Abstract
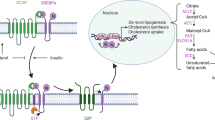
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1) is a known transcription factor of lipogenic genes, which plays important roles in regulating de novo lipogenesis. Accumulating evidences indicate SREBP1 is involved in tumorigenesis, yet its role in pancreatic cancer remains unclear. Here, we explored the expression characteristic and function of SREBP1 in pancreatic cancer. Analysis of 60 patients with pancreatic ducat cancer showed that SREBP1 level was significantly higher in pancreatic cancer than that in adjacent normal tissues. High expression of SREBP1 predicted poor prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer. Multivariate analysis revealed that SREBP1 was an independent factor affecting overall survival. SREBP1 silencing resulted in proliferation inhibition and induction of apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells. Mechanistically, lipogenic genes (acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), fatty acid synthase (FASN), and stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1)) and de novo lipogenesis were promoted by SREBP1. Inhibition of lipogenic genes through specific inhibitors ablated SREBP1-mediated growth regulation. Furthermore, depletion of SREBP1 could suppress lipid metabolism and tumor growth in vivo. Our results indicate that SREBP1 had important role in tumor progression and appears to be a novel prognostic marker for pancreatic cancer.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30. doi:10.3322/caac.21166.
Klapman J, Malafa MP. Early detection of pancreatic cancer: why, who, and how to screen. Cancer Control. 2008;15(4):280–7.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144(5):646–74. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.02.013.
Ward PS, Thompson CB. Metabolic reprogramming: a cancer hallmark even Warburg did not anticipate. Cancer Cell. 2012;21(3):297–308. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2012.02.014.
Tennant DA, Duran RV, Gottlieb E. Targeting metabolic transformation for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10(4):267–77. doi:10.1038/nrc2817.
Sun Y, Zhao X, Zhou Y, Hu Y. miR-124, miR-137 and miR-340 regulate colorectal cancer growth via inhibition of the Warburg effect. Oncol Rep. 2012;28(4):1346–52. doi:10.3892/or.2012.1958.
Sun Y, Zhao X, Luo M, Zhou Y, Ren W, Wu K, et al. The pro-apoptotic role of the regulatory feedback loop between miR-124 and PKM1/HNF4alpha in colorectal cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4318–32. doi:10.3390/ijms15034318.
Menendez JA, Lupu R. Fatty acid synthase and the lipogenic phenotype in cancer pathogenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7(10):763–77. doi:10.1038/nrc2222.
Walter K, Hong SM, Nyhan S, Canto M, Fedarko N, Klein A, et al. Serum fatty acid synthase as a marker of pancreatic neoplasia. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18(9):2380–5. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0144.
Zhao X, Feng D, Wang Q, Abdulla A, Xie XJ, Zhou J, et al. Regulation of lipogenesis by cyclin-dependent kinase 8-mediated control of SREBP-1. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(7):2417–27. doi:10.1172/JCI61462.
Freed-Pastor WA, Mizuno H, Zhao X, Langerod A, Moon SH, Rodriguez-Barrueco R, et al. Mutant p53 disrupts mammary tissue architecture via the mevalonate pathway. Cell. 2012;148(1–2):244–58. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.12.017.
Yang F, Vought BW, Satterlee JS, Walker AK, Jim Sun ZY, Watts JL, et al. An ARC/mediator subunit required for SREBP control of cholesterol and lipid homeostasis. Nature. 2006;442(7103):700–4. doi:10.1038/nature04942.
Walker AK, Jacobs RL, Watts JL, Rottiers V, Jiang K, Finnegan DM, et al. A conserved SREBP-1/phosphatidylcholine feedback circuit regulates lipogenesis in metazoans. Cell. 2011;147(4):840–52. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.09.045.
Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS. SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(9):1125–31. doi:10.1172/JCI15593.
Porstmann T, Santos CR, Griffiths B, Cully M, Wu M, Leevers S, et al. SREBP activity is regulated by mTORC1 and contributes to Akt-dependent cell growth. Cell Metab. 2008;8(3):224–36. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2008.07.007.
Guo D, Bell EH, Chakravarti A. Lipid metabolism emerges as a promising target for malignant glioma therapy. CNS Oncol. 2013;2(3):289–99. doi:10.2217/cns.13.20.
Huang WC, Li X, Liu J, Lin J, Chung LW. Activation of androgen receptor, lipogenesis, and oxidative stress converged by SREBP-1 is responsible for regulating growth and progression of prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 2012;10(1):133–42. doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-11-0206.
Ettinger SL, Sobel R, Whitmore TG, Akbari M, Bradley DR, Gleave ME, et al. Dysregulation of sterol response element-binding proteins and downstream effectors in prostate cancer during progression to androgen independence. Cancer Res. 2004;64(6):2212–21.
Li W, Tai Y, Zhou J, Gu W, Bai Z, Zhou T, et al. Repression of endometrial tumor growth by targeting SREBP1 and lipogenesis. Cell Cycle. 2012;11(12):2348–58. doi:10.4161/cc.20811.
Sun Y, Zhao X, Yao Y, Qi X, Yuan Y, Hu Y. Connexin 43 interacts with Bax to regulate apoptosis of pancreatic cancer through a gap junction-independent pathway. Int J Oncol. 2012;41(3):941–8. doi:10.3892/ijo.2012.1524.
Zhao X, Xiaoli, Zong H, Abdulla A, Yang ES, Ji JY, et al. Inhibition of SREBP transcriptional activity by a boron-containing compound improves lipid homeostasis in diet-induced obesity. Diabetes. 2014. doi:10.2337/db13-0835.
Griffiths B, Lewis CA, Bensaad K, Ros S, Zhang Q, Ferber EC, et al. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-dependent regulation of lipid synthesis supports cell survival and tumor growth. Cancer Metab. 2013;1(1):3. doi:10.1186/2049-3002-1-3.
Mashima T, Seimiya H, Tsuruo T. De novo fatty-acid synthesis and related pathways as molecular targets for cancer therapy. Br J Cancer. 2009;100(9):1369–72. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6605007.
Ameer F, Scandiuzzi L, Hasnain S, Kalbacher H, Zaidi N. De novo lipogenesis in health and disease. Metabolism. 2014;63(7):895–902. doi:10.1016/j.metabol.2014.04.003.
Calvisi DF, Wang C, Ho C, Ladu S, Lee SA, Mattu S, et al. Increased lipogenesis, induced by AKT-mTORC1-RPS6 signaling, promotes development of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2011;140(3):1071–83. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2010.12.006.
Yamashita T, Honda M, Takatori H, Nishino R, Minato H, Takamura H, et al. Activation of lipogenic pathway correlates with cell proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2009;50(1):100–10. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2008.07.036.
Israel M, Schwartz L. The metabolic advantage of tumor cells. Mol Cancer. 2011;10:70. doi:10.1186/1476-4598-10-70.
Swierczynski J, Hebanowska A, Sledzinski T. Role of abnormal lipid metabolism in development, progression, diagnosis and therapy of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(9):2279–303. doi:10.3748/wjg.v20.i9.2279.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by research grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81201532 and 81372195), Young Teacher Scientific Capability Promotion Project of Fudan University (No. 20520133490), Shanghai Pujiang Program (No. 13PJ1406000), Program for Professor of Special Appointment (Eastern Scholar) at Shanghai Institutions of Higher Learning (No. 1410000157),Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (No. 134119a5600) and Shanghai Municipal Commission of Health and Family Planning (XYQ2013109).
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yan Sun and Weiwei He contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., He, W., Luo, M. et al. SREBP1 regulates tumorigenesis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer through targeting lipid metabolism. Tumor Biol. 36, 4133–4141 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3047-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3047-5