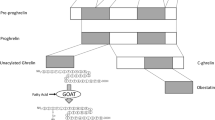
Abstract
Purpose
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by insulin resistance and impaired glucose homeostasis. In recent years, there has been growing interest in the role of hunger and satiety hormones such as ghrelin and leptin in the development and progression of T2DM. In this context, the present literature review aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current understanding of how ghrelin and leptin influences food intake and maintain energy balance and its implications in the pathophysiology of T2DM.
Methods
A thorough literature search was performed using PubMed and Google Scholar to choose the studies that associated leptin and ghrelin with T2DM. Original articles and reviews were included, letters to editors and case reports were excluded.
Results
This narrative review article provides a comprehensive summary on mechanism of action of leptin and ghrelin, its association with obesity and T2DM, how they regulate energy and glucose homeostasis and potential therapeutic implications of leptin and ghrelin in managing T2DM.
Conclusion
Ghrelin, known for its appetite-stimulating effects, and leptin, a hormone involved in the regulation of energy balance, have been implicated in insulin resistance and glucose metabolism. Understanding the complexities of ghrelin and leptin interactions in the context of T2DM may offer insights into novel therapeutic strategies for this prevalent metabolic disorder. Further research is warranted to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying these hormone actions and to explore their clinical implications for T2DM prevention and management.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruze R, Liu T, Zou X, Song J, Chen Y, Xu R, et al. Obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus: connections in epidemiology, pathogenesis, and treatments. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1161521. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1161521
Ogurtsova K, Guariguata L, Barengo NC, Ruiz PL-D, Sacre JW, Karuranga S, et al. IDF diabetes Atlas: global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults for 2021. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109118. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109118
Sun H, Saeedi P, Karuranga S, Pinkepank M, Ogurtsova K, Duncan BB, et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022;183:109119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2021.109119
Papatheodorou K, Papanas N, Banach M, Papazoglou D, Edmonds M. Complications of diabetes 2016. Hindawi. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6989453
Chan JC, Malik V, Jia W, Kadowaki T, Yajnik CS, Yoon K-H, et al. Diabetes in Asia: epidemiology, risk factors, and pathophysiology. JAMA. 2009;301(20):2129–40. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2009.726
Mozaffarian D. Dietary and policy priorities for cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and obesity: a comprehensive review. Circulation. 2016;133(2):187–225. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018585
Geary N. Endocrine controls of eating: CCK, leptin, and ghrelin. Physiol Behav. 2004;81(5):719–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.04.013
Churm R, Davies J, Stephens J, Prior S. Ghrelin function in human obesity and type 2 diabetes: a concise review. Obes Rev. 2017;18(2):140–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12474
Poykko SM, Kellokoski E, Horkko S, Kauma H, Kesaniemi YA, Ukkola O. Low plasma ghrelin is associated with insulin resistance, hypertension, and the prevalence of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2003;52(10):2546–53. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.10.2546
Katsiki N, Mikhailidis DP, Banach M. Leptin, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2018;39(7):1176–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2018.40
Münzberg H, Björnholm M, Bates S, Myers M. Leptin receptor action and mechanisms of leptin resistance. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005;62:642–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4432-1
Gruzdeva O, Borodkina D, Uchasova E, Dyleva Y, Barbarash O. Leptin resistance: underlying mechanisms and diagnosis. Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome Obesity: Targets Therapy. 2019:191–8. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S182406
Bouloumié A, Drexler HC, Lafontan M, Busse R. Leptin, the product of ob gene, promotes angiogenesis. Circul Res. 1998;83(10):1059–66. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.83.10.1059
Myers MG, Cowley MA, Münzberg H. Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2008;70:537–56. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.physiol.70.113006.100707
Robertson SA, Leinninger GM, Myers MG Jr. Molecular and neural mediators of leptin action. Physiol Behav. 2008;94(5):637–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.04.005
Obradovic M, Sudar-Milovanovic E, Soskic S, Essack M, Arya S, Stewart AJ, et al. Leptin and obesity: role and clinical implication. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:585887. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.585887
Sanchez-Margalet V, Martin-Romero C. Human leptin signaling in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: activation of the JAK-STAT pathway. Cell Immunol. 2001;211(1):30–6. https://doi.org/10.1006/cimm.2001.1815
St-Pierre J, Tremblay ML. Modulation of leptin resistance by protein tyrosine phosphatases. Cell Metabol. 2012;15(3):292–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2012.02.004
Amitani M, Asakawa A, Amitani H, Inui A. The role of leptin in the control of insulin-glucose axis. Front NeuroSci. 2013;7:51. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00051
Münzberg H, Morrison CD. Structure, production and signaling of leptin. Metabolism. 2015;64(1):13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2014.09.010
Saxton RA, Caveney NA, Moya-Garzon MD, Householder KD, Rodriguez GE, Burdsall KA, et al. Structural insights into the mechanism of leptin receptor activation. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):1797. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37169-6
Morris DL, Rui L. Recent advances in understanding leptin signaling and leptin resistance. Am J Physiology-Endocrinology Metabolism. 2009;297(6):E1247–59. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00274.2009
Morris A. Mechanisms of leptin resistance revealed. Nat Reviews Endocrinol. 2018;14(11):628. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-018-0091-4
Scarpace PJ, Zhang Y. Leptin resistance: a prediposing factor for diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. 2009;296(3):R493–500. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.90669.2008
Zhang Y, Scarpace PJ. The role of leptin in leptin resistance and obesity. Physiol Behav. 2006;88(3):249–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2006.05.038
Hosoi T, Sasaki M, Miyahara T, Hashimoto C, Matsuo S, Yoshii M, et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress induces leptin resistance. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;74(6):1610–9. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.108.050070
Tups A. Physiological models of leptin resistance. J Neuroendocrinol. 2009;21(11):961–71. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2009.01916.x
Wabitsch M, Funcke J-B, Lennerz B, Kuhnle-Krahl U, Lahr G, Debatin K-M, et al. Biologically inactive leptin and early-onset extreme obesity. N Engl J Med. 2015;372(1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1406653
Friedman J. Leptin at 20: an overview. J Endocrinol. 2014;223(1):T1–8. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-14-0405
Dietrich MO, Spuch C, Antequera D, Rodal I, de Yébenes JG, Molina JA, et al. Megalin mediates the transport of leptin across the blood-CSF barrier. Neurobiol Aging. 2008;29(6):902–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.01.008
Banks WA, Coon AB, Robinson SM, Moinuddin A, Shultz JM, Nakaoke R, et al. Triglycerides induce leptin resistance at the blood-brain barrier. Diabetes. 2004;53(5):1253–60. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.53.5.1253
Hsuchou H, Kastin AJ, Mishra PK, Pan W. C-reactive protein increases BBB permeability: implications for obesity and neuroinflammation. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2012;30(5):1109–19. https://doi.org/10.1159/000343302
Halaas JL, Gajiwala KS, Maffei M, Cohen SL, Chait BT, Rabinowitz D, et al. Weight-reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science. 1995;269(5223):543–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7624777
Chua SC Jr, Chung WK, Wu-Peng XS, Zhang Y, Liu S-M, Tartaglia L, et al. Phenotypes of mouse diabetes and rat fatty due to mutations in the OB (leptin) receptor. Science. 1996;271(5251):994–6. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.271.5251.994
Li Z, Zhou Y, Carter-Su C, Myers MG Jr, Rui L. SH2B1 enhances leptin signaling by both Janus kinase 2 Tyr813 phosphorylation-dependent and-independent mechanisms. Mol Endocrinol. 2007;21(9):2270–81. https://doi.org/10.1210/me.2007-0111
Baumann H, Morella KK, White DW, Dembski M, Bailon PS, Kim H et al. The full-length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 1996;93(16):8374-8. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.93.16.8374
Maffei á, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley R, Lee G, Zhang Y, et al. Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med. 1995;1(11):1155–61. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1195-1155
Halaas JL, Boozer C, Blair-West J, Fidahusein N, Denton DA, Friedman JM. Physiological response to long-term peripheral and central leptin infusion in lean and obese mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 1997;94(16):8878–83. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.16.8878
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(5):292–5. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199602013340503
Morrison CD. Leptin resistance and the response to positive energy balance. Physiol Behav. 2008;94(5):660–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2008.04.009
Stefan N, Vozarova B, Del Parigi A, Ossowski V, Thompson DB, Hanson R, et al. The Gln223Arg polymorphism of the leptin receptor in Pima indians: influence on energy expenditure, physical activity and lipid metabolism. Int J Obes. 2002;26(12):1629–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802161
Ravussin E, Pratley RE, Maffei M, Wang H, Friedman JM, Bennett PH, et al. Relatively low plasma leptin concentrations precede weight gain in Pima indians. Nat Med. 1997;3(2):238–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm0297-238
Münzberg H. Leptin-signaling pathways and leptin resistance. Front Eat Weight Regul. 2010;63:123–32. https://doi.org/10.1159/000264400
Mark AL. Selective leptin resistance revisited. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;305(6):R566–81. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00180.2013
Knight ZA, Hannan KS, Greenberg ML, Friedman JM. Hyperleptinemia is required for the development of leptin resistance. PLoS ONE. 2010;5(6):e11376. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0011376
Shapiro A, Tümer N, Gao Y, Cheng K-Y, Scarpace PJ. Prevention and reversal of diet-induced leptin resistance with a sugar-free diet despite high fat content. Br J Nutr. 2011;106(3):390–7. https://doi.org/10.1017/S000711451100033X
Haring SJ, Harris RB. The relation between dietary fructose, dietary fat and leptin responsiveness in rats. Physiol Behav. 2011;104(5):914–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.05.032
Shapiro A, Mu W, Roncal C, Cheng K-Y, Johnson RJ, Scarpace PJ. Fructose-induced leptin resistance exacerbates weight gain in response to subsequent high-fat feeding. Am J physiology-regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. 2008;295(5):R1370–5. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00195.2008
Dekker MJ, Su Q, Baker C, Rutledge AC, Adeli K. Fructose: a highly lipogenic nutrient implicated in insulin resistance, hepatic steatosis, and the metabolic syndrome. Am J Physiology-Endocrinology Metabolism. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00283.2010
Spezani R, da Silva RR, Martins FF, de Souza Marinho T, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA. Intermittent fasting, adipokines, insulin sensitivity, and hypothalamic neuropeptides in a dietary overload with high-fat or high-fructose diet in mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2020;83:108419. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jnutbio.2020.108419
Moonishaa TM, Nanda SK, Shamraj M, Sivaa R, Sivakumar P, Ravichandran K. Evaluation of leptin as a marker of insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Appl Basic Med Res. 2017;7(3):176. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijabmr.IJABMR_278_16
Pérez-Pérez A, Sánchez-Jiménez F, Vilariño-García T, Sánchez-Margalet V. Role of leptin in inflammation and vice versa. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5887. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21165887
Poetsch MS, Strano A, Guan K. Role of leptin in cardiovascular diseases. Front Endocrinol. 2020;11:354. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2020.00354
Friedman JM. Leptin and the endocrine control of energy balance. Nat Metabolism. 2019;1(8):754–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-019-0095-y
Date Y, Nakazato M, Hashiguchi S, Dezaki K, Mondal MS, Hosoda H, et al. Ghrelin is present in pancreatic α-cells of humans and rats and stimulates insulin secretion. Diabetes. 2002;51(1):124–9. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.51.1.124
De La Cour CD, Björkqvist M, Sandvik A, Bakke I, Zhao C-M, Chen D, et al. A-like cells in the rat stomach contain ghrelin and do not operate under gastrin control. Regul Pept. 2001;99(2–3):141–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-0115(01)00243-9
Nunez-Salces M, Li H, Feinle‐Bisset C, Young RL, Page AJ. The regulation of gastric ghrelin secretion. Acta Physiol. 2021;231(3):e13588. https://doi.org/10.1111/apha.13588
Seim I, Herington AC, Chopin LK. New insights into the molecular complexity of the ghrelin gene locus. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009;20(4):297–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.07.006
Gahete MD, Rincon-Fernandez D, Villa-Osaba A, Hormaechea-Agulla D, Ibanez-Costa A, Martinez-Fuentes AJ, et al. Ghrelin gene products, receptors, and GOAT enzyme: biological and pathophysiological insight. J Endocrinol. 2014;220(1):R1–24. https://doi.org/10.1530/JOE-13-0391
Perelló-Amorós M, Vélez EJ, Vela-Albesa J, Sánchez-Moya A, Riera-Heredia N, Hedén I, et al. Ghrelin and its receptors in gilthead sea bream: nutritional regulation. Front Endocrinol. 2018;9:399. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00399
Davenport AP, Bonner TI, Foord SM, Harmar AJ, Neubig RR, Pin J-P, et al. International union of pharmacology. LVI. Ghrelin receptor nomenclature, distribution, and function. Pharmacol Rev. 2005;57(4):541–6. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.57.4.1
Hosoda H, Kojima M, Mizushima T, Shimizu S, Kangawa K. Structural divergence of human ghrelin: identification of multiple ghrelin-derived molecules produced by post-translational processing. J Biol Chem. 2003;278(1):64–70. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M205366200
Smith JM, Maas JA, Garnsworthy PC, Owen MR, Coombes S, Pillay TS, et al. Mathematical modeling of glucose homeostasis and its relationship with energy balance and body fat. Obesity. 2009;17(4):632. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2008.604
Wiedmer P, Nogueiras R, Broglio F, D’alessio D, Tschöp MH. Ghrelin, obesity and diabetes. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007;3(10):705–12. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpendmet0625
Camina J. Cell biology of the ghrelin receptor. J Neuroendocrinol. 2006;18(1):65–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2005.01379.x
Nogueiras R, Perez-Tilve D, Wortley K, Tschop M. Growth hormone secretagogue (ghrelin-) receptors-a complex drug target for the regulation of body weight. CNS Neurol Disorders-Drug Targets (Formerly Curr Drug Targets-CNS Neurol Disorders). 2006;5(3):335–43. https://doi.org/10.2174/187152706777452227
Date Y, Murakami N, Toshinai K, Matsukura S, Niijima A, Matsuo H, et al. The role of the gastric afferent vagal nerve in ghrelin-induced feeding and growth hormone secretion in rats. Gastroenterology. 2002;123(4):1120–8. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2002.35954
Dalvi PS, Nazarians-Armavil A, Purser MJ, Belsham DD. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, exendin-4, regulates feeding-associated neuropeptides in hypothalamic neurons in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology. 2012;153(5):2208–22. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2011-1795
Wang L, Saint-Pierre DH, Taché Y. Peripheral ghrelin selectively increases Fos expression in neuropeptide Y–synthesizing neurons in mouse hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Neurosci Lett. 2002;325(1):47–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-3940(02)00241-0
Williams G, Harrold JA, Cutler DJ. The hypothalamus and the regulation of energy homeostasis: lifting the lid on a black box. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society. 2000;59(3):385–96. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0029665100000434
Yanagi S, Sato T, Kangawa K, Nakazato M. The homeostatic force of ghrelin. Cell Metabol. 2018;27(4):786–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.02.008
Gruzman A, Babai G, Sasson S. Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) as a new target for antidiabetic drugs: a review on metabolic, pharmacological and chemical considerations. Rev Diabet Studies: RDS. 2009;6(1):13. https://doi.org/10.1900/RDS.2009.6.13
Wang B, Cheng KK-Y. Hypothalamic AMPK as a mediator of hormonal regulation of energy balance. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19(11):3552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113552
Lopez M, Nogueiras R, Tena-Sempere M, Dieguez C. Hypothalamic AMPK: a canonical regulator of whole-body energy balance. Nat Reviews Endocrinol. 2016;12(7):421–32. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrendo.2016.67
López M, Lage R, Saha AK, Pérez-Tilve D, Vázquez MJ, Varela L, et al. Hypothalamic fatty acid metabolism mediates the orexigenic action of ghrelin. Cell Metabol. 2008;7(5):389–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2008.03.006
Perelló M, Cornejo MP, De Francesco PN, Fernandez G, Gautron L, Valdivia LS. The controversial role of the vagus nerve in mediating ghrelin’s actions: gut feelings and beyond. IBRO Neurosci Rep. 2022;12:228–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibneur.2022.03.003
Perello M, Dickson S. Ghrelin signalling on food reward: a salient link between the gut and the mesolimbic system. J Neuroendocrinol. 2015;27(6):424–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/jne.12236
Davis EA, Wald HS, Suarez AN, Zubcevic J, Liu CM, Cortella AM, et al. Ghrelin signaling affects feeding behavior, metabolism, and memory through the vagus nerve. Curr Biol. 2020;30(22):4510–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2020.08.069
Veedfald S, Plamboeck A, Hartmann B, Vilsbøll T, Knop F, Deacon C, et al. Ghrelin secretion in humans–a role for the vagus nerve? Neurogastroenterology Motil. 2018;30(6):e13295. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.13295
Sovetkina A, Nadir R, Fung JNM, Nadjarpour A, Beddoe B. The physiological role of ghrelin in the regulation of energy and glucose homeostasis. Cureus. 2020;12(5). https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.7941
Nogueiras R. MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: the gut–brain axis: regulating energy balance independent of food intake. Eur J Endocrinol. 2021;185(3):R75–91. https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-21-0277
Sato T, Ida T, Nakamura Y, Shiimura Y, Kangawa K, Kojima M. Physiological roles of ghrelin on obesity. Obes Res Clin Pract. 2014;8(5):e405–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2013.10.002
Stengel A, Goebel M, Wang L, Taché Y. Ghrelin, Des-acyl ghrelin and nesfatin-1 in gastric X/A-like cells: role as regulators of food intake and body weight. Peptides. 2010;31(2):357–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2009.11.019
Schalla MA, Stengel A. Pharmacological modulation of ghrelin to induce weight loss: successes and challenges. Curr Diab Rep. 2019;19:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11892-019-1211-9
Schüssler P, Kluge M, Yassouridis A, Dresler M, Uhr M, Steiger A. Ghrelin levels increase after pictures showing food. Obesity. 2012;20(6):1212–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2011.385
Drazen DL, Vahl TP, D’Alessio DA, Seeley RJ, Woods SC. Effects of a fixed meal pattern on ghrelin secretion: evidence for a learned response independent of nutrient status. Endocrinology. 2006;147(1):23–30. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2005-0973
Zigman JM, Nakano Y, Coppari R, Balthasar N, Marcus JN, Lee CE, et al. Mice lacking ghrelin receptors resist the development of diet-induced obesity. J Clin Investig. 2005;115(12):3564–72. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI26002
McFarlane MR, Brown MS, Goldstein JL, Zhao T-J. Induced ablation of ghrelin cells in adult mice does not decrease food intake, body weight, or response to high-fat diet. Cell Metabol. 2014;20(1):54–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2014.04.007
Briggs DI, Lockie SH, Wu Q, Lemus MB, Stark R, Andrews ZB. Calorie-restricted weight loss reverses high-fat diet-induced ghrelin resistance, which contributes to rebound weight gain in a ghrelin-dependent manner. Endocrinology. 2013;154(2):709–17. https://doi.org/10.1210/en.2012-1421
Uchida A, Zigman JM, Perelló M. Ghrelin and eating behavior: evidence and insights from genetically-modified mouse models. Front NeuroSci. 2013;7:121. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2013.00121
Charbonneau VR. Validation of FHH-GhsrM1Mcwi GHSR KO rat as a model to study ghrelin biology. Carleton University; 2012. https://doi.org/10.22215/etd/2012-06893
Delhanty P, van der Lely A-J. Ghrelin and glucose homeostasis. Peptides. 2011;32(11):2309–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2011.03.001
Heijboer A, Pijl H, Van den Hoek AM, Havekes L, Romijn J, Corssmit E. Gut–brain axis: regulation of glucose metabolism. J Neuroendocrinol. 2006;18(12):883–94. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2826.2006.01492.x
Nikolopoulos D, Theocharis S, Kouraklis G. Ghrelin’s role on gastrointestinal tract cancer. Surg Oncol. 2010;19(1):e2–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suronc.2009.02.011
Airapetov MI, Eresko SO, Lebedev AA, Bychkov ER, Shabanov PD. Expression of the growth hormone secretagogue receptor 1a (GHS-R1a) in the brain. Physiological Rep. 2021;9(21):e15113. https://doi.org/10.14814/phy2.15113
Landgren S, Engel JA, Hyytiä P, Zetterberg H, Blennow K, Jerlhag E. Expression of the gene encoding the ghrelin receptor in rats selected for differential alcohol preference. Behav Brain Res. 2011;221(1):182–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.03.003
Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, Morris DG, McGee P, Fairclough P, et al. The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metabolism. 2002;87(6):2988–91. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.87.6.8739
Sakata I, Park W-M, Walker AK, Piper PK, Chuang J-C, Osborne-Lawrence S, et al. Glucose-mediated control of ghrelin release from primary cultures of gastric mucosal cells. Am J Physiology-Endocrinology Metabolism. 2012;302(10):E1300–10. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpendo.00041.2012
Shankar K, Takemi S, Gupta D, Varshney S, Mani BK, Osborne-Lawrence S, et al. Ghrelin cell–expressed insulin receptors mediate meal-and obesity-induced declines in plasma ghrelin. JCI Insight. 2021;6(18). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.146983
UK Hypoglycemia Study Group. Risk of hypoglycaemia in types 1 and 2 diabetes: effects of treatment modalities and their duration. Diabetologia. 2007;50:1140–7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0599-y
Shankar K, Gupta D, Mani BK, Findley BG, Lord CC, Osborne-Lawrence S, et al. Acyl-ghrelin is permissive for the normal counterregulatory response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Diabetes. 2020;69(2):228–37. https://doi.org/10.2337/db19-0438
Shankar K, Varshney S, Gupta D, Mani BK, Osborne-Lawrence S, Metzger NP, et al. Ghrelin does not impact the blunted counterregulatory response to recurrent hypoglycemia in mice. Front Endocrinol. 2023;14:1181856. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2023.1181856
Ukkola O. Ghrelin and metabolic disorders. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2009;10(1):2–7. https://doi.org/10.2174/138920309787315220
Poher A-L, Tschöp MH, Müller TD. Ghrelin regulation of glucose metabolism. Peptides. 2018;100:236–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2017.12.015
Kohno D, Gao H-Z, Muroya S, Kikuyama S, Yada T. Ghrelin directly interacts with neuropeptide-Y-containing neurons in the rat arcuate nucleus: Ca2 + signaling via protein kinase A and N-type channel-dependent mechanisms and cross-talk with leptin and orexin. Diabetes. 2003;52(4):948–56. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.4.948
Vohra MS, Benchoula K, Serpell CJ, Hwa WE. AgRP/NPY and POMC neurons in the arcuate nucleus and their potential role in treatment of obesity. Eur J Pharmacol. 2022;915:174611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174611
Kalra S, Kalra P. NPY and cohorts in regulating appetite, obesity and metabolic syndrome: beneficial effects of gene therapy. Neuropeptides. 2004;38(4):201–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.npep.2004.06.003
Barb C, Hausman G, Lents C. Energy metabolism and leptin: effects on neuroendocrine regulation of reproduction in the gilt and sow. Reprod Domest Anim. 2008;43:324–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0531.2008.01173.x
Le N, Sayers S, Mata-Pacheco V, Wagner EJ. The PACAP paradox: dynamic and surprisingly pleiotropic actions in the central regulation of energy homeostasis. Front Endocrinol. 2022;13:877647. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2022.877647
Xu Y, Jiang Z, Li H, Cai J, Jiang Y, Otiz-Guzman J, et al. Lateral septum as a melanocortin downstream site in obesity development. Cell Rep. 2023;42(5). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112502
Kalra SP, Bagnasco M, Otukonyong EE, Dube MG, Kalra PS. Rhythmic, reciprocal ghrelin and leptin signaling: new insight in the development of obesity. Regul Pept. 2003;111(1–3):1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0167-0115(02)00305-1
Ahmadian-Moghadam H, Sadat-Shirazi M-S, Zarrindast M-R. Cocaine-and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART): a multifaceted neuropeptide. Peptides. 2018;110:56–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2018.10.008
Baltatzi M, Hatzitolios A, Tziomalos K, Iliadis F, Zamboulis C. Neuropeptide Y and alpha-melanocyte‐stimulating hormone: interaction in obesity and possible role in the development of hypertension. Int J Clin Pract. 2008;62(9):1432–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1742-1241.2008.01823.x
Kalra SP, Ueno N, Kalra PS. Stimulation of appetite by ghrelin is regulated by leptin restraint: peripheral and central sites of action. J Nutr. 2005;135(5):1331–5. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/135.5.1331
Sutton AK, Myers MG Jr, Olson DP. The role of PVH circuits in leptin action and energy balance. Annu Rev Physiol. 2016;78:207–21. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021115-105347
Zhang S, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Li C, Jiang H. Expression of ghrelin and leptin during the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a rat model. Mol Med Rep. 2013;7(1):223–8. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.1154
Ukkola O, Pöykkö S, Päivänsalo M, Kesäniemi YA. Interactions between ghrelin, leptin and IGF-I affect metabolic syndrome and early atherosclerosis. Ann Med. 2008;40(6):465–73. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890802084860
Serra-Prat M, Alfaro SR, Palomera E, Casamitjana R, Buquet X, Fernández‐Fernández C, et al. Relationship between ghrelin and the metabolic syndrome in the elderly: a longitudinal population‐based study. Clin Endocrinol. 2009;70(2):227–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2265.2008.03307.x
Sharifi F, Yamini M, Esmaeilzadeh A, Mousavinasab N, Shajari Z. Acylated ghrelin and leptin concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, people with prediabetes and first degree relatives of patients with diabetes, a comparative study. J Diabetes Metabolic Disorders. 2013;12:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1186/2251-6581-12-51
Mantzoros CS, Flier JS, Rogol AD. A longitudinal assessment of hormonal and physical alterations during normal puberty in boys. V. rising leptin levels may signal the onset of puberty. J Clin Endocrinol Metabolism. 1997;82(4):1066–70. https://doi.org/10.1210/jcem.82.4.3878
Lord GM, Matarese G, Howard JK, Baker RJ, Bloom SR, Lechler RI. Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature. 1998;394(6696):897–901. https://doi.org/10.1038/29795
Fantuzzi G, Faggioni R. Leptin in the regulation of immunity, inflammation, and hematopoiesis. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;68(4):437–46.
Jequier E. Leptin signaling, adiposity, and energy balance. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002;967(1):379–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1749-6632.2002.tb04293.x
Picó C, Palou M. Leptin and metabolic programming. MDPI; 2021. p. 114. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14010114
Mendoza-Herrera K, Florio AA, Moore M, Marrero A, Tamez M, Bhupathiraju SN, et al. The leptin system and diet: a mini review of the current evidence. Front Endocrinol. 2021;12:749050. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.749050
Cinti S, de Matteis R, Ceresi E, Pico C, Oliver J, Oliver P, et al. Leptin in the human stomach. Gut. 2001;49(1):155. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.49.1.155
Friedman J. The long road to leptin. J Clin Investig. 2016;126(12):4727–34. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI91578
Blüher S, Mantzoros CS. Leptin in humans: lessons from translational research. Am J Clin Nutr. 2009;89(3):S991–7. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.26788E
Rayner DV, Trayhurn P. Regulation of leptin production: sympathetic nervous system interactions. J Mol Med. 2001;79:8–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s001090100198
Hausman GJ, Barb CR, Lents CA. Leptin and reproductive function. Biochimie. 2012;94(10):2075–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biochi.2012.02.022
Chan JL, Mantzoros CS. Role of leptin in energy-deprivation states: normal human physiology and clinical implications for hypothalamic amenorrhoea and anorexia nervosa. Lancet. 2005;366(9479):74–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(05)66830-4
Allaway HC, Southmayd EA, De Souza MJ. The physiology of functional hypothalamic amenorrhea associated with energy deficiency in exercising women and in women with anorexia nervosa. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig. 2016;25(2):91–119. https://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2015-0053
Tschöp M, Smiley DL, Heiman ML. Ghrelin induces adiposity in rodents. Nature. 2000;407(6806):908–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/35038090
Benelam B. Satiation, satiety and their effects on eating behaviour. Nutr Bull. 2009;34(2):126–73. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-3010.2009.01753.x
Brown SD, Duncan J, Crabtree D, Powell D, Hudson M, Allan JL. We are what we (think we) eat: the effect of expected satiety on subsequent calorie consumption. Appetite. 2020;152:104717. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2020.104717
Howick K, Griffin BT, Cryan JF, Schellekens H. From belly to brain: targeting the ghrelin receptor in appetite and food intake regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(2):273. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020273
Asakawa A, Inui A, Kaga O, Yuzuriha H, Nagata T, Ueno N, et al. Ghrelin is an appetite-stimulatory signal from stomach with structural resemblance to motilin. Gastroenterology. 2001;120(2):337–45. https://doi.org/10.1053/gast.2001.22158
Lv Y, Liang T, Wang G, Li Z. Ghrelin, a gastrointestinal hormone, regulates energy balance and lipid metabolism. Biosci Rep. 2018;38(5):BSR20181061. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20181061
Zigman JM, Bouret SG, Andrews ZB. Obesity impairs the action of the neuroendocrine ghrelin system. Trends Endocrinol Metabolism. 2016;27(1):54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2015.09.010
Crujeiras A, Díaz-Lagares A, Abete I, Goyenechea E, Amil M, Martínez J, et al. Pre-treatment circulating leptin/ghrelin ratio as a non-invasive marker to identify patients likely to regain the lost weight after an energy restriction treatment. J Endocrinol Investig. 2014;37:119–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40618-013-0004-2
Labayen I, Ortega FB, Ruiz JR, Lasa A, Simon E, Margareto J. Role of baseline leptin and ghrelin levels on body weight and fat mass changes after an energy-restricted diet intervention in obese women: effects on energy metabolism. J Clin Endocrinol Metabolism. 2011;96(6):E996–1000. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-3006
Adamska-Patruno E, Ostrowska L, Goscik J, Pietraszewska B, Kretowski A, Gorska M. The relationship between the leptin/ghrelin ratio and meals with various macronutrient contents in men with different nutritional status: a randomized crossover study. Nutr J. 2018;17(1):1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12937-018-0427-x
Kalra SP, Kalra PS. Gene-transfer technology: a preventive neurotherapy to curb obesity, ameliorate metabolic syndrome and extend life expectancy. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2005;26(10):488–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2005.08.008
Wang Y, Asakawa A, Inui A, Kosai K-i. Leptin gene therapy in the fight against diabetes. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2010;10(10):1405–14. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2010.512286
Wang M-y, Chen L, Clark GO, Lee Y, Stevens RD, Ilkayeva OR et al. Leptin therapy in insulin-deficient type I diabetes. Proceedings of the national academy of Sciences. 2010;107(11):4813-9. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0909422107
Denroche HC, Levi J, Wideman RD, Sequeira RM, Huynh FK, Covey SD, et al. Leptin therapy reverses hyperglycemia in mice with streptozotocin-induced diabetes, independent of hepatic leptin signaling. Diabetes. 2011;60(5):1414–23. https://doi.org/10.2337/db10-0958
Müller TD, Blüher M, Tschöp MH, DiMarchi RD. Anti-obesity drug discovery: advances and challenges. Nat Rev Drug Discovery. 2022;21(3):201–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-021-00337-8
Altabas V, Zjačić-Rotkvić V. Anti-ghrelin antibodies in appetite suppression: recent advances in obesity pharmacotherapy. ImmunoTargets Therapy. 2015:123–30. https://doi.org/10.2147/ITT.S60398
Iyer MR, Wood CM, Kunos G. Recent progress in the discovery of ghrelin O-acyltransferase (GOAT) inhibitors. RSC Med Chem. 2020;11(10):1136–44. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0md00210k
Mosa R, Huang L, Li H, Grist M, LeRoith D, Chen C. Long-term treatment with the ghrelin receptor antagonist [d-Lys3]-GHRP-6 does not improve glucose homeostasis in nonobese diabetic MKR mice. Am J Physiology-Regulatory Integr Comp Physiol. 2018;314(1):R71–83. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00157.2017
Walker A, Rivera P, Wang Q, Chuang J, Tran S, Osborne-Lawrence S, et al. The P7C3 class of neuroprotective compounds exerts antidepressant efficacy in mice by increasing hippocampal neurogenesis. Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20(4):500–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2014.34
Buntwal L, Sassi M, Morgan AH, Andrews ZB, Davies JS. Ghrelin-mediated hippocampal neurogenesis: implications for health and disease. Trends Endocrinol Metabolism. 2019;30(11):844–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tem.2019.07.001
Hornsby AK, Redhead YT, Rees DJ, Ratcliff MS, Reichenbach A, Wells T, et al. Short-term calorie restriction enhances adult hippocampal neurogenesis and remote fear memory in a ghsr-dependent manner. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2016;63:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2015.09.023
Rouach V, Bloch M, Rosenberg N, Gilad S, Limor R, Stern N, et al. The acute ghrelin response to a psychological stress challenge does not predict the post-stress urge to eat. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2007;32(6):693–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psyneuen.2007.04.010
Raspopow K, Abizaid A, Matheson K, Anisman H. Anticipation of a psychosocial stressor differentially influences ghrelin, cortisol and food intake among emotional and non-emotional eaters. Appetite. 2014;74:35–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appet.2013.11.018
Yousufzai MIA, Harmatz ES, Shah M, Malik MO, Goosens KA. Ghrelin is a persistent biomarker for chronic stress exposure in adolescent rats and humans. Translational Psychiatry. 2018;8(1):74. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-018-0135-5
Stone LA, Harmatz ES, Goosens KA. Ghrelin as a stress hormone: implications for psychiatric illness. Biol Psychiatry. 2020;88(7):531–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.05.013
Kuliczkowska-Płaksej J, Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska A, Zembska A, Kolačkov K, Syrycka J, Kałużny M, et al. Ghrelin and leptin concentrations in patients after SARS-CoV2 infection. J Clin Med. 2023;12(10):3551. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12103551
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank JSS Academy of Higher Education & Research for providing support and facilities.
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Vijayashankar, U., Ramashetty, R., Rajeshekara, M. et al. Leptin and ghrelin dynamics: unraveling their influence on food intake, energy balance, and the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Diabetes Metab Disord 23, 427–440 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-024-01418-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40200-024-01418-2