemic interference of Hedgehog signaling in mice. Mech Dev. 2005;122(2):223–30.
Stecca B, Mas C, Clement V, Zbinden M, Correa R, Piguet V, et al. Melanomas require HEDGEHOG-GLI signaling regulated by interactions between GLI1 and the RAS-MEK/AKT pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(14):5895–900.
Campbell VT, Nadesan P, Ali SA, Wang CY, Whetstone H, Poon R, et al. Hedgehog pathway inhibition in chondrosarcoma using the smoothened inhibitor IPI-926 directly inhibits sarcoma cell growth. Mol Cancer Ther. 2014;13(5):1259–69.
Lee MJ, Hatton BA, Villavicencio EH, Khanna PC, Friedman SD, Ditzler S, et al. Hedgehog pathway inhibitor saridegib (IPI-926) increases lifespan in a mouse medulloblastoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(20):7859–64.
Lo WW, Wunder JS, Dickson BC, Campbell V, McGovern K, Alman BA, et al. Involvement and targeted intervention of dysregulated Hedgehog signaling in osteosarcoma. Cancer. 2014;120(4):537–47.
McCann CK, Growdon WB, Kulkarni-Datar K, Curley MD, Friel AM, Proctor JL, et al. Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling antagonizes serous ovarian cancer growth in a primary xenograft model. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e28077.
Tremblay MR, Lescarbeau A, Grogan MJ, Tan E, Lin G, Austad BC, et al. Discovery of a potent and orally active hedgehog pathway antagonist (IPI-926). J Med Chem. 2009;52(14):4400–18.
Bowles DW, Keysar SB, Eagles JR, Wang G, Glogowska MJ, McDermott JD, et al. A pilot study of cetuximab and the hedgehog inhibitor IPI-926 in recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2016;53:74–9.
Jimeno A, Weiss GJ, Miller WH Jr, Gettinger S, Eigl BJ, Chang AL, et al. Phase I study of the Hedgehog pathway inhibitor IPI-926 in adult patients with solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(10):2766–74.
Ko AH, LoConte N, Tempero MA, Walker EJ, Kate Kelley R, Lewis S, et al. A phase I study of FOLFIRINOX Plus IPI-926, a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor, for advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Pancreas. 2016;45(3):370–5.
Smith S, Hoyt J, Whitebread N, Manna J, Peluso M, Faia K, et al. The pre-clinical absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion properties of IPI-926, an orally bioavailable antagonist of the hedgehog signal transduction pathway. Xenobiotica. 2013;43(10):875–85.
Sasaki K, Gotlib JR, Mesa RA, Newberry KJ, Ravandi F, Cortes JE, et al. Phase II evaluation of IPI-926, an oral Hedgehog inhibitor, in patients with myelofibrosis. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(7):2092–7.
Riedlinger D, Bahra M, Boas-Knoop S, Lippert S, Bradtmoller M, Guse K, et al. Hedgehog pathway as a potential treatment target in human cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepato-Biliary-Pancreat Sci. 2014;21(8):607–15.
Zaidi AH, Komatsu Y, Kelly LA, Malhotra U, Rotoloni C, Kosovec JE, et al. Smoothened inhibition leads to decreased proliferation and induces apoptosis in esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Cancer Investig. 2013;31(7):480–9.
Ishiwata T, Iwasawa S, Ebata T, Fan M, Tada Y, Tatsumi K, et al. Inhibition of Gli leads to antitumor growth and enhancement of cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity in large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma of the lung. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(3):1148–54.
Wilkinson SE, Furic L, Buchanan G, Larsson O, Pedersen J, Frydenberg M, et al. Hedgehog signaling is active in human prostate cancer stroma and regulates proliferation and differentiation of adjacent epithelium. Prostate. 2013;73(16):1810–23.
Munchhof MJ, Li Q, Shavnya A, Borzillo GV, Boyden TL, Jones CS, et al. Discovery of PF-04449913, a potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor of Smoothened. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2012;3(2):106–11.
Chaudhry P, Singh M, Triche TJ, Guzman M, Merchant AA. GLI3 repressor determines Hedgehog pathway activation and is required for response to SMO antagonist glasdegib in AML. Blood. 2017;129(26):3465–75.
Fukushima N, Minami Y, Kakiuchi S, Kuwatsuka Y, Hayakawa F, Jamieson C, et al. Small-molecule Hedgehog inhibitor attenuates the leukemia-initiation potential of acute myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(10):1422–9.
Sadarangani A, Pineda G, Lennon KM, Chun HJ, Shih A, Schairer AE, et al. GLI2 inhibition abrogates human leukemia stem cell dormancy. J Transl Med. 2015;13:98.
Giri N, Lam LH, LaBadie RR, Krzyzaniak JF, Jiang H, Hee B, et al. Evaluation of the effect of new formulation, food, or a proton pump inhibitor on the relative bioavailability of the smoothened inhibitor glasdegib (PF-04449913) in healthy volunteers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2017;80(6):1249–60.
Lam JL, Vaz A, Hee B, Liang Y, Yang X, Shaik MN. Metabolism, excretion and pharmacokinetics of [(14)C]glasdegib (PF-04449913) in healthy volunteers following oral administration. Xenobiotica. 2017;47(12):1064–76.
Martinelli G, Oehler VG, Papayannidis C, Courtney R, Shaik MN, Zhang X, et al. Treatment with PF-04449913, an oral smoothened antagonist, in patients with myeloid malignancies: a phase 1 safety and pharmacokinetics study. Lancet Haematol. 2015;2(8):e339–46.
Minami H, Ando Y, Ma BB, Hsiang Lee J, Momota H, Fujiwara Y, et al. Phase I, multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study of sonidegib in Asian patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Sci. 2016;107(10):1477–83.
Savona MR, Pollyea DA, Stock W, Oehler VG, Schroeder MA, Lancet J, et al. Phase Ib study of glasdegib, a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor, in combination with standard chemotherapy in patients with AML or high-risk MDS. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(10):2294–303.
Shaik MN, Hee B, Wei H, LaBadie RR. Evaluation of the effect of rifampin on the pharmacokinetics of the Smoothened inhibitor glasdegib in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2018;84(6):1346–53.
Shaik MN, LaBadie RR, Rudin D, Levin WJ. Evaluation of the effect of food and ketoconazole on the pharmacokinetics of the smoothened inhibitor PF-04449913 in healthy volunteers. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2014;74(2):411–8.
Wagner AJ, Messersmith WA, Shaik MN, Li S, Zheng X, McLachlan KR, et al. A phase I study of PF-04449913, an oral hedgehog inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(5):1044–51.
Cortes JE, Douglas Smith B, Wang ES, Merchant A, Oehler VG, Arellano M, et al. Glasdegib in combination with cytarabine and daunorubicin in patients with AML or high-risk MDS: phase 2 study results. Am J Hematol. 2018;93(11):1301–10.
Ohashi T, Oguro Y, Tanaka T, Shiokawa Z, Tanaka Y, Shibata S, et al. Discovery of the investigational drug TAK-441, a pyrrolo[3,2-c]pyridine derivative, as a highly potent and orally active hedgehog signaling inhibitor: modification of the core skeleton for improved solubility. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012;20(18):5507–17.
Lubik AA, Nouri M, Truong S, Ghaffari M, Adomat HH, Corey E, et al. Paracrine sonic hedgehog signaling contributes significantly to acquired steroidogenesis in the prostate tumor microenvironment. Int J Cancer. 2017;140(2):358–69.
Ibuki N, Ghaffari M, Pandey M, Iu I, Fazli L, Kashiwagi M, et al. TAK-441, a novel investigational smoothened antagonist, delays castration-resistant progression in prostate cancer by disrupting paracrine hedgehog signaling. Int J Cancer. 2013;133(8):1955–66.
Kogame A, Tagawa Y, Shibata S, Tojo H, Miyamoto M, Tohyama K, et al. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic modeling of hedgehog inhibitor TAK-441 for the inhibition of Gli1 messenger RNA expression and antitumor efficacy in xenografted tumor model mice. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(4):727–34.
Lauressergues E, Heusler P, Lestienne F, Troulier D, Rauly-Lestienne I, Tourette A, et al. Pharmacological evaluation of a series of smoothened antagonists in signaling pathways and after topical application in a depilated mouse model. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2016;4(2):e00214.
Dijkgraaf GJ, Alicke B, Weinmann L, Januario T, West K, Modrusan Z, et al. Small molecule inhibition of GDC-0449 refractory smoothened mutants and downstream mechanisms of drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2011;71(2):435–44.
Ishii T, Shimizu Y, Nakashima K, Kondo S, Ogawa K, Sasaki S, et al. Inhibition mechanism exploration of investigational drug TAK-441 as inhibitor against vismodegib-resistant smoothened mutant. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014;723:305–13.
Shimizu Y, Ishii T, Ogawa K, Sasaki S, Matsui H, Nakayama M. Biochemical characterization of smoothened receptor antagonists by binding kinetics against drug-resistant mutant. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;764:220–7.
Goldman J, Eckhardt SG, Borad MJ, Curtis KK, Hidalgo M, Calvo E, et al. Phase I dose-escalation trial of the oral investigational Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitor TAK-441 in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(5):1002–9.
Bai Q, Shen Y, Jin N, Liu H, Yao X. Molecular modeling study on the dynamical structural features of human smoothened receptor and binding mechanism of antagonist LY2940680 by metadynamics simulation and free energy calculation. Biochem Biophys Acta. 2014;1840(7):2128–38.
Bender MH, Hipskind PA, Capen AR, Cockman M, Credille KM, Gao H, et al. Abstract 2819: Identification and characterization of a novel smoothened antagonist for the treatment of cancer with deregulated hedgehog signaling. Cancer Res. 2011;71(8 Suppl):2819.
Sinha N, Chowdhury S, Sarkar RR. Deciphering structural stability and binding mechanisms of potential antagonists with smoothened protein. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2018;36(11):2917–37.
Bendell J, Andre V, Ho A, Kudchadkar R, Migden M, Infante J, et al. Phase I study of LY2940680, a Smo antagonist, in patients with advanced cancer including treatment-naive and previously treated basal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24(9):2082–91.
Ueno H, Kondo S, Yoshikawa S, Inoue K, Andre V, Tajimi M, et al. A phase I and pharmacokinetic study of taladegib, a Smoothened inhibitor, in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors. Investig New Drugs. 2018;36(4):647–56.
Peukert S, He F, Dai M, Zhang R, Sun Y, Miller-Moslin K, et al. Discovery of NVP-LEQ506, a second-generation inhibitor of smoothened. ChemMedChem. 2013;8(8):1261–5.
Tu J, Li JJ, Song LT, Zhai HL, Wang J, Zhang XY. Molecular modeling study on resistance of WT/D473H SMO to antagonists LDE-225 and LEQ-506. Pharmacol Res. 2018;129:491–9.
Kim J, Aftab BT, Tang JY, Kim D, Lee AH, Rezaee M, et al. Itraconazole and arsenic trioxide inhibit Hedgehog pathway activation and tumor growth associated with acquired resistance to smoothened antagonists. Cancer Cell. 2013;23(1):23–34.
Porter JA, Young KE, Beachy PA. Cholesterol modification of hedgehog signaling proteins in animal development. Science. 1996;274(5285):255–9.
Wahid M, Jawed A, Mandal RK, Dar SA, Khan S, Akhter N, et al. Vismodegib, itraconazole and sonidegib as hedgehog pathway inhibitors and their relative competencies in the treatment of basal cell carcinomas. Crit Rev Oncol/Hematol. 2016;98:235–41.
Antonarakis ES, Heath EI, Smith DC, Rathkopf D, Blackford AL, Danila DC, et al. Repurposing itraconazole as a treatment for advanced prostate cancer: a noncomparative randomized phase II trial in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Oncologist. 2013;18(2):163–73.
Kim DJ, Kim J, Spaunhurst K, Montoya J, Khodosh R, Chandra K, et al. Open-label, exploratory phase II trial of oral itraconazole for the treatment of basal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(8):745–51.
Rudin CM, Brahmer JR, Juergens RA, Hann CL, Ettinger DS, Sebree R, et al. Phase 2 study of pemetrexed and itraconazole as second-line therapy for metastatic nonsquamous non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2013;8(5):619–23.
Fan P, Fan S, Wang H, Mao J, Shi Y, Ibrahim MM, et al. Genistein decreases the breast cancer stem-like cell population through Hedgehog pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2013;4(6):146.
Li W, Frame LT, Hoo KA, Li Y, D’Cunha N, Cobos E. Genistein inhibited proliferation and induced apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia, lymphoma and multiple myeloma cells in vitro. Leuk Lymphoma. 2011;52(12):2380–90.
Slusarz A, Shenouda NS, Sakla MS, Drenkhahn SK, Narula AS, MacDonald RS, et al. Common botanical compounds inhibit the hedgehog signaling pathway in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70(8):3382–90.
Yu D, Shin HS, Lee YS, Lee D, Kim S, Lee YC. Genistein attenuates cancer stem cell characteristics in gastric cancer through the downregulation of Gli1. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(2):673–8.
Zhang L, Li L, Jiao M, Wu D, Wu K, Li X, et al. Genistein inhibits the stemness properties of prostate cancer cells through targeting Hedgehog-Gli1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2012;323(1):48–57.
El-Rayes BF, Philip PA, Sarkar FH, Shields AF, Ferris AM, Hess K, et al. A phase II study of isoflavones, erlotinib, and gemcitabine in advanced pancreatic cancer. Investig New Drugs. 2011;29(4):694–9.
Lazarevic B, Boezelijn G, Diep LM, Kvernrod K, Ogren O, Ramberg H, et al. Efficacy and safety of short-term genistein intervention in patients with localized prostate cancer prior to radical prostatectomy: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind Phase 2 clinical trial. Nutr Cancer. 2011;63(6):889–98.
Lohr JM, Karimi M, Omazic B, Kartalis N, Verbeke CS, Berkenstam A, et al. A phase I dose escalation trial of AXP107-11, a novel multi-component crystalline form of genistein, in combination with gemcitabine in chemotherapy-naive patients with unresectable pancreatic cancer. Pancreatology. 2016;16(4):640–5.
Messing E, Gee JR, Saltzstein DR, Kim K, diSant’Agnese A, Kolesar J, et al. A phase 2 cancer chemoprevention biomarker trial of isoflavone G-2535 (genistein) in presurgical bladder cancer patients. Cancer Prev Res. 2012;5(4):621–30.
Pendleton JM, Tan WW, Anai S, Chang M, Hou W, Shiverick KT, et al. Phase II trial of isoflavone in prostate-specific antigen recurrent prostate cancer after previous local therapy. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:132.
Takimoto CH, Glover K, Huang X, Hayes SA, Gallot L, Quinn M, et al. Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analysis of unconjugated soy isoflavones administered to individuals with cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2003;12(11 Pt 1):1213–21.
Lauth M, Bergstrom A, Shimokawa T, Toftgard R. Inhibition of GLI-mediated transcription and tumor cell growth by small-molecule antagonists. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(20):8455–60.
Benvenuto M, Masuelli L, De Smaele E, Fantini M, Mattera R, Cucchi D, et al. In vitro and in vivo inhibition of breast cancer cell growth by targeting the Hedgehog/GLI pathway with SMO (GDC-0449) or GLI (GANT-61) inhibitors. Oncotarget. 2016;7(8):9250–70.
Chen Q, Xu R, Zeng C, Lu Q, Huang D, Shi C, et al. Down-regulation of Gli transcription factor leads to the inhibition of migration and invasion of ovarian cancer cells via integrin beta4-mediated FAK signaling. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88386.
Geng L, Lu K, Li P, Li X, Zhou X, Li Y, et al. GLI1 inhibitor GANT61 exhibits antitumor efficacy in T-cell lymphoma cells through down-regulation of p-STAT3 and SOCS3. Oncotarget. 2017;8(30):48701–10.
Gonnissen A, Isebaert S, McKee CM, Dok R, Haustermans K, Muschel RJ. The hedgehog inhibitor GANT61 sensitizes prostate cancer cells to ionizing radiation both in vitro and in vivo. Oncotarget. 2016;7(51):84286–98.
Gonnissen A, Isebaert S, McKee CM, Muschel RJ, Haustermans K. The effect of metformin and GANT61 combinations on the radiosensitivity of prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(2):E399.
Koike Y, Ohta Y, Saitoh W, Yamashita T, Kanomata N, Moriya T, et al. Anti-cell growth and anti-cancer stem cell activities of the non-canonical hedgehog inhibitor GANT61 in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer. 2017;24(5):683–93.
Kurebayashi J, Koike Y, Ohta Y, Saitoh W, Yamashita T, Kanomata N, et al. Anti-cancer stem cell activity of a hedgehog inhibitor GANT61 in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer cells. Cancer Sci. 2017;108(5):918–30.
Li J, Cai J, Zhao S, Yao K, Sun Y, Li Y, et al. GANT61, a GLI inhibitor, sensitizes glioma cells to the temozolomide treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016;35(1):184.
Shahi MH, Holt R, Rebhun RB. Blocking signaling at the level of GLI regulates downstream gene expression and inhibits proliferation of canine osteosarcoma cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96593.
Srivastava RK, Kaylani SZ, Edrees N, Li C, Talwelkar SS, Xu J, et al. GLI inhibitor GANT-61 diminishes embryonal and alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma growth by inhibiting Shh/AKT-mTOR axis. Oncotarget. 2014;5(23):12151–65.
Tong W, Qiu L, Qi M, Liu J, Hu K, Lin W, et al. GANT-61 and GDC-0449 induce apoptosis of prostate cancer stem cells through a GLI-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(4):3641–52.
Vlckova K, Reda J, Ondrusova L, Krayem M, Ghanem G, Vachtenheim J. GLI inhibitor GANT61 kills melanoma cells and acts in synergy with obatoclax. Int J Oncol. 2016;49(3):953–60.
Wickstrom M, Dyberg C, Shimokawa T, Milosevic J, Baryawno N, Fuskevag OM, et al. Targeting the hedgehog signal transduction pathway at the level of GLI inhibits neuroblastoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(7):1516–24.
Yang H, Hu L, Liu Z, Qin Y, Li R, Zhang G, et al. Inhibition of Gli1-mediated prostate cancer cell proliferation by inhibiting the mTOR/S6K1 signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 2017;14(6):7970–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Richard L. Carpenter and Haimanti Ray have no conflicts of interests to declare.
Funding
The authors would like to acknowledge their funding source, National Cancer Institute Grant K22CA207575 (RLC) and Indiana University School of Medicine.
Additional information
Part of a theme issue on “Safety of Novel Anticancer Therapies: Future Perspectives”. Guest Editors: Rashmi R. Shah, Giuseppe Curigliano.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carpenter, R.L., Ray, H. Safety and Tolerability of Sonic Hedgehog Pathway Inhibitors in Cancer. Drug Saf 42, 263–279 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-018-0777-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40264-018-0777-5