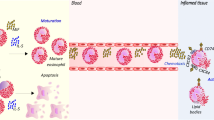
Abstract
The development of the allergic airway disease conveys several cell types, such as T-cells, eosinophils, mast cells, and dendritic cells, which act in a special and temporal synchronization. Cellular mobilization and its complex interactions are coordinated by a broad range of bioactive mediators known as chemokines. These molecules are an increasing family of small proteins with common structural motifs and play an important role in the recruitment and cell activation of both leukocytes and resident cells at the allergic inflammatory site via their receptors. Trafficking and recruitment of cell populations with specific chemokines receptors assure the presence of reactive allergen-specific T-cells in the lung, and therefore the establishment of an allergic inflammatory process. Different approaches directed against chemokines receptors have been developed during the last decades with promising therapeutic results in the treatment of asthma. In this review we explore the role of the chemokines and chemokine receptors in allergy and asthma and discuss their potential as targets for therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baggiolini M, Dahinden CA (1994) CC chemokines in allergic inflammation. Immunol Today 15:127–133
Miller MD, Krangel MS (1992) Biology and biochemistry of the chemokines: a family of chemotactic and inflammatory cytokines. Crit Rev Immunol 12:17–46
Oppenheim JJ, Zachariae CO, Mukaida N, Matsushima K (1991) Properties of the novel proinflammatory supergene "Intercrine" cytokine family. Annu Rev Immunol 9:617–648
Baggiolini M (1993) Chemotactic and inflammatory cytokines—CXC and CC proteins. Adv Exp Med Biol 351:1–11
Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B (1997) Human chemokines: an update. Annu Rev Immunol 15:675–705
Baggiolini M (1998) Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature 392:565–568
Schlondorff D, Nelson PJ, Luckow B, Banas B (1997) Chemokines and renal disease. Kidney Int 51:610–621
Kelner GS, Kennedy J, Bacon KB, Kleyensteuber S, Largaespada DA, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Bazan JF, Moore KW, Schall TJ (1994) Lymphotactin: a cytokine that represents a new class of chemokine. Science 266:1395–1399
Kennedy J, Kelner GS, Kleyensteuber S, Schall TJ, Weiss MC, Yssel H, Schneider PV, Cocks BG, Bacon KB, Zlotnik A (1995) Molecular cloning and functional characterization of human lymphotactin. J Immunol 155:203–209
Bazan JF, Bacon KB, Hardiman G, Wang W, Soo K, Rossi D, Greaves DR, Zlotnik A, Schall TJ (1997) A new class of membrane-bound chemokine with a CX3C motif. Nature 385:640–644
Baggiolini M, Dewald B, Moser B (1994) Interleukin-8 and related chemotactic cytokines—CXC and CC chemokines. Adv Immunol 55:97–179
Murphy PM (1994) The molecular biology of leukocyte chemoattractant receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 12:593–633
Koch AE, Polverini PJ, Kunkel SL, Harlow LA, DiPietro LA, Elner VM, Elner SG, Strieter RM (1992) Interleukin-8 as a macrophage-derived mediator of angiogenesis. Science 258:1798–1801
Schall TJ, Bacon KB (1994) Chemokines, leukocyte trafficking, and inflammation. Curr Opin Immunol 6:865–873
Alam R, York J, Boyars M, Stafford S, Grant JA, Lee J, Forsythe P, Sim T, Ida N (1996) Increased MCP-1, RANTES, and MIP-1alpha in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of allergic asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 153:1398–1404
Finkelman FD, Shea-Donohue T, Morris SC, Gildea L, Strait R, Madden KB, Schopf L, Urban JF Jr (2004) Interleukin-4- and Interleukin-13-mediated host protection against intestinal nematode parasites. Immunol Rev 201:139–155
Medoff BD, Thomas SY, Luster AD (2008) T cell trafficking in allergic asthma: the ins and outs. Annu Rev Immunol 26:205–232
Schwarz MK, Wells TN (2002) New therapeutics that modulate chemokine networks. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:347–358
Holt PG, Schon-Hegrad MA, Oliver J, Holt BJ, McMenamin PG (1990) A contiguous network of dendritic antigen-presenting cells within the respiratory epithelium. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol 91:155–159
Huh JC, Strickland DH, Jahnsen FL, Turner DJ, Thomas JA, Napoli S, Tobagus I, Stumbles PA, Sly PD, Holt PG (2003) Bidirectional interactions between antigen-bearing respiratory tract dendritic cells (DCs) and T cells precede the late phase reaction in experimental asthma: DC activation occurs in the airway mucosa but not in the lung parenchyma. J Exp Med 198:19–30
van Rijt LS, Lambrecht BN (2005) Dendritic cells in asthma: a function beyond sensitization. Clin Exp Allergy 35:1125–1134
Eisenbarth SC, Piggott DA, Bottomly K (2003) The master regulators of allergic inflammation: dendritic cells in Th2 sensitization. Curr Opin Immunol 15:620–626
Eisenbarth SC, Cassel S, Bottomly K (2004) Understanding asthma pathogenesis: linking innate and adaptive immunity. Curr Opin Pediatr 16:659–666
Herrick CA, Bottomly K (2003) To respond or not to respond: T cells in allergic asthma. Nat Rev Immunol 3:405–412
Piggott DA, Eisenbarth SC, Xu L, Constant SL, Huleatt JW, Herrick CA, Bottomly K (2005) MyD88-dependent induction of allergic Th2 responses to intranasal antigen. J Clin Invest 115:459–467
Marathias KP, Preffer FI, Pinto C, Kradin RL (1991) Most human pulmonary infiltrating lymphocytes display the surface immune phenotype and functional responses of sensitized T cells. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 5:470–476
Medoff BD, Thomas SY, Banerji A, Wain JC, Zhang H, Lilly CM, Ginns LC, Luster AD (2005) Pathogenic T-cell recruitment into the airway in human disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1062:220–241
Strickland D, Kees UR, Holt PG (1996) Regulation of T-cell activation in the lung: isolated lung T cells exhibit surface phenotypic characteristics of recent activation including down-modulated T-cell receptors, but are locked into the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. Immunology 87:242–249
Upham JW, McMenamin C, Schon-Hegrad MA, Robinson BW, Holt PG (1994) Functional analysis of human bronchial mucosal T cells extracted with interleukin-2. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149:1608–1613
Mathew A, MacLean JA, DeHaan E, Tager AM, Green FH, Luster AD (2001) Signal transducer and activator of transcription 6 controls chemokine production and T helper cell type 2 cell trafficking in allergic pulmonary inflammation. J Exp Med 193:1087–1096
Chan WL, Pejnovic N, Lee CA, Al Ali NA (2001) Human IL-18 receptor and ST2L are stable and selective markers for the respective type 1 and type 2 circulating lymphocytes. J Immunol 167:1238–1244
Murray LA, Syed F, Li L, Griswold DE, Das AM (2006) Role of chemokines in severe asthma. Curr Drug Targets 7:579–588
Sallusto F, Mackay CR, Lanzavecchia A (1997) Selective expression of the eotaxin receptor CCR3 by human T helper 2 cells. Science 277:2005–2007
Bradley BL, Azzawi M, Jacobson M, Assoufi B, Collins JV, Irani AM, Schwartz LB, Durham SR, Jeffery PK, Kay AB (1991) Eosinophils, T-lymphocytes, mast cells, neutrophils, and macrophages in bronchial biopsy specimens from atopic subjects with asthma: comparison with biopsy specimens from atopic subjects without asthma and normal control subjects and relationship to bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol 88:661–674
Humbert M, Corrigan CJ, Kimmitt P, Till SJ, Kay AB, Durham SR (1997) Relationship between IL-4 and IL-5 MRNA expression and disease severity in atopic asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:704–708
Lloyd CM, Delaney T, Nguyen T, Tian J, Martinez A, Coyle AJ, Gutierrez-Ramos JC (2000) CC chemokine receptor (CCR)3/eotaxin is followed by CCR4/monocyte-derived chemokine in mediating pulmonary T helper lymphocyte type 2 recruitment after serial antigen challenge in vivo. J Exp Med 191:265–274
Reibman J, Hsu Y, Chen LC, Bleck B, Gordon T (2003) Airway epithelial cells release MIP-3alpha/CCL20 in response to cytokines and ambient particulate matter. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 28:648–654
Montes-Vizuet R, Vega-Miranda A, Valencia-Maqueda E, Negrete-Garcia MC, Velasquez JR, Teran LM (2006) CC chemokine ligand 1 is released into the airways of atopic asthmatics. Eur Respir J 28:59–67
Panina-Bordignon P, Papi A, Mariani M, Di Lucia P, Casoni G, Bellettato C, Buonsanti C, Miotto D, Mapp C, Villa A, Arrigoni G, Fabbri LM, Sinigaglia F (2001) The C-C chemokine receptors CCR4 and CCR8 identify airway T cells of allergen-challenged atopic asthmatics. J Clin Invest 107:1357–1364
Kato A, Schleimer RP (2007) Beyond inflammation: airway epithelial cells are at the interface of innate and adaptive immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 19:711–720
Carr MW, Roth SJ, Luther E, Rose SS, Springer TA (1994) Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 acts as a T-lymphocyte chemoattractant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:3652–3656
Mikhak Z, Fleming CM, Medoff BD, Thomas SY, Tager AM, Campanella GS, Luster AD (2006) STAT1 in peripheral tissue differentially regulates homing of antigen-specific Th1 and Th2 cells. J Immunol 176:4959–4967
Sauty A, Dziejman M, Taha RA, Iarossi AS, Neote K, Garcia-Zepeda EA, Hamid Q, Luster AD (1999) The T cell-specific CXC chemokines IP-10, Mig, and I-TAC are expressed by activated human bronchial epithelial cells. J Immunol 162:3549–3558
Komiya A, Nagase H, Yamada H, Sekiya T, Yamaguchi M, Sano Y, Hanai N, Furuya A, Ohta K, Matsushima K, Yoshie O, Yamamoto K, Hirai K (2003) Concerted expression of eotaxin-1, eotaxin-2, and eotaxin-3 in human bronchial epithelial cells. Cell Immunol 225:91–100
Ying S, Meng Q, Zeibecoglou K, Robinson DS, Macfarlane A, Humbert M, Kay AB (1999) Eosinophil chemotactic chemokines (Eotaxin, Eotaxin-2, RANTES, monocyte chemoattractant protein-3 (MCP-3), and MCP-4), and C-C chemokine receptor 3 expression in bronchial biopsies from atopic and nonatopic (Intrinsic) asthmatics. J Immunol 163:6321–6329
Brown JR, Kleimberg J, Marini M, Sun G, Bellini A, Mattoli S (1998) Kinetics of eotaxin expression and its relationship to eosinophil accumulation and activation in bronchial biopsies and bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) of asthmatic patients after allergen inhalation. Clin Exp Immunol 114:137–146
Ying S, Robinson DS, Meng Q, Rottman J, Kennedy R, Ringler DJ, Mackay CR, Daugherty BL, Springer MS, Durham SR, Williams TJ, Kay AB (1997) Enhanced expression of eotaxin and CCR3 MRNA and protein in atopic asthma. Association with airway hyperresponsiveness and predominant co-localization of eotaxin MRNA to bronchial epithelial and endothelial cells. Eur J Immunol 27:3507–3516
HogenEsch H (2004) Chemokines in allergic inflammation: human disease and animal models. Curr Med Chem Anti-Inflamm Anti-Allerg Agents 3:351–361
Cuvelier SL, Patel KD (2001) Shear-dependent eosinophil transmigration on interleukin 4-stimulated endothelial cells: a role for endothelium-associated eotaxin-3. J Exp Med 194:1699–1709
Yuan Q, Campanella GS, Colvin RA, Hamilos DL, Jones KJ, Mathew A, Means TK, Luster AD (2006) Membrane-bound eotaxin-3 mediates eosinophil transepithelial migration in IL-4-stimulated epithelial cells. Eur J Immunol 36:2700–2714
Humbles AA, Lu B, Friend DS, Okinaga S, Lora J, Al Garawi A, Martin TR, Gerard NP, Gerard C (2002) The murine CCR3 receptor regulates both the role of eosinophils and mast cells in allergen-induced airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:1479–1484
Lukacs NW (2001) Role of chemokines in the pathogenesis of asthma. Nat Rev Immunol 1:108–116
Fujisawa T, Kato Y, Nagase H, Atsuta J, Terada A, Iguchi K, Kamiya H, Morita Y, Kitaura M, Kawasaki H, Yoshie O, Hirai K (2000) Chemokines induce eosinophil degranulation through CCR-3. J Allergy Clin Immunol 106:507–513
Imai T, Baba M, Nishimura M, Kakizaki M, Takagi S, Yoshie O (1997) The T cell-directed CC chemokine TARC is a highly specific biological ligand for CC chemokine receptor 4. J Biol Chem 272:15036–15042
Imai T, Chantry D, Raport CJ, Wood CL, Nishimura M, Godiska R, Yoshie O, Gray PW (1998) Macrophage-derived chemokine is a functional ligand for the CC chemokine receptor 4. J Biol Chem 273:1764–1768
Sekiya T, Miyamasu M, Imanishi M, Yamada H, Nakajima T, Yamaguchi M, Fujisawa T, Pawankar R, Sano Y, Ohta K, Ishii A, Morita Y, Yamamoto K, Matsushima K, Yoshie O, Hirai K (2000) Inducible expression of a Th2-type CC chemokine thymus- and activation-regulated chemokine by human bronchial epithelial cells. J Immunol 165:2205–2213
Lezcano-Meza D, Negrete-Garcia MC, Dante-Escobedo M, Teran LM (2003) The monocyte-derived chemokine is released in the bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of steady-state asthmatics. Allergy 58:1125–1130
Bochner BS, Hudson SA, Xiao HQ, Liu MC (2003) Release of both CCR4-active and CXCR3-active chemokines during human allergic pulmonary late-phase reactions. J Allergy Clin Immunol 112:930–934
Liu L, Jarjour NN, Busse WW, Kelly EA (2004) Enhanced generation of helper T type 1 and 2 chemokines in allergen-induced asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 169:1118–1124
Roos RS, Loetscher M, Legler DF, Clark-Lewis I, Baggiolini M, Moser B (1997) Identification of CCR8, the receptor for the human CC chemokine I-309. J Biol Chem 272:17251–17254
Bernardini G, Hedrick J, Sozzani S, Luini W, Spinetti G, Weiss M, Menon S, Zlotnik A, Mantovani A, Santoni A, Napolitano M (1998) Identification of the CC chemokines TARC and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 beta as novel functional ligands for the CCR8 receptor. Eur J Immunol 28:582–588
Howard OM, Dong HF, Shirakawa AK, Oppenheim JJ (2000) LEC induces chemotaxis and adhesion by interacting with CCR1 and CCR8. Blood 96:840–845
Luttichau HR, Stine J, Boesen TP, Johnsen AH, Chantry D, Gerstoft J, Schwartz TW (2000) A highly selective CC chemokine receptor (CCR)8 antagonist encoded by the poxvirus molluscum contagiosum. J Exp Med 191:171–180
Kremer L, Carramolino L, Goya I, Zaballos A, Gutierrez J, del Moreno-Ortiz M, Martinez A, Marquez G (2001) The transient expression of C-C chemokine receptor 8 in thymus identifies a thymocyte subset committed to become CD4+ single-positive T cells. J Immunol 166:218–225
Napolitano M, Zingoni A, Bernardini G, Spinetti G, Nista A, Storlazzi CT, Rocchi M, Santoni A (1996) Molecular cloning of TER1, a chemokine receptor-like gene expressed by lymphoid tissues. J Immunol 157:2759–2763
Tiffany HL, Lautens LL, Gao JL, Pease J, Locati M, Combadiere C, Modi W, Bonner TI, Murphy PM (1997) Identification of CCR8: a human monocyte and thymus receptor for the CC chemokine I-309. J Exp Med 186:165–170
Bishop B, Lloyd CM (2003) CC chemokine ligand 1 promotes recruitment of eosinophils but not Th2 cells during the development of allergic airways disease. J Immunol 170:4810–4817
Chung CD, Kuo F, Kumer J, Motani AS, Lawrence CE, Henderson WR Jr, Venkataraman C (2003) CCR8 is not essential for the development of inflammation in a mouse model of allergic airway disease. J Immunol 170:581–587
Goya I, Villares R, Zaballos A, Gutierrez J, Kremer L, Gonzalo JA, Varona R, Carramolino L, Serrano A, Pallares P, Criado LM, Kolbeck R, Torres M, Coyle AJ, Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Martinez A, Marquez G (2003) Absence of CCR8 does not impair the response to ovalbumin-induced allergic airway disease. J Immunol 170:2138–2146
Menten P, Wuyts A, Van Damme J (2002) Macrophage inflammatory protein-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:455–481
Holgate ST, Bodey KS, Janezic A, Frew AJ, Kaplan AP, Teran LM (1997) Release of RANTES, MIP-1 alpha, and MCP-1 into asthmatic airways following endobronchial allergen challenge. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:1377–1383
Tillie-Leblond I, Hammad H, Desurmont S, Pugin J, Wallaert B, Tonnel AB, Gosset P (2000) CC chemokines and interleukin-5 in bronchial lavage fluid from patients with status asthmaticus. Potential implication in eosinophil recruitment. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 162:586–592
Bensch GW, Nelson HS, Borish LC (2002) Evaluation of cytokines in nasal secretions after nasal antigen challenge: lack of influence of antihistamines. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 88:457–462
Kramer MF, Ostertag P, Pfrogner E, Rasp G (2001) Nasal IL-16 and MIP-1 alpha in late-phase allergic response. Allergy Asthma Proc 22:127–132
Pease JE (2006) Asthma, allergy and chemokines. Curr Drug Targets 7:3–12
Blease K, Mehrad B, Standiford TJ, Lukacs NW, Kunkel SL, Chensue SW, Lu B, Gerard CJ, Hogaboam CM (2000) Airway remodeling is absent in CCR1−/− mice during chronic fungal allergic airway disease. J Immunol 165:1564–1572
Joubert P, Lajoie-Kadoch S, Welman M, Dragon S, Letuvee S, Tolloczko B, Halayko AJ, Gounni AS, Maghni K, Hamid Q (2008) Expression and regulation of CCR1 by airway smooth muscle cells in asthma. J Immunol 180:1268–1275
Campbell EM, Charo IF, Kunkel SL, Strieter RM, Boring L, Gosling J, Lukacs NW (1999) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 mediates cockroach allergen-induced bronchial hyperreactivity in normal but not CCR2−/− mice: the role of mast cells. J Immunol 163:2160–2167
Francis JN, Jacobson MR, Lloyd CM, Sabroe I, Durham SR, Till SJ (2004) CXCR1+CD4+ T cells in human allergic disease. J Immunol 172:268–273
Bonecchi R, Bianchi G, Bordignon PP, D'Ambrosio D, Lang R, Borsatti A, Sozzani S, Allavena P, Gray PA, Mantovani A, Sinigaglia F (1998) Differential expression of chemokine receptors and chemotactic responsiveness of type 1 T helper cells (Th1s) and Th2s. J Exp Med 187:129–134
Inngjerdingen M, Damaj B, Maghazachi AA (2001) Expression and regulation of chemokine receptors in human natural killer cells. Blood 97:367–375
Loetscher P, Uguccioni M, Bordoli L, Baggiolini M, Moser B, Chizzolini C, Dayer JM (1998) CCR5 is characteristic of Th1 lymphocytes. Nature 391:344–345
Sallusto F, Lenig D, Mackay CR, Lanzavecchia A (1998) Flexible programs of chemokine receptor expression on human polarized T helper 1 and 2 lymphocytes. J Exp Med 187:875–883
Cole KE, Strick CA, Paradis TJ, Ogborne KT, Loetscher M, Gladue RP, Lin W, Boyd JG, Moser B, Wood DE, Sahagan BG, Neote K (1998) Interferon-inducible T cell alpha chemoattractant (I-TAC): a novel non-ELR CXC chemokine with potent activity on activated T cells through selective high affinity binding to CXCR3. J Exp Med 187:2009–2021
Farber JM (1990) A macrophage MRNA selectively induced by gamma-interferon encodes a member of the platelet factor 4 family of cytokines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87:5238–5242
Luster AD, Ravetch JV (1987) Biochemical characterization of a gamma interferon-inducible cytokine (IP-10). J Exp Med 166:1084–1097
Campbell JJ, Brightling CE, Symon FA, Qin S, Murphy KE, Hodge M, Andrew DP, Wu L, Butcher EC, Wardlaw AJ (2001) Expression of chemokine receptors by lung T cells from normal and asthmatic subjects. J Immunol 166:2842–2848
Loetscher P, Pellegrino A, Gong JH, Mattioli I, Loetscher M, Bardi G, Baggiolini M, Clark-Lewis I (2001) The ligands of CXC chemokine receptor 3, I-TAC, Mig, and IP10, are natural antagonists for CCR3. J Biol Chem 276:2986–2991
Xanthou G, Duchesnes CE, Williams TJ, Pease JE (2003) CCR3 functional responses are regulated by both CXCR3 and its ligands CXCL9, CXCL10 and CXCL11. Eur J Immunol 33:2241–2250
Campbell JD, Gangur V, Simons FE, HayGlass KT (2004) Allergic humans are hyporesponsive to a CXCR3 ligand-mediated Th1 immunity-promoting loop. FASEB J 18:329–331
Fulkerson PC, Zimmermann N, Brandt EB, Muntel EE, Doepker MP, Kavanaugh JL, Mishra A, Witte DP, Zhang H, Farber JM, Yang M, Foster PS, Rothenberg ME (2004) Negative regulation of eosinophil recruitment to the lung by the chemokine monokine induced by IFN-gamma (Mig, CXCL9). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:1987–1992
Busillo JM, Benovic JL (2007) Regulation of CXCR4 signaling. Biochim Biophys Acta 1768:952–963
Gleichmann M, Gillen C, Czardybon M, Bosse F, Greiner-Petter R, Auer J, Muller HW (2000) Cloning and characterization of SDF-1gamma, a novel SDF-1 chemokine transcript with developmentally regulated expression in the nervous system. Eur J Neurosci 12:1857–1866
McQuibban GA, Butler GS, Gong JH, Bendall L, Power C, Clark-Lewis I, Overall CM (2001) Matrix metalloproteinase activity inactivates the CXC chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1. J Biol Chem 276:43503–43508
Atluri P, Woo YJ (2008) Pro-angiogenic cytokines as cardiovascular therapeutics: assessing the potential. BioDrugs 22:209–222
Chen M, Xie HQ, Deng L, Li XQ, Wang Y, Zhi W, Yang ZM (2008) Stromal cell-derived factor-1 promotes bone marrow-derived cells differentiation to cardiomyocyte phenotypes in vitro. Cell Prolif 41:336–347
Hernandez-Lopez C, Valencia J, Hidalgo L, Martinez VG, Zapata AG, Sacedon R, Varas A, Vicente A (2008) CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling promotes human thymic dendritic cell survival regulating the Bcl-2/Bax ratio. Immunol Lett 120:72–78
Schonemeier B, Kolodziej A, Schulz S, Jacobs S, Hoellt V, Stumm R (2008) Regional and cellular localization of the CXCl12/SDF-1 chemokine receptor CXCR7 in the developing and adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol 510:207–220
Zhang S, Qi L, Li M, Zhang D, Xu S, Wang N, Sun B (2008) Chemokine CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 expression are associated with perineural invasion of prostate cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 27:62
Gonzalo JA, Lloyd CM, Peled A, Delaney T, Coyle AJ, Gutierrez-Ramos JC (2000) Critical involvement of the chemotactic axis CXCR4/stromal cell-derived factor-1 alpha in the inflammatory component of allergic airway disease. J Immunol 165:499–508
Lukacs NW, Berlin A, Schols D, Skerlj RT, Bridger GJ (2002) AMD3100, a CxCR4 antagonist, attenuates allergic lung inflammation and airway hyperreactivity. Am J Pathol 160:1353–1360
Hoshino M, Aoike N, Takahashi M, Nakamura Y, Nakagawa T (2003) Increased immunoreactivity of stromal cell-derived factor-1 and angiogenesis in asthma. Eur Respir J 21:804–809
Ansel KM, Ngo VN, Hyman PL, Luther SA, Forster R, Sedgwick JD, Browning JL, Lipp M, Cyster JG (2000) A chemokine-driven positive feedback loop organizes lymphoid follicles. Nature 406:309–314
Gunn MD, Ngo VN, Ansel KM, Ekland EH, Cyster JG, Williams LT (1998) A B-cell-homing chemokine made in lymphoid follicles activates Burkitt's lymphoma receptor-1. Nature 391:799–803
Kanemitsu N, Ebisuno Y, Tanaka T, Otani K, Hayasaka H, Kaisho T, Akira S, Katagiri K, Kinashi T, Fujita N, Tsuruo T, Miyasaka M (2005) CXCL13 is an arrest chemokine for B cells in high endothelial venules. Blood 106:2613–2618
Reif K, Ekland EH, Ohl L, Nakano H, Lipp M, Forster R, Cyster JG (2002) Balanced responsiveness to chemoattractants from adjacent zones determines B-Cell position. Nature 416:94–99
Hardy RR (2006) B-1 B cell development. J Immunol 177:2749–2754
Ansel KM, Harris RB, Cyster JG (2002) CXCL13 is required for B1 cell homing, natural antibody production, and body cavity immunity. Immunity 16:67–76
Aloisi F, Pujol-Borrell R (2006) Lymphoid neogenesis in chronic inflammatory diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 6:205–217
Rangel-Moreno J, Moyron-Quiroz JE, Hartson L, Kusser K, Randall TD (2007) Pulmonary expression of CXC chemokine ligand 13, CC chemokine ligand 19, and CC chemokine ligand 21 is essential for local immunity to influenza. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:10577–10582
Fulkerson PC, Zimmermann N, Hassman LM, Finkelman FD, Rothenberg ME (2004) Pulmonary chemokine expression is coordinately regulated by STAT1, STAT6, and IFN-gamma. J Immunol 173:7565–7574
Barnes PJ (1999) Therapeutic strategies for allergic diseases. Nature 402:B31–B38
Barnes PJ (2000) New directions in allergic diseases: mechanism-based anti-inflammatory therapies. J Allergy Clin Immunol 106:5–16
Onuffer JJ, Horuk R (2002) Chemokines, chemokine receptors and small-molecule antagonists: recent developments. Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:459–467
Baribaud F, Edwards TG, Sharron M, Brelot A, Heveker N, Price K, Mortari F, Alizon M, Tsang M, Doms RW (2001) Antigenically distinct conformations of CXCR4. J Virol 75:8957–8967
Blanpain C, Vanderwinden JM, Cihak J, Wittamer V, Le Poul E, Issafras H, Stangassinger M, Vassart G, Marullo S, Schlndorff D, Parmentier M, Mack M (2002) Multiple active states and oligomerization of CCR5 revealed by functional properties of monoclonal antibodies. Mol Biol Cell 13:723–737
Lee B, Sharron M, Blanpain C, Doranz BJ, Vakili J, Setoh P, Berg E, Liu G, Guy HR, Durell SR, Parmentier M, Chang CN, Price K, Tsang M, Doms RW (1999) Epitope mapping of CCR5 reveals multiple conformational states and distinct but overlapping structures involved in chemokine and coreceptor function. J Biol Chem 274:9617–9626
Gutierrez-Ramos JC, Lloyd C, Gonzalo JA (1999) Eotaxin: from an eosinophilic chemokine to a major regulator of allergic reactions. Immunol Today 20:500–504
Gonzalo JA, Lloyd CM, Kremer L, Finger E, Martinez A, Siegelman MH, Cybulsky M, Gutierrez-Ramos JC (1996) Eosinophil recruitment to the lung in a murine model of allergic inflammation. The role of T cells, chemokines, and adhesion receptors. J Clin Invest 98:2332–2345
Sabroe I, Peck MJ, Van Keulen BJ, Jorritsma A, Simmons G, Clapham PR, Williams TJ, Pease JE (2000) A small molecule antagonist of chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR3. Potent inhibition of eosinophil function and CCR3-mediated HIV-1 entry. J Biol Chem 275:25985–25992
White JR, Lee JM, Dede K, Imburgia CS, Jurewicz AJ, Chan G, Fornwald JA, Dhanak D, Christmann LT, Darcy MG, Widdowson KL, Foley JJ, Schmidt DB, Sarau HM (2000) Identification of potent, selective non-peptide CC chemokine receptor-3 antagonist that inhibits eotaxin-, eotaxin-2-, and monocyte chemotactic protein-4-induced eosinophil migration. J Biol Chem 275:36626–36631
Elsner J, Petering H, Hochstetter R, Kimmig D, Wells TN, Kapp A, Proudfoot AE (1997) The CC chemokine antagonist met-RANTES inhibits eosinophil effector functions through the chemokine receptors CCR1 and CCR3. Eur J Immunol 27:2892–2898
Morokata T, Suzuki K, Masunaga Y, Taguchi K, Morihira K, Sato I, Fujii M, Takizawa S, Torii Y, Yamamoto N, Kaneko M, Yamada T, Takahashi K, Shimizu Y (2006) A novel, selective, and orally available antagonist for CC chemokine receptor 3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317:244–250
Suzuki K, Morokata T, Morihira K, Sato I, Takizawa S, Kaneko M, Takahashi K, Shimizu Y (2006) In vitro and in vivo characterization of a novel CCR3 antagonist, YM-344031. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339:1217–1223
Warrior U, McKeegan EM, Rottinghaus SM, Garcia L, Traphagen L, Grayson G, Komater V, McNally T, Helfrich R, Harris RR, Bell RL, Burns DJ (2003) Identification and characterization of novel antagonists of the CCR3 receptor. J Biomol Screen 8:324–331
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Biomedicine in the Post-genomic Era A.C. The style review of the manuscript by Ms. Maggie Brunner, Coordinación de Investigación en Salud, IMSS, is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Velazquez, J.R., Teran, L.M. Chemokines and Their Receptors in the Allergic Airway Inflammatory Process. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 41, 76–88 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8202-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-010-8202-6