Abstract
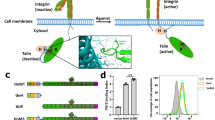
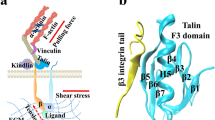
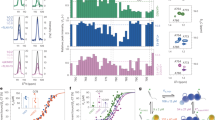
Increases in ligand binding to cellular integrins (activation) play an important role in platelet and leukocyte function. Talin is necessary in vivo and sufficient in vitro for integrin αIIbβ3 activation. The precise mechanisms by which talin activates integrin are still being elucidated. In particular, talin undergoes conformational changes (around the F3 helix) and inserts the F3 helix into lipid bilayer; however, the connection between this lipid-inserting mechanism of talin and talin’s capacity to activate integrin has never been explored before. In this work, we used rational mutagenesis, modeled cell systems, and structural modeling to study the potential role of membrane-induced talin conformational changes in talin-mediated integrin activation. Mutations of the residues critical for talin F3 helix to insert into membrane completely abolished talin-mediated integrin activation without affecting the binding of talin to integrins. Furthermore, mutations of the lipid-binding sequences in talin F3 helix significantly reduced the capacity of talin to activate integrin. Our results suggest that the F3 helix may contribute to talin-mediated integrin activation.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DSC:
-
Differential scanning calorimetry
- F3 helix:
-
The helix in talin F3 domain
- FERM:
-
Four-point-one, ezrin, radixin, moesin domain
- MFI:
-
Mean fluorescence intensity
- pK401 or polyK401:
-
Poly-Lys from Lys401 to Lys404
- TM:
-
Transmembrane domain
References
Kim, C., Ye, F., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2011). Regulation of integrin activation. Annual Review of Cell and Developmental Biology, 27, 321–345.
Shattil, S. J., Kim, C., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2010). The final steps of integrin activation: The end game. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 11, 288–300.
Hynes, R. O. (2002). Integrins: Bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell, 110, 673–687.
Shimaoka, M., Takagi, J., & Springer, T. A. (2002). Conformational regulation of integrin structure and function. Annual Review of Biophysics and Biomolecular Structure, 31, 485–516.
Moser, M., Legate, K. R., Zent, R., & Fassler, R. (2009). The tail of integrins, talin, and kindlins. Science, 324, 895–899.
Ye, F., Snider, A. K., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2014). Talin and kindlin: The one-two punch in integrin activation. Frontiers of Medicine, 8, 6–16.
Ye, F., Kim, C., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2011). Molecular mechanism of inside-out integrin regulation. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 9(Suppl 1), 20–25.
Calderwood, D. A., Campbell, I. D., & Critchley, D. R. (2013). Talins and kindlins: Partners in integrin-mediated adhesion. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 14, 503–517.
Wegener, K. L., Partridge, A. W., Han, J., Pickford, A. R., Liddington, R. C., Ginsberg, M. H., & Campbell, I. D. (2007). Structural basis of integrin activation by talin. Cell, 128, 171–182.
Ye, F., Hu, G., Taylor, D., Ratnikov, B., Bobkov, A. A., McLean, M. A., Sligar, S. G., Taylor, K. A., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2010). Recreation of the terminal events in physiological integrin activation. The Journal of Cell Biology, 188, 157–173.
Ye, F., Petrich, B. G., Anekal, P., Lefort, C. T., Kasirer-Friede, A., Shattil, S. J., Ruppert, R., Moser, M., Fassler, R., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2013). The mechanism of kindlin-mediated activation of integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Current Biology, 23, 2288–2295.
Lau, T. L., Kim, C., Ginsberg, M. H., & Ulmer, T. S. (2009). The structure of the integrin alphaIIbbeta3 transmembrane complex explains integrin transmembrane signalling. The EMBO Journal, 28, 1351–1361.
Hughes, P. E., Diaz-Gonzalez, F., Leong, L., Wu, C., McDonald, J. A., Shattil, S. J., & Ginsberg, M. H. (1996). Breaking the integrin hinge: A defined structural constraint regulates integrin signaling. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 271, 6571–6574.
Zhu, J., Luo, B. H., Barth, P., Schonbrun, J., Baker, D., & Springer, T. A. (2009). The structure of a receptor with two associating transmembrane domains on the cell surface: Integrin alphaIIbbeta3. Molecular Cell, 34, 234–249.
Kim, C., Schmidt, T., Cho, E. G., Ye, F., Ulmer, T. S., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2012). Basic amino-acid side chains regulate transmembrane integrin signalling. Nature, 481, 209–213.
Kim, C., Ye, F., Hu, X., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2012). Talin activates integrins by altering the topology of the beta transmembrane domain. The Journal of Cell Biology, 197, 605–611.
Li, A., Guo, Q., Kim, C., Hu, W., & Ye, F. (2014). Integrin alphaII β tail distal of GFFKR participates in inside-out alphaII b beta3 activation. Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 12, 1145–1155.
Arcario, M. J., & Tajkhorshid, E. (2014). Membrane-induced structural rearrangement and identification of a novel membrane anchor in talin F2F3. Biophysical Journal, 107, 2059–2069.
Critchley, D. R. (2009). Biochemical and structural properties of the integrin-associated cytoskeletal protein talin. Annual Review of Biophysics, 38, 235–254.
Anthis, N. J., Wegener, K. L., Ye, F., Kim, C., Goult, B. T., Lowe, E. D., Vakonakis, I., Bate, N., Critchley, D. R., Ginsberg, M. H., & Campbell, I. D. (2009). The structure of an integrin/talin complex reveals the basis of inside-out signal transduction. The EMBO Journal, 28, 3623–3632.
Kalli, A. C., Campbell, I. D., & Sansom, M. S. (2011). Multiscale simulations suggest a mechanism for integrin inside-out activation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA, 108, 11890–11895.
Takeda, S., Saitoh, A., Furuta, M., Satomi, N., Ishino, A., Nishida, G., Sudo, H., Hotani, H., & Takiguchi, K. (2006). Opening of holes in liposomal membranes is induced by proteins possessing the FERM domain. Journal of Molecular Biology, 362, 403–413.
Saitoh, A., Takiguchi, K., Tanaka, Y., & Hotani, H. (1998). Opening-up of liposomal membranes by talin. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 95, 1026–1031.
Isenberg, G., Doerhoefer, S., Hoekstra, D., & Goldmann, W. H. (2002). Membrane fusion induced by the major lipid-binding domain of the cytoskeletal protein talin. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 295, 636–643.
Seelig, A., Blatter, X. L., Frentzel, A., & Isenberg, G. (2000). Phospholipid binding of synthetic talin peptides provides evidence for an intrinsic membrane anchor of talin. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 275, 17954–17961.
Scott, D. L., Diez, G., & Goldmann, W. H. (2006). Protein-lipid interactions: Correlation of a predictive algorithm for lipid-binding sites with three-dimensional structural data. Theoretical Biology & Medical Modelling, 3, 17.
Arias-Salgado, E. G., Lizano, S., Shattil, S. J., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2005). Specification of the direction of adhesive signaling by the integrin beta cytoplasmic domain. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280, 29699–29707.
Pfaff, M., Liu, S., Erle, D. J., & Ginsberg, M. H. (1998). Integrin beta cytoplasmic domains differentially bind to cytoskeletal proteins. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 6104–6109.
Calderwood, D. A., Zent, R., Grant, R., Rees, D. J., Hynes, R. O., & Ginsberg, M. H. (1999). The talin head domain binds to integrin beta subunit cytoplasmic tails and regulates integrin activation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 274, 28071–28074.
Shattil, S. J., Hoxie, J. A., Cunningham, M., & Brass, L. F. (1985). Changes in the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb.IIIa complex during platelet activation. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 260, 11107–11114.
Calderwood, D. A., Fujioka, Y., de Pereda, J. M., Garcia-Alvarez, B., Nakamoto, T., Margolis, B., McGlade, C. J., Liddington, R. C., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2003). Integrin beta cytoplasmic domain interactions with phosphotyrosine-binding domains: A structural prototype for diversity in integrin signaling. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 2272–2277.
Garcia-Alvarez, B., de Pereda, J. M., Calderwood, D. A., Ulmer, T. S., Critchley, D., Campbell, I. D., Ginsberg, M. H., & Liddington, R. C. (2003). Structural determinants of integrin recognition by talin. Molecular Cell, 11, 49–58.
Gingras, A. R., Liu, J. J., & Ginsberg, M. H. (2012). Structural basis of the junctional anchorage of the cerebral cavernous malformations complex. The Journal of Cell Biology, 199, 39–48.
Elliott, P. R., Goult, B. T., Kopp, P. M., Bate, N., Grossmann, J. G., Roberts, G. C., Critchley, D. R., & Barsukov, I. L. (2010). The structure of the talin head reveals a novel extended conformation of the FERM domain. Structure, 18, 1289–1299.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr. Mark Ginsberg for his generous gifts of many research reagents. All of the authors contributed to the collection and analysis of the data and to the preparation of the report. The corresponding author had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. This work is supported by the Sichuan Provincial Department of Science and Technology Supporting Project (No. 2015SZ0074 to Dr. Ang Li).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Ang Li and Qiang Guo have contributed equally to this study.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, A., Guo, Q., Wei, A. et al. Role of the Helix in Talin F3 Domain (F3 Helix) in Talin-Mediated Integrin Activation. Cell Biochem Biophys 75, 79–86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-017-0781-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-017-0781-x