Abstract
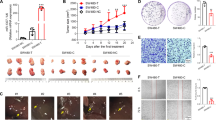
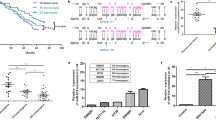
Identifying biomarkers for predicting radiotherapy efficacy is crucial for optimizing personalized treatments. We previously reported that rs1553867776 in the miR-4274 seed region can predict survival in patients with rectal cancer receiving postoperative chemoradiation therapy. Hence, to investigate the molecular mechanism of the genetic variation and its impact on the radiosensitivity of colorectal cancer (CRC), in this study, bioinformatics analysis is combined with functional experiments to confirm peroxisomal biogenesis factor 5 (PEX5) as a direct target of miR-4274. The miR-4274 rs1553867776 variant influences the binding of miR-4274 and PEX5 mRNA, which subsequently regulates PEX5 protein expression. The interaction between PEX5 and Ku70 was verified by co-immunoprecipitation and immunofluorescence. A xenograft tumor model was established to validate the effects of miR-4274 and PEX5 on CRC progression and radiosensitivity in vivo. The overexpression of PEX5 enhances radiosensitivity by preventing Ku70 from entering the nucleus and reducing the repair of ionizing radiation (IR)-induced DNA damage by the Ku70/Ku80 complex in the nucleus. In addition, the enhanced expression of PEX5 is associated with increased IR-induced ferroptosis. Thus, targeting this mechanism might effectively increase the radiosensitivity of CRC. These findings offer novel insights into the mechanism of cancer radioresistance and have important implications for clinical radiotherapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin 2023; 73(1): 17–48
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM, Wallace MB. Colorectal cancer. Lancet 2019; 394(10207): 1467–1480
Pucci S, Polidoro C, Joubert A, Mastrangeli F, Tolu B, Benassi M, Fiaschetti V, Greco L, Miceli R, Floris R, Novelli G, Orlandi A, Santoni R. Ku70, Ku80, and sClusterin: acluster of predicting factors for response to neoadjuvant chemoradiation therapy in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2017; 97(2): 381–388
Liu W, Miao C, Zhang S, Liu Y, Niu X, Xi Y, Guo W, Chu J, Lin A, Liu H, Yang X, Chen X, Zhong C, Ma Y, Wang Y, Zhu S, Liu S, Tan W, Lin D, Wu C. VAV2 is required for DNA repair and implicated in cancer radiotherapy resistance. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2021; 6(1): 322
Bartel DP. Metazoan MicroRNAs. Cell 2018; 173(1): 20–51
Salzman DW, Weidhaas JB. SNPing cancer in the bud: microRNA and microRNA-target site polymorphisms as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers in cancer. Pharmacol Ther 2013; 137(1): 55–63
Shen C, Yan T, Wang Z, Su HC, Zhu X, Tian X, Fang JY, Chen H, Hong J. Variant of SNP rs1317082 at CCSlnc362 (RP11-362K14.5) creates a binding site for miR-4658 and diminishes the susceptibility to CRC. Cell Death Dis 2018; 9(12): 1177
Wang W, Yang C, Nie H, Qiu X, Zhang L, Xiao Y, Zhou W, Zeng Q, Zhang X, Wu Y, Liu J, Ying M. LIMK2 acts as an oncogene in bladder cancer and its functional SNP in the microRNA-135a binding site affects bladder cancer risk. Int J Cancer 2019; 144(6): 1345–1355
Chen H, Yin L, Yang J, Ren N, Chen J, Lu Q, Huang Y, Feng Y, Wang W, Wang S, Liu Y, Song Y, Li Y, Jin J, Tan W, Lin D. Genetic polymorphisms in genes regulating cell death and prognosis of patients with rectal cancer receiving postoperative chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Biol Med 2023; 20(4): 297–316
Huang Y, Feng Y, Ren H, Zhang M, Li H, Qiao Y, Feng T, Yang J, Wang W, Wang S, Liu Y, Song Y, Li Y, Jin J, Tan W, Lin D. Associations of genetic variations in microRNA seed regions with acute adverse events and survival in patients with rectal cancer receiving postoperative chemoradiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2018; 100(4): 1026–1033
Landeros N, Corvalan AH, Musleh M, Quinones LA, Varela NM, Gonzalez-Hormazabal P. Novel risk associations between microRNA polymorphisms and gastric cancer in a Chilean population. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 23(1): 467
Shkurnikov M, Nikulin S, Nersisyan S, Poloznikov A, Zaidi S, Baranova A, Schumacher U, Wicklein D, Tonevitsky A. LAMA4-regulating miR-4274 and its host gene SORCS2 play a role in IGFBP6-dependent effects on phenotype of basal-like breast cancer. Front Mol Biosci 2019; 6: 122
Liu S, Zhang HL, Li J, Ye ZP, Du T, Li LC, Guo YQ, Yang D, Li ZL, Cao JH, Hu BX, Chen YH, Feng GK, Li ZM, Deng R, Huang JJ, Zhu XF. Tubastatin A potently inhibits GPX4 activity to potentiate cancer radiotherapy through boosting ferroptosis. Redox Biol 2023; 62: 102677
Lei G, Mao C, Yan Y, Zhuang L, Gan B. Ferroptosis, radiotherapy, and combination therapeutic strategies. Protein Cell 2021; 12(11): 836–857
Wang X, Zhou Y, Min J, Wang F. Zooming in and out of ferroptosis in human disease. Front Med 2023; 17(2): 173–206
Zou Y, Henry WS, Ricq EL, Graham ET, Phadnis VV, Maretich P, Paradkar S, Boehnke N, Deik AA, Reinhardt F, Eaton JK, Ferguson B, Wang W, Fairman J, Keys HR, Dancik V, Clish CB, Clemons PA, Hammond PT, Boyer LA, Weinberg RA, Schreiber SL. Plasticity of ether lipids promotes ferroptosis susceptibility and evasion. Nature 2020; 585(7826): 603–608
Ravindran R, Bacellar IOL, Castellanos-Girouard X, Wahba HM, Zhang Z, Omichinski JG, Kisley L, Michnick SW. Peroxisome biogenesis initiated by protein phase separation. Nature 2023; 617(7961): 608–615
Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Organelle-specific regulation of ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ 2021; 28(10): 2843–2856
Fujiki Y, Okumoto K, Honsho M, Abe Y. Molecular insights into peroxisome homeostasis and peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 2022; 1869(11): 119330
Yan H, Talty R, Aladelokun O, Bosenberg M, Johnson CH. Ferroptosis in colorectal cancer: a future target? Br J Cancer 2023; 128(8): 1439–1451
Sticht C, De La Torre C, Parveen A, Gretz N. miRWalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS One 2018; 13(10): e0206239
Bandyopadhyay S, Mitra R. TargetMiner: microRNA target prediction with systematic identification of tissue-specific negative examples. Bioinformatics 2009; 25(20): 2625–2631
Bhattacharya A, Ziebarth JD, Cui Y. PolymiRTS Database 3.0: linking polymorphisms in microRNAs and their target sites with human diseases and biological pathways. Nucleic Acids Res 2014; 42(Database issue): D86–D91
Paraskevopoulou MD, Georgakilas G, Kostoulas N, Vlachos IS, Vergoulis T, Reczko M, Filippidis C, Dalamagas T, Hatzigeorgiou AG. DIANA- microT web server v5.0: service integration into miRNA functional analysis workflows. Nucleic Acids Res 2013; 41(W1): W169–W173
Chen Y, Wang X. miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic Acids Res 2020; 48(D1): D127–D131
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW, Bartel DP. Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs. eLife 2015; 4: e05005
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Netto GJ, Qin ZS, Kumar S, Manne U, Creighton CJ, Varambally S. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022; 25: 18–27
Li T, Fu J, Zeng Z, Cohen D, Li J, Chen Q, Li B, Liu XS. TIMER2.0 for analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2020; 48(W1): W509–W514
Zhou Y, Zhou B, Pache L, Chang M, Khodabakhshi AH, Tanaseichuk O, Benner C, Chanda SK. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat Commun 2019; 10(1): 1523
Huang S, Fantini D, Merrill BJ, Bagchi S, Guzman G, Raychaudhuri P. DDB2 is a novel regulator of Wnt signaling in colon cancer. Cancer Res 2017; 77(23): 6562–6575
Burdak-Rothkamm S, Rothkamm K, McClelland K, Al Rashid ST, Prise KM. BRCA1, FANCD2 and Chk1 are potential molecular targets for the modulation of a radiation-induced DNA damage response in bystander cells. Cancer Lett 2015; 356(2 2 Pt B): 454–461
Han C, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Shen A, Dong C, Zhang A, Moore C, Ren Z, Lu C, Cao X, Zhang CL, Qiao J, Fu YX. Tumor cells suppress radiation-induced immunity by hijacking caspase 9 signaling. Nat Immunol 2020; 21(5): 546–554
Sándor N, Schilling-Tóth B, Kis E, Fodor L, Mucsányi F, Sáfrány G, Hegyesi H. TP53inp1 gene is implicated in early radiation response in human fibroblast cells. Int J Mol Sci 2015; 16(10): 25450–25465
Bracker TU, Sommer A, Fichtner I, Faus H, Haendler B, Hess-Stumpp H. Efficacy of MS-275, a selective inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases, in human colon cancer models. Int J Oncol 2009; 35(4): 909–920
Cancer Genome Atlas Network. Comprehensive molecular characterization of human colon and rectal cancer. Nature 2012; 487(7407): 330–337
Huang D, Du C, Ji D, Xi J, Gu J. Overexpression of LAMC2 predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients and promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. Tumour Biol 2017; 39(6): 1010428317705849
Vasilogianni AM, Al-Majdoub ZM, Achour B, Peters SA, Rostami-Hodjegan A, Barber J. Proteomic quantification of receptor tyrosine kinases involved in the development and progression of colorectal cancer liver metastasis. Front Oncol 2023; 13: 1010563
Liu Y, Deguchi Y, Tian R, Wei D, Wu L, Chen W, Xu W, Xu M, Liu F, Gao S, Jaoude JC, Chrieki SP, Moussalli MJ, Gagea M, Morris J, Broaddus RR, Zuo X, Shureiqi I. Pleiotropic effects of PPARD accelerate colorectal tumorigenesis, progression, and invasion. Cancer Res 2019; 79(5): 954–969
Köse B, Laar RV, Beekhuizen HV, Kemenade FV, Baykal AT, Luider T, Güzel C. Quantitative proteomic analysis of MCM3 in ThinPrep samples of patients with cervical preinvasive cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2023; 24(13): 10473
Lou J, Wei L, Wang H. SCNN1A overexpression correlates with poor prognosis and immune infiltrates in ovarian cancer. Int J Gen Med 2022; 15: 1743–1763
Cheng WL, Feng PH, Lee KY, Chen KY, Sun WL, Van Hiep N, Luo CS, Wu SM. The role of EREG/EGFR pathway in tumor progression. Int J Mol Sci 2021; 22(23): 12828
Sui H, Hao M, Chang W, Imamichi T. The role of Ku70 as a cytosolic DNA sensor in innate immunity and beyond. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2021; 11: 761983
Yang MD, Tsai CW, Chang WS, Tsou YA, Wu CN, Bau DT. Predictive role of XRCC5/XRCC6 genotypes in digestive system cancers. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2011; 3(12): 175–181
Liao P, Wang W, Wang W, Kryczek I, Li X, Bian Y, Sell A, Wei S, Grove S, Johnson JK, Kennedy PD, Gijón M, Shah YM, Zou W. CD8+ T cells and fatty acids orchestrate tumor ferroptosis and immunity via ACSL4. Cancer Cell 2022; 40(4): 365–378.e6
Quan J, Bode AM, Luo X. ACSL family: The regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic implications in cancer. Eur J Pharmacol 2021; 909: 174397
Lei G, Zhang Y, Koppula P, Liu X, Zhang J, Lin SH, Ajani JA, Xiao Q, Liao Z, Wang H, Gan B. The role of ferroptosis in ionizing radiation-induced cell death and tumor suppression. Cell Res 2020; 30(2): 146–162
Lang X, Green MD, Wang W, Yu J, Choi JE, Jiang L, Liao P, Zhou J, Zhang Q, Dow A, Saripalli AL, Kryczek I, Wei S, Szeliga W, Vatan L, Stone EM, Georgiou G, Cieslik M, Wahl DR, Morgan MA, Chinnaiyan AM, Lawrence TS, Zou W. Radiotherapy and immunotherapy promote tumoral lipid oxidation and ferroptosis via synergistic repression of SLC7A11. Cancer Discov 2019; 9(12): 1673–1685
Cai M, Sun X, Wang W, Lian Z, Wu P, Han S, Chen H, Zhang P. Disruption of peroxisome function leads to metabolic stress, mTOR inhibition, and lethality in liver cancer cells. Cancer Lett 2018; 421: 82–93
Zhu H, Lin Y, Lu D, Wang S, Liu Y, Dong L, Meng Q, Gao J, Wang Y, Song N, Suo Y, Ding L, Wang P, Zhang B, Gao D, Fan J, Gao Q, Zhou H. Proteomics of adjacent-to-tumor samples uncovers clinically relevant biological events in hepatocellular carcinoma. Natl Sci Rev 2023; 10(8): nwad167
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 81972859 to W.T.), CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences (CIFMS) (Grant No. 2021-I2M-1-013 to D.L. and W.T.), and State Key Laboratory of Molecular Oncology Grants (Grant No. SKLMO-2021-03 to W.T. and SKLMO-KF-2023-03 to D.L.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest Qixuan Lu, Ningxin Ren, Hongxia Chen, Shaosen Zhang, Ruoqing Yan, Mengjie Li, Linlin Zheng, Wen Tan, and Dongxin Lin declare that they have no conflict of interest.
The study was approved by the appropriate institutional and/or national research ethics committee and the study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Q., Ren, N., Chen, H. et al. Polymorphism in the Hsa-miR-4274 seed region influences the expression of PEX5 and enhances radiotherapy resistance in colorectal cancer. Front. Med. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-024-1082-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-024-1082-6