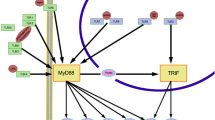
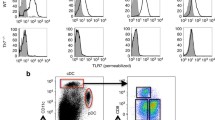
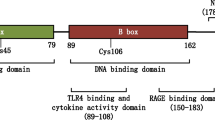
Abstract
Autoimmune diseases are immune disorders characterized by T cell hyperactivity and B cell overstimulation leading to overproduction of autoantibodies. Although the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases remains to be elucidated, environmental factors have been thought to contribute to the initiation and maintenance of auto-respond inflammation. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are pattern recognition receptors belonging to innate immunity that recognize and defend invading microorganisms. Besides these exogenous pathogen-associated molecular patterns, TLRs can also bind with damage-associated molecular patterns produced under strike or by tissue damage or cells apoptosis. It is believed that TLRs build a bridge between innate immunity and autoimmunity. There are five adaptors to TLRs including MyD88, TRIF, TIRAP/MAL, TRAM, and SARM. Upon activation, TLRs recruit specific adaptors to initiate the downstream signaling pathways leading to the production of inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. Under certain circumstances, ligation of TLRs drives to aberrant activation and unrestricted inflammatory responses, thereby contributing to the perpetuation of inflammation in autoimmune diseases. In the past, most studies focused on the intracellular TLRs, such as TLR3, TLR7, and TLR9, but recent studies reveal that cell surface TLRs, especially TLR2 and TLR4, also play an essential role in the development of autoimmune diseases and afford multiple therapeutic targets. In this review, we summarized the biological characteristics, signaling mechanisms of TLR2/4, the negative regulators of TLR2/4 pathway, and the pivotal function of TLR2/4 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, Sjogren’s syndrome, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, and autoimmune diabetes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sabroe I, Read RC, Whyte MK, Dockrell DH, Vogel SN, Dower SK (2003) Toll-like receptors in health and disease: complex questions remain. Journal of immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 171:1630–1635
O’Neill LA (2008) The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: 10 years of progress. Immunological reviews 226:10–18
Brown J, Wang H, Hajishengallis GN, Martin M (2011) TLR-signaling networks: an integration of adaptor molecules, kinases, and cross-talk. Journal of dental research 90:417–427
Medzhitov R, Preston-Hurlburt P, Janeway CA Jr (1997) A human homologue of the Drosophila Toll protein signals activation of adaptive immunity. Nature 388:394–397
Kawai T, Akira S (2010) The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nature immunology 11:373–384
Estruch M, Bancells C, Beloki L, Sanchez-Quesada JL, Ordonez-Llanos J, Benitez S (2013) CD14 and TLR4 mediate cytokine release promoted by electronegative LDL in monocytes. Atherosclerosis 229:356–362
Sadanaga A, Nakashima H, Akahoshi M, Masutani K, Miyake K, Igawa T et al (2007) Protection against autoimmune nephritis in MyD88-deficient MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis and rheumatism 56:1618–1628
Matsushima N, Tanaka T, Enkhbayar P, Mikami T, Taga M, Yamada K et al (2007) Comparative sequence analysis of leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) within vertebrate toll-like receptors. BMC genomics 8:124
Wang Y, Ge P, Zhu Y (2013) TLR2 and TLR4 in the brain injury caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Mediators of inflammation, 2013:124614
Botos I, Segal DM, Davies DR (2011) The structural biology of Toll-like receptors. Structure (London, England : 1993) 19:447–459
Virtue A, Wang H, Yang XF (2012) MicroRNAs and toll-like receptor/interleukin-1 receptor signaling. Journal of hematology & oncology 5:66
Ciechomska M, Cant R, Finnigan J, van Laar JM, O’Reilly S (2013) Role of toll-like receptors in systemic sclerosis. Expert Reviews in Molecular Medicine 15:e9
Huang QQ, Pope RM (2009) The role of toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Current Rheumatology Reports 11:357–364
Shi B, Huang Q, Tak PP, Vervoordeldonk MJ, Huang CC, Dorfleutner A et al (2012) SNAPIN: an endogenous Toll-like receptor ligand in rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 71:1411–1417
Richez C, Blanco P, Rifkin I, Moreau JF, Schaeverbeke T (2011) Role for toll-like receptors in autoimmune disease: the example of systemic lupus erythematosus. Joint, bone, spine : revue du rhumatisme 78:124–130
Kawai T, Akira S (2011) Toll-like receptors and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and immunity. Immunity 34:637–650
Loiarro M, Volpe E, Ruggiero V, Gallo G, Furlan R, Maiorino C et al (2013) Mutational analysis identifies residues crucial for homodimerization of Myeloid Differentiation Factor 88 (MyD88) and for its function in immune cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry
Lorne E, Dupont H, Abraham E (2010) Toll-like receptors 2 and 4: initiators of non-septic inflammation in critical care medicine? Intensive care medicine 36:1826–1835
Frazao JB, Errante PR, Condino-Neto A (2013) Toll-like receptors’ pathway disturbances are associated with increased susceptibility to infections in humans. Archivum immunologiae et therapiae experimentalis
Ori D, Kato H, Sanjo H, Tartey S, Mino T, Akira S et al (2013) Essential roles of K63-linked polyubiquitin-binding proteins TAB2 and TAB3 in B cell activation via MAPKs. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 190:4037–4045
Xia ZP, Sun L, Chen X, Pineda G, Jiang X, Adhikari A et al (2009) Direct activation of protein kinases by unanchored polyubiquitin chains. Nature 461:114–119
Clark K, Nanda S, Cohen P (2013) Molecular control of the NEMO family of ubiquitin-binding proteins. Nature Reviews Cancer 13:673–685
Qian C, Cao X (2013) Regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling pathways in innate immune responses. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1283:67–74
Picard C, Casanova JL, Puel A (2011) Infectious diseases in patients with IRAK-4, MyD88, NEMO, or IkappaBalpha deficiency. Clinical Microbiology Reviews 24:490–497
Geurts J, van den Brand BT, Wolf A, Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Arntz OJ, Kracht M et al (2011) Toll-like receptor 4 signalling is specifically TGF-beta-activated kinase 1 independent in synovial fibroblasts. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50:1216–1225
Ve T, Gay NJ, Mansell A, Kobe B, Kellie S (2012) Adaptors in toll-like receptor signaling and their potential as therapeutic targets. Current Drug Targets 13:1360–1374
Yang Y, Liao B, Wang S, Yan B, Jin Y, Shu HB et al (2013) E3 ligase WWP2 negatively regulates TLR3-mediated innate immune response by targeting TRIF for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:5115–5120
Zhang M, Wang L, Zhao X, Zhao K, Meng H, Zhao W et al (2012) TRAF-interacting protein (TRIP) negatively regulates IFN-beta production and antiviral response by promoting proteasomal degradation of TANK-binding kinase 1. The Journal of experimental medicine 209:1703–1711
Sethurathinam S, Singh LP, Panneerselvam P, Byrne B, Ding JL (2013) UXT plays dual opposing roles on SARM-induced apoptosis. FEBS Letters 587:3296–3302
Perkins DJ, Polumuri SK, Pennini ME, Lai W, Xie P, Vogel SN (2013) Reprogramming of murine macrophages through TLR2 confers viral resistance via TRAF3-mediated, enhanced interferon production. PLoS Pathogens 9:e1003479
Jeong E, Lee JY (2011) Intrinsic and extrinsic regulation of innate immune receptors. Yonsei Medical Journal 52:379–392
Trengove MC, Ward AC (2013) SOCS proteins in development and disease. American Journal of Clinical and Experimental Immunology 2:1–29
Ahmed S, Maratha A, Butt AQ, Shevlin E, Miggin SM (2013) TRIF-mediated TLR3 and TLR4 signaling is negatively regulated by ADAM15. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 190:2217–2228
Shio MT, Hassani K, Isnard A, Ralph B, Contreras I, Gomez MA et al (2012) Host cell signalling and leishmania mechanisms of evasion. Journal of Tropical Medicine 2012:819512
Kim EJ, Lee SM, Suk K, Lee WH (2012) CD300a and CD300f differentially regulate the MyD88 and TRIF-mediated TLR signalling pathways through activation of SHP-1 and/or SHP-2 in human monocytic cell lines. Immunology 135:226–235
Kim EJ, Suk K, Lee WH et al (2013) SHPS-1 and a synthetic peptide representing its ITIM inhibit the MyD88, but not TRIF, pathway of TLR signaling through activation of SHP and PI3K in THP-1 cells. Inflammation Research : Official Journal of the European Histamine Research Society 62:377–386
Sung NY, Yang MS, Song DS, Kim JK, Park JH, Song BS et al (2013) Procyanidin dimer B2-mediated IRAK-M induction negatively regulates TLR4 signaling in macrophages. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 438:122–128
Lee HJ, Chung KC (2012) PINK1 positively regulates IL-1beta-mediated signaling through Tollip and IRAK1 modulation. Journal of Neuroinflammation 9:271
Srivastav S, Kar S, Chande AG, Mukhopadhyaya R, Das PK (2012) Leishmania donovani exploits host deubiquitinating enzyme A20, a negative regulator of TLR signaling, to subvert host immune response. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 189:924–934
Zhong B, Liu X, Wang X, Liu X, Li H, Darnay BG et al (2013) Ubiquitin-specific protease 25 regulates TLR4-dependent innate immune responses through deubiquitination of the adaptor protein TRAF3. Science Signaling 6:ra35
Lin YC, Huang DY, Chu CL, Lin YL, Lin WW (2013) The tyrosine kinase Syk differentially regulates Toll-like receptor signaling downstream of the adaptor molecules TRAF6 and TRAF3. Science Signaling 6:ra71
Chuang TH, Ulevitch RJ (2004) Triad3A, an E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase regulating Toll-like receptors. Nature immunology 5:495–502
Nakhaei P, Mesplede T, Solis M, Sun Q, Zhao T, Yang L et al (2009) The E3 ubiquitin ligase Triad3A negatively regulates the RIG-I/MAVS signaling pathway by targeting TRAF3 for degradation. PLoS Pathogens 5:e1000650
Goh FG, Midwood KS (2012) Intrinsic danger: activation of Toll-like receptors in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:7–23
Takagi M (2011) Toll-like receptor—a potent driving force behind rheumatoid arthritis. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Hematopathology : JCEH 51:77–92
Neumann E, Lefevre S, Zimmermann B, Gay S, Muller-Ladner U (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis progression mediated by activated synovial fibroblasts. Trends in Molecular Medicine 16:458–468
Ospelt C, Brentano F, Rengel Y, Stanczyk J, Kolling C, Tak PP et al (2008) Overexpression of toll-like receptors 3 and 4 in synovial tissue from patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: toll-like receptor expression in early and longstanding arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58:3684–3692
Radstake TR, Roelofs MF, Jenniskens YM, Oppers-Walgreen B, van Riel PL, Barrera P et al (2004) Expression of toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in rheumatoid synovial tissue and regulation by proinflammatory cytokines interleukin-12 and interleukin-18 via interferon-gamma. Arthritis and Rheumatism 50:3856–3865
Kowalski ML, Wolska A, Grzegorczyk J, Hilt J, Jarzebska M, Drobniewski M et al (2008) Increased responsiveness to toll-like receptor 4 stimulation in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Mediators of Inflammation 2008:132732
Saber T, Veale DJ, Balogh E, McCormick J, NicAnUltaigh S, Connolly M et al (2011) Toll-like receptor 2 induced angiogenesis and invasion is mediated through the Tie2 signalling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis. PloS one 6:e23540
Chovanova L, Vlcek M, Krskova K, Penesova A, Radikova Z, Rovensky J et al (2013) Increased production of IL-6 and IL-17 in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated peripheral mononuclears from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. General Physiology and Biophysics 32:395–404
Tang CH, Hsu CJ, Yang WH, Fong YC (2010) Lipoteichoic acid enhances IL-6 production in human synovial fibroblasts via TLR2 receptor, PKCdelta and c-Src dependent pathways. Biochemical Pharmacology 79:1648–1657
Lorenz W, Buhrmann C, Mobasheri A, Lueders C, Shakibaei M (2013) Bacterial lipopolysaccharides form procollagen-endotoxin complexes that trigger cartilage inflammation and degeneration: implications for the development of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy 15:R111
Chen Y, Sun W, Gao R, Su Y, Umehara H, Dong L et al (2013) The role of high mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 52:1739–1747
Hu F, Mu R, Zhu J, Shi L, Li Y, Liu X et al. (2013) Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha provoke toll-like receptor signalling-induced inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Annals of the rheumatic diseases
Luo XJ, Mo XR, Zhou LL (2013) [The role of TLR2/4 in the IL-10 expression in synoviocytes of rheumatoid arthritis induced by Hsp72]. Zhongguo ying yong sheng li xue za zhi = Zhongguo yingyong shenglixue zazhi = Chinese journal of applied physiology, 29:212–3, 8
Huang QQ, Koessler RE, Birkett R, Dorfleutner A, Perlman H, Haines GK 3rd et al (2012) Glycoprotein 96 perpetuates the persistent inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and rheumatism 64:3638–3648
Wahamaa H, Schierbeck H, Hreggvidsdottir HS, Palmblad K, Aveberger AC, Andersson U et al (2011) High mobility group box protein 1 in complex with lipopolysaccharide or IL-1 promotes an increased inflammatory phenotype in synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis research & therapy 13:R136
He Z, Shotorbani SS, Jiao Z, Su Z, Tong J, Liu Y et al (2012) HMGB1 promotes the differentiation of Th17 via up-regulating TLR2 and IL-23 of CD14+ monocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scandinavian journal of immunology 76:483–490
Campo GM, Avenoso A, D’Ascola A, Prestipino V, Scuruchi M, Nastasi G et al (2012) Hyaluronan differently modulates TLR-4 and the inflammatory response in mouse chondrocytes. BioFactors (Oxford, England) 38:69–76
Abdollahi-Roodsaz S, Joosten LA, Koenders MI, Devesa I, Roelofs MF, Radstake TR et al (2008) Stimulation of TLR2 and TLR4 differentially skews the balance of T cells in a mouse model of arthritis. The Journal of clinical investigation 118:205–216
Hou Y, Lin H, Zhu L, Liu Z, Hu F, Shi J et al. (2013) LPS increases the incidence of collagen-induced arthritis in mice through induction of protease HTRA1 expression. Arthritis and rheumatism
Pierer M, Wagner U, Rossol M, Ibrahim S (2011) Toll-like receptor 4 is involved in inflammatory and joint destructive pathways in collagen-induced arthritis in DBA1J mice. PloS one 6:e23539
Ohto U, Yamakawa N, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K, Shimizu T (2012) Structural analyses of human Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms D299G and T399I. The Journal of biological chemistry 287:40611–40617
Emonts M, Hazes MJ, Houwing-Duistermaat JJ, van der Gaast-de Jongh CE, de Vogel L, Han HK et al. (2011) Polymorphisms in genes controlling inflammation and tissue repair in rheumatoid arthritis: a case control study. BMC medical genetics,12:36
Radstake TR, Franke B, Hanssen S, Netea MG, Welsing P, Barrera P et al (2004) The Toll-like receptor 4 Asp299Gly functional variant is associated with decreased rheumatoid arthritis disease susceptibility but does not influence disease severity and/or outcome. Arthritis and rheumatism 50:999–1001
Lee YH, Bae SC, Kim JH, Song GG (2013) Toll-like receptor polymorphisms and rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Rheumatology International
Xu WD, Liu SS, Pan HF, Ye DQ (2012) Lack of association of TLR4 polymorphisms with susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: a meta-analysis. Joint, bone, spine: revue du rhumatisme 79:566–569
Yang H, Wei C, Li Q, Shou T, Yang Y, Xiao C et al (2013) Association of TLR4 gene non-missense single nucleotide polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese Han population. Rheumatology International 33:1283–1288
Han EC (2012) Systemic lupus erythematosus. The New England Journal of Medicine 366:573–574, author reply 4
Conti G, Coppo R, Amore A (2012) Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (LES)]. Giornale italiano di nefrologia : organo ufficiale della Societa italiana di nefrologia 29(Suppl 54):S84–S90
Jallouli M, Frigui M, Marzouk S, Maaloul I, Kaddour N, Bahloul Z (2008) Infectious complications in systemic lupus erythematosus: a series of 146 patients. La Revue de medecine interne/fondee par la Societe nationale francaise de medecine interne 29:626–631
Kirchner M, Sonnenschein A, Schoofs S, Schmidtke P, Umlauf VN, Mannhardt-Laakmann W (2013) Surface expression and genotypes of Toll-like receptors 2 and 4 in patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Pediatric Rheumatology Online Journal 11:9
Komatsuda A, Wakui H, Iwamoto K, Ozawa M, Togashi M, Masai R et al (2008) Up-regulated expression of Toll-like receptors mRNAs in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Clinical and experimental immunology 152:482–487
Fujita K, Akasaka Y, Kuwabara T, Wang B, Tanaka K, Kamata I et al (2012) Pathogenesis of lupus-like nephritis through autoimmune antibody produced by CD180-negative B lymphocytes in NZBWF1 mouse. Immunology Letters 144:1–6
Tsao JT, Hsieh SC, Chiang BL, Yu CL, Lin SC (2012) Altered IL-10 and TNF-alpha production in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of systemic lupus erythematosus patients after Toll-like receptor 2, 4, or 9 activation. Clinical and experimental medicine 12:153–158
Wen Z, Xu L, Chen X, Xu W, Yin Z, Gao X et al (2013) Autoantibody induction by DNA-containing immune complexes requires HMGB1 with the TLR2/microRNA-155 pathway. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md: 1950) 190:5411–5422
Loser K, Vogl T, Voskort M, Lueken A, Kupas V, Nacken W et al (2010) The Toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 are crucial in the development of autoreactive CD8+ T cells. Nature Medicine 16:713–717
Lartigue A, Colliou N, Calbo S, Francois A, Jacquot S, Arnoult C et al (2009) Critical role of TLR2 and TLR4 in autoantibody production and glomerulonephritis in lpr mutation-induced mouse lupus. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 183:6207–6216
Moreth K, Brodbeck R, Babelova A, Gretz N, Spieker T, Zeng-Brouwers J et al (2010) The proteoglycan biglycan regulates expression of the B cell chemoattractant CXCL13 and aggravates murine lupus nephritis. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 120:4251–4272
Lee TP, Tang SJ, Wu MF, Song YC, Yu CL, Sun KH (2010) Transgenic overexpression of anti-double-stranded DNA autoantibody and activation of Toll-like receptor 4 in mice induce severe systemic lupus erythematosus syndromes. Journal of Autoimmunity 35:358–367
Summers SA, Hoi A, Steinmetz OM, O’Sullivan KM, Ooi JD, Odobasic D et al (2010) TLR9 and TLR4 are required for the development of autoimmunity and lupus nephritis in pristane nephropathy. Journal of Autoimmunity 35:291–298
Castiblanco J, Varela DC, Castano-Rodriguez N, Rojas-Villarraga A, Hincapie ME, Anaya JM (2008) TIRAP (MAL) S180L polymorphism is a common protective factor against developing tuberculosis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Infection, Genetics and Evolution : Journal of Molecular Epidemiology and Evolutionary Genetics in Infectious Diseases 8:541–544
Wu M, Assassi S (2013) The role of type 1 interferon in systemic sclerosis. Frontiers in Immunology 4:266
Fuschiotti P, Larregina AT, Ho J, Feghali-Bostwick C, Medsger TA Jr (2013) Interleukin-13-producing CD8+ T cells mediate dermal fibrosis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 65:236–246
van Lieshout AW, Vonk MC, Bredie SJ, Joosten LB, Netea MG, van Riel PL et al (2009) Enhanced interleukin-10 production by dendritic cells upon stimulation with Toll-like receptor 4 agonists in systemic sclerosis that is possibly implicated in CCL18 secretion. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 38:282–290
van Bon L, Popa C, Huijbens R, Vonk M, York M, Simms R et al (2010) Distinct evolution of TLR-mediated dendritic cell cytokine secretion in patients with limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 69:1539–1547
Fineschi S, Goffin L, Rezzonico R, Cozzi F, Dayer JM, Meroni PL et al (2008) Antifibroblast antibodies in systemic sclerosis induce fibroblasts to produce profibrotic chemokines, with partial exploitation of toll-like receptor 4. Arthritis and Rheumatism 58:3913–3923
Bhattacharyya S, Kelley K, Melichian DS, Tamaki Z, Fang F, Su Y et al (2013) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling augments transforming growth factor-beta responses: a novel mechanism for maintaining and amplifying fibrosis in scleroderma. The American Journal of Pathology 182:192–205
Wermuth PJ, Jimenez SA (2012) Gadolinium compounds signaling through TLR4 and TLR7 in normal human macrophages: establishment of a proinflammatory phenotype and implications for the pathogenesis of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950 189:318–327
Yoshizaki A, Iwata Y, Komura K, Ogawa F, Hara T, Muroi E et al (2008) CD19 regulates skin and lung fibrosis via Toll-like receptor signaling in a model of bleomycin-induced scleroderma. The American Journal of Pathology 172:1650–1663
Vakaloglou KM, Mavragani CP (2011) Activation of the type I interferon pathway in primary Sjogren’s syndrome: an update. Current Opinion in Rheumatology 23:459–464
Nguyen CQ, Peck AB (2013) The interferon-signature of Sjogren’s syndrome: how unique biomarkers can identify underlying inflammatory and immunopathological mechanisms of specific diseases. Frontiers in Immunology 4:142
Kawakami A, Nakashima K, Tamai M, Nakamura H, Iwanaga N, Fujikawa K et al (2007) Toll-like receptor in salivary glands from patients with Sjogren’s syndrome: functional analysis by human salivary gland cell line. The Journal of Rheumatology 34:1019–1026
Kwok SK, Cho ML, Her YM, Oh HJ, Park MK, Lee SY et al (2012) TLR2 ligation induces the production of IL-23/IL-17 via IL-6, STAT3 and NF-kB pathway in patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Arthritis Research & Therapy 14:R64
Spachidou MP, Bourazopoulou E, Maratheftis CI, Kapsogeorgou EK, Moutsopoulos HM, Tzioufas AG et al (2007) Expression of functional Toll-like receptors by salivary gland epithelial cells: increased mRNA expression in cells derived from patients with primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 147:497–503
Chong HT, Kopecki Z, Cowin AJ (2013) Lifting the silver flakes: the pathogenesis and management of chronic plaque psoriasis. BioMed Research International 2013:168321
Carrasco S, Neves FS, Fonseca MH, Goncalves CR, Saad CG, Sampaio-Barros PD et al (2011) Toll-like receptor (TLR) 2 is upregulated on peripheral blood monocytes of patients with psoriatic arthritis: a role for a gram-positive inflammatory trigger? Clinical and Experimental Rheumatology 29:958–962
Garcia-Rodriguez S, Arias-Santiago S, Perandres-Lopez R, Castellote L, Zumaquero E, Navarro P et al (2013) Increased gene expression of Toll-like receptor 4 on peripheral blood mononuclear cells in patients with psoriasis. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology : JEADV 27:242–250
Castrop F, Haslinger B, Hemmer B, Buck D (2013) Review of the pharmacoeconomics of early treatment of multiple sclerosis using interferon beta. Neuropsychiatric Disease and Treatment 9:1339–1349
Shaw PJ, Barr MJ, Lukens JR, McGargill MA, Chi H, Mak TW et al (2011) Signaling via the RIP2 adaptor protein in central nervous system-infiltrating dendritic cells promotes inflammation and autoimmunity. Immunity 34:75–84
Sloane JA, Batt C, Ma Y, Harris ZM, Trapp B, Vartanian T (2010) Hyaluronan blocks oligodendrocyte progenitor maturation and remyelination through TLR2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:11555–11560
Andersson A, Covacu R, Sunnemark D, Danilov AI, Dal Bianco A, Khademi M et al (2008) Pivotal advance: HMGB1 expression in active lesions of human and experimental multiple sclerosis. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 84:1248–1255
Reynolds JM, Martinez GJ, Chung Y, Dong C (2012) Toll-like receptor 4 signaling in T cells promotes autoimmune inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:13064–13069
Bustamante MF, Fissolo N, Rio J, Espejo C, Costa C, Mansilla MJ et al (2011) Implication of the Toll-like receptor 4 pathway in the response to interferon-beta in multiple sclerosis. Annals of Neurology 70:634–645
Nokoff N, Rewers M (2013) Pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes: lessons from natural history studies of high-risk individuals. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1281:1–15
Lien E, Zipris D (2009) The role of Toll-like receptor pathways in the mechanism of type 1 diabetes. Current Molecular Medicine 9:52–68
Devaraj S, Jialal I, Yun JM, Bremer A (2011) Demonstration of increased toll-like receptor 2 and toll-like receptor 4 expression in monocytes of type 1 diabetes mellitus patients with microvascular complications. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental 60:256–259
Ururahy MA, Loureiro MB, Freire-Neto FP, de Souza KS, Zuhl I, Brandao-Neto J et al (2012) Increased TLR2 expression in patients with type 1 diabetes: evidenced risk of microalbuminuria. Pediatric Diabetes 13:147–154
Li M, Song L, Gao X, Chang W, Qin X (2012) Toll-like receptor 4 on islet beta cells senses expression changes in high-mobility group box 1 and contributes to the initiation of type 1 diabetes. Experimental & Molecular Medicine 44:260–267
Jagannathan M, McDonnell M, Liang Y, Hasturk H, Hetzel J, Rubin D et al (2010) Toll-like receptors regulate B cell cytokine production in patients with diabetes. Diabetologia 53:1461–1471
Yin J, Peng Y, Wu J, Wang Y, Yao L (2013) Toll-like receptor 2/4 links to free fatty acid-induced inflammation and beta-cell dysfunction. Journal of Leukocyte Biology
Dong B, Qi D, Yang L, Huang Y, Xiao X, Tai N et al (2012) TLR4 regulates cardiac lipid accumulation and diabetic heart disease in the nonobese diabetic mouse model of type 1 diabetes. American journal of Physiology Heart and Circulatory Physiology 303:H732–H742
Devaraj S, Tobias P, Jialal I (2011) Knockout of toll-like receptor-4 attenuates the pro-inflammatory state of diabetes. Cytokine 55:441–445
Devaraj S, Tobias P, Kasinath BS, Ramsamooj R, Afify A, Jialal I (2011) Knockout of toll-like receptor-2 attenuates both the proinflammatory state of diabetes and incipient diabetic nephropathy. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology 31:1796–1804
Lee MS, Kim DH, Lee JC, Kim S, Kim HS (2011) Role of TLR2 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diabetes and its therapeutic implication. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 27:797–801
Filippi CM, Ehrhardt K, Estes EA, Larsson P, Oldham JE, von Herrath MG (2011) TLR2 signaling improves immunoregulation to prevent type 1 diabetes. European Journal of Immunology 41:1399–1409
Kim DH, Lee JC, Kim S, Oh SH, Lee MK, Kim KW et al (2011) Inhibition of autoimmune diabetes by TLR2 tolerance. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md : 1950) 187:5211–5220
Li J, Wang X, Zhang F, Yin H (2013) Toll-like receptors as therapeutic targets for autoimmune connective tissue diseases. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 138:441–451
Li G, Liu D, Zhang Y, Qian Y, Zhang H, Guo S et al (2013) Celastrol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-stimulated rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocyte invasion through suppression of TLR4/NF-kappaB-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. PloS One 8:e68905
Wang J, Lu J, Lan Y, Zhou H, Li W, Xiang M (2013) Total coumarins from Urtica dentata Hand prevent murine autoimmune diabetes via suppression of the TLR4-signaling pathways. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 146:379–392
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81220108017, no. 81373205, and no. 81270024), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (grant no. 20120162130003), and the Programs of Science-Technology Commission of Hunan province (2013FJ4202, 2011TP4019-7) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Yin, H., Zhao, M. et al. TLR2 and TLR4 in Autoimmune Diseases: a Comprehensive Review. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 47, 136–147 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8402-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-013-8402-y