Abstract
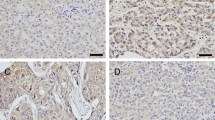
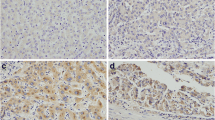
The small GTPase Rab17 is a member of the Rab family and plays a critical role in the regulation of membrane trafficking polarized eukaryotic cells. However, the role of Rab17 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is not clear. In the present study, we investigated the role of Rab17 in HCC tumourgenesis. The expressions of Rab17 in non-tumour hepatic tissues and HCCs were detected via immunohistochemistry. Rab17 was found in 31 of 48 (64.6 %) and in 23 of 62 (37.1 %) of non-tumour hepatic tissue samples and HCCs (P = 0.0068), respectively, and there were significant correlations between Rab17 reductions and unfavourable variables including tumour size (P = 0.0171), differentiation level (P = 0.0126), and lymph nodal (P = 0.0044) and distant metastases (P = 0.0047). To elucidate the role of Rab17 in HCC, we generated two Rab17-overexpressing HCC cell lines. Rab17 overexpression significantly inhibited the tumourigenic properties of HCC cells in vitro and in vivo as demonstrated by reduced cell proliferation and migration, elevated G1 arrest, and decreased tumour xenograft growth. However, the attenuated tumourigenic properties of the HCC cells that were induced by Rab17 overexpression were significantly rescued by the activator of the Erk pathway EGF, which indicates that the Erk pathway plays a critical role in the Rab17 up-regulation-induced reduced tumourigenic properties of HCC cells. Rab17 might act as a tumour suppressor gene in HCCs, and the anti-tumour effects of Rab17 might be partially mediated by the Erk pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berasain C, Perugorria MJ, Latasa MU, Castillo J, Goni S, Santamaria M, et al. The epidermal growth factor receptor: a link between inflammation and liver cancer. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009;234:713–25.
Sherman M. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, risk factors, and screening. Semin Liver Dis. 2005;25:143–54.
El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:2557–76.
Kremsdorf D, Soussan P, Paterlini-Brechot P, Brechot C. Hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: paradigms for viral-related human carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2006;25:3823–33.
Lupberger J, Hildt E. Hepatitis B virus-induced oncogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:74–81.
Friedman SL. Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2008;134:1655–69.
Markiewski MM, DeAngelis RA, Lambris JD. Liver inflammation and regeneration: two distinct biological phenomena or parallel pathophysiologic processes? Mol Immunol. 2006;43:45–56.
Bruix J, Sherman M. Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2005;42:1208–36.
Llovet JM, Burroughs A, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2003;362:1907–17.
Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves survival. Hepatology. 2003;37:429–42.
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–90.
Agarwal R, Jurisica I, Mills GB, Cheng KW. The emerging role of the rab25 small gtpase in cancer. Traffic. 2009;10:1561–8.
Cheng KW, Lahad JP, Gray JW, Mills GB. Emerging role of rab gtpases in cancer and human disease. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2516–9.
Mitra S, Cheng KW, Mills GB. Rab25 in cancer: a brief update. Biochem Soc Trans. 2012;40:1404–8.
Liu YJ, Wang Q, Li W, Huang XH, Zhen MC, Huang SH, et al. Rab23 is a potential biological target for treating hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:1010–7.
McMurtrie EB, Barbosa MD, Zerial M, Kingsmore SF. Rab17 and rab18, small gtpases with specificity for polarized epithelial cells: genetic mapping in the mouse. Genomics. 1997;45:623–5.
Lutcke A, Jansson S, Parton RG, Chavrier P, Valencia A, Huber LA, et al. Rab17, a novel small gtpase, is specific for epithelial cells and is induced during cell polarization. J Cell Biol. 1993;121:553–64.
Mori Y, Matsui T, Furutani Y, Yoshihara Y, Fukuda M. Small gtpase rab17 regulates dendritic morphogenesis and postsynaptic development of hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem. 2012;287:8963–73.
von Thun A, Birtwistle M, Kalna G, Grindlay J, Strachan D, Kolch W, et al. Erk2 drives tumour cell migration in three-dimensional microenvironments by suppressing expression of rab17 and liprin-beta2. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:1465–77.
Datta J, Majumder S, Kutay H, Motiwala T, Frankel W, Costa R, et al. Metallothionein expression is suppressed in primary human hepatocellular carcinomas and is mediated through inactivation of ccaat/enhancer binding protein alpha by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling cascade. Cancer Res. 2007;67:2736–46.
Zhang M, Zhang X, Bai CX, Chen J, Wei MQ. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor expression by rna interference in a549 cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2004;25:61–7.
Marrero JA. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 2005;21:308–12.
Espelt MV, Croci DO, Bacigalupo ML, Carabias P, Manzi M, Elola MT, et al. Novel roles of galectin-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell adhesion, polarization, and in vivo tumor growth. Hepatology. 2011;53:2097–106.
Dong WW, Mou Q, Chen J, Cui JT, Li WM, Xiao WH. Differential expression of rab27a/b correlates with clinical outcome in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:1806–13.
You X, Liu F, Zhang T, Li Y, Ye L, Zhang X. Hepatitis B virus x protein upregulates oncogene rab18 to result in the dysregulation of lipogenesis and proliferation of hepatoma cells. Carcinogenesis. 2013;34:1644–52.
Cao C, Lu C, Xu J, Zhang J, Zhang J, Li M. Expression of rab25 correlates with the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer. Chin J Cancer Res. 2013;25:192–9.
Jean S, Kiger AA. Coordination between rab gtpase and phosphoinositide regulation and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:463–70.
Cheng KW, Lahad JP, Kuo WL, Lapuk A, Yamada K, Auersperg N, et al. The rab25 small gtpase determines aggressiveness of ovarian and breast cancers. Nat Med. 2004;10:1251–6.
Caswell PT, Spence HJ, Parsons M, White DP, Clark K, Cheng KW, et al. Rab25 associates with alpha5beta1 integrin to promote invasive migration in 3d microenvironments. Dev Cell. 2007;13:496–510.
Dozynkiewicz MA, Jamieson NB, Macpherson I, Grindlay J, van den Berghe PV, von Thun A, et al. Rab25 and clic3 collaborate to promote integrin recycling from late endosomes/lysosomes and drive cancer progression. Dev Cell. 2012;22:131–45.
Nam KT, Lee HJ, Smith JJ, Lapierre LA, Kamath VP, Chen X, et al. Loss of rab25 promotes the development of intestinal neoplasia in mice and is associated with human colorectal adenocarcinomas. J Clin Invest. 2010;120:840–9.
Cheng JM, Volk L, Janaki DK, Vyakaranam S, Ran S, Rao KA. Tumor suppressor function of rab25 in triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2010;126:2799–812.
Tong M, Chan KW, Bao JY, Wong KY, Chen JN, Kwan PS, et al. Rab25 is a tumor suppressor gene with antiangiogenic and anti-invasive activities in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2012;72:6024–35.
Satoh Y, Endo S, Ikeda T, Yamada K, Ito M, Kuroki M, et al. Extracellular signal-regulated kinase 2 (erk2) knockdown mice show deficits in long-term memory; erk2 has a specific function in learning and memory. J Neurosci. 2007;27:10765–76.
Vantaggiato C, Formentini I, Bondanza A, Bonini C, Naldini L, Brambilla R. Erk1 and erk2 mitogen-activated protein kinases affect ras-dependent cell signaling differentially. J Biol. 2006;5:14.
Reddy KB, Nabha SM, Atanaskova N. Role of map kinase in tumor progression and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2003;22:395–403.
Ueoka Y, Kato K, Kuriaki Y, Horiuchi S, Terao Y, Nishida J, et al. Hepatocyte growth factor modulates motility and invasiveness of ovarian carcinomas via ras-mediated pathway. Br J Cancer. 2000;82:891–9.
Delcroix JD, Valletta JS, Wu C, Hunt SJ, Kowal AS, Mobley WC. Ngf signaling in sensory neurons: evidence that early endosomes carry ngf retrograde signals. Neuron. 2003;39:69–84.
Villanueva A, Hernandez-Gea V, Llovet JM. Medical therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma: a critical view of the evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;10:34–42.
De Minicis S, Marzioni M, Benedetti A, Svegliati-Baroni G. New insights in hepatocellular carcinoma: from bench to bedside. Ann Transl Med. 2013;1:15.
Gao Q, Shi Y, Wang X, Zhou J, Qiu S, Fan J. Translational medicine in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Med. 2012;6:122–33.
Lachance V, Angers S, Parent JL. New insights in the regulation of rab gtpases by g protein-coupled receptors. Small GTPases. 2014;5:e29039.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81270880) and the Chinese Ministry of Science and Technology (2009CB521902).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Kejia Wang and Zhujun Mao contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Mao, Z., Liu, L. et al. Rab17 inhibits the tumourigenic properties of hepatocellular carcinomas via the Erk pathway. Tumor Biol. 36, 5815–5824 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3251-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3251-3