Abstract
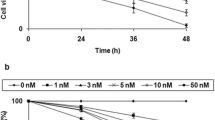
Mitochondrial GTPase mitofusin-2 gene (Mfn2) is a novel gene characterised as a cell proliferation inhibitor. Mfn2 protein over-expression, mediated by an adenovirus, has a significant anti-tumour effect in A548 and HT-29 cells. However, there is no report on the effect of Mfn2 on urinary bladder carcinoma (UBCC). In this study, we sought to investigate the function of Mfn2 in UBCC. Mfn2 expression in 36 paired UBCC samples was investigated by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analyses. An adenovirus encoding the complete Mfn2 open reading frame (Ad-Mfn2) was used to infect UBCC cells, and an adenoviral vector encoding green fluorescent protein (Ad-GFP) was used as a control. The effects of Mfn2 on cell-cycle distribution and apoptosis were assessed by flow cytometry and Western blot analyses. The Mfn2 protein showed significantly lower expression in UBCC tissues than nearby non-tumourous tissues. Ad-Mfn2 exhibited a significant anti-tumour effect in T24 and 5,637 cells. Mfn2 overexpression in T24 cells significantly inhibited cell proliferation, by arresting the transition of the cell cycle from the G1 to S phase, and induced apoptosis by upregulating active caspase-3 and cleaved PARP levels. Mfn2 also induced increased p21 and p27 expression levels, but down-regulated PCNA levels. These findings indicate that Mfn2 is a potential UBCC tumour suppressor gene, which showed significantly lower expression in tumour tissues than adjacent non-tumourous tissues and could promote apoptosis and inhibit the proliferation of UBCC cells. Mfn2 may become an important therapeutic target for treating UBCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin DM. The global burden of urinary bladder cancer. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 2008;218:12–20.
Stein JP, Grossfeld GD, Ginsberg DA, Esrig D, Freeman JA, Figueroa AJ, et al. Prognostic markers in bladder cancer: a contemporary review of the literature. J Urol. 1998;160(3 Pt 1):645–59.
Sanchez-Carbayo M. Recent advances in bladder cancer diagnostics. Clin Biochem. 2004;37(7):562–71.
Kausch I, Bohle A. Molecular aspects of bladder cancer III. Prognostic markers of bladder cancer. Eur Urol. 2002;41(1):15–29.
Dey P. Urinary markers of bladder carcinoma. Clin Chim Acta. 2004;340(1–2):57–65.
Chen G, Zhang C, Zhu Y. Cloning and expression of a novel gene related to hypertension. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 1997;77(11):823–8.
Chen KH, Guo X, Ma D, Guo Y, Li Q, Yang D, et al. Dysregulation of HSG triggers vascular proliferative disorders. Nat Cell Biol. 2004;6(9):872–83.
Karbowski M, Norris KL, Cleland MM, Jeong SY, Youle RJ. Role of Bax and Bak in mitochondrial morphogenesis. Nature. 2006;443(7112):658–62.
Karbowski M, Lee YJ, Gaume B, Jeong SY, Frank S, Nechushtan A, et al. Spatial and temporal association of Bax with mitochondrial fission sites, Drp1, and Mfn2 during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 2002;159(6):931–8.
Wu L, Li Z, Zhang Y, Zhang P, Zhu X, Huang J, et al. Adenovirus-expressed human hyperplasia suppressor gene induces apoptosis in cancer cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 2008;7(1):222–32.
Landman J, Chang Y, Kavaler E, Droller MJ, Liu BC. Sensitivity and specificity of NMP-22, telomerase, and BTA in the detection of human bladder cancer. Urology. 1998;52(3):398–402.
Schmetter BS, Habicht KK, Lamm DL, Morales A, Bander NH, Grossman HB, et al. A multicenter trial evaluation of the fibrin/fibrinogen degradation products test for detection and monitoring of bladder cancer. J Urol. 1997;158(3 Pt 1):801–5.
Bagchi A, Mills AA. The quest for the 1p36 tumor suppressor. Cancer Res. 2008;68(8):2551–6.
Steidl C, Simon R, Burger H, Brinkschmidt C, Hertle L, Bocker W, et al. Patterns of chromosomal aberrations in urinary bladder tumours and adjacent urothelium. J Pathol. 2002;198(1):115–20.
Matsumoto H, Matsuyama H, Fukunaga K, Yoshihiro S, Wada T, Naito K. Allelic imbalance at 1p36 may predict prognosis of chemoradiation therapy for bladder preservation in patients with invasive bladder cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;91(6):1025–31.
Guo Y, Xiao P, Lei S, Deng F, Xiao GG, Liu Y, et al. How is mRNA expression predictive for protein expression? A correlation study on human circulating monocytes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2008;40(5):426–36.
Teng J, Wang ZY, Jarrard DF, Bjorling DE. Roles of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in modulating urothelial cell proliferation. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2008;15(1):351–64.
Stein JP, Ginsberg DA, Grossfeld GD, Chatterjee SJ, Esrig D, Dickinson MG, et al. Effect of p21WAF1/CIP1 expression on tumor progression in bladder cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1998;90(14):1072–9.
Philipp-Staheli J, Payne SR, Kemp CJ. p27(Kip1): regulation and function of a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor and its misregulation in cancer. Exp Cell Res. 2001;264(1):148–68.
Maga G, Hubscher U. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA): a dancer with many partners. J Cell Sci. 2003;116(Pt 15):3051–60.
Moldovan GL, Pfander B, Jentsch S. PCNA, the maestro of the replication fork. Cell. 2007;129(4):665–79.
Skopelitou A, Hadjiyannakis M, Dimopoulos D, Kamina S, Krikoni O, Alexopoulou V, et al. p53 and c-jun expression in urinary bladder transitional cell carcinoma: correlation with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) histological grade and clinical stage. Eur Urol. 1997;31(4):464–71.
Yoshikawa H, Ikeuchi T, Iguchi H, Onodera Y, Kai Y. Expression of PCNA/cyclin, p53, C-erbB-2 versus histological grade in transitional cell carcinoma of urinary bladder. Hinyokika Kiyo. 1995;41(4):253–8.
Chen H, Detmer SA, Ewald AJ, Griffin EE, Fraser SE, Chan DC. Mitofusins Mfn1 and Mfn2 coordinately regulate mitochondrial fusion and are essential for embryonic development. J Cell Biol. 2003;160(2):189–200.
Guo X, Chen KH, Guo Y, Liao H, Tang J, Xiao RP. Mitofusin 2 triggers vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis via mitochondrial death pathway. Circ Res. 2007;101(11):1113–22.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Major Program of Science and Technology Bureau of Zhejiang Province (No. I20100034).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, B., Fu, G., Pan, H. et al. Anti-tumour efficacy of mitofusin-2 in urinary bladder carcinoma. Med Oncol 28 (Suppl 1), 373–380 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9662-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-010-9662-5