Abstract
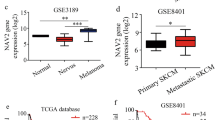
Melanoma is the most aggressive cutaneous tumor. Neuropilin and tolloid-like 2 (NETO2) is closely related to tumorigenesis. However, the functional significance of NETO2 in melanoma progression remains unclear. Herein, we found that NETO2 expression was augmented in melanoma clinical tissues and associated with poor prognosis in melanoma patients. Disrupting NETO2 expression markedly inhibited melanoma proliferation, malignant growth, migration, and invasion by downregulating the levels of calcium ions (Ca2+) and the expression of key genes involved in the calcium signaling pathway. By contrast, NETO2 overexpression had the opposite effects. Importantly, pharmacological inhibition of CaMKII/CREB activity with the CaMKII inhibitor KN93 suppressed NETO2-induced proliferation and melanoma metastasis. Overall, this study uncovered the crucial role of NETO2-mediated regulation in melanoma progression, indicating that targeting NETO2 may effectively improve melanoma treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Lipp P. Calcium—a life and death signal. Nature 1998; 395(6703): 645–648
Berridge MJ, Bootman MD, Roderick HL. Calcium signalling: dynamics, homeostasis and remodelling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2003; 4(7): 517–529
Stewart TA, Yapa KT, Monteith GR. Altered calcium signaling in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015; 1848(10 Pt B): 2502–2511
Long T, Su J, Tang W, Luo Z, Liu S, Liu Z, Zhou H, Qi M, Zeng W, Zhang J, Chen X. A novel interaction between calcium-modulating cyclophilin ligand and basigin regulates calcium signaling and matrix metalloproteinase activities in human melanoma cells. Cancer Lett 2013; 339(1): 93–101
Lin Q, Balasubramanian K, Fan D, Kim SJ, Guo L, Wang H, Bar-Eli M, Aldape KD, Fidler IJ. Reactive astrocytes protect melanoma cells from chemotherapy by sequestering intracellular calcium through gap junction communication channels. Neoplasia 2010; 12(9): 748–754
Miller AJ, Mihm MC Jr. Melanoma N Engl J Med 2006; 355(1): 51–65
Luke JJ, Flaherty KT, Ribas A, Long GV. Targeted agents and immunotherapies: optimizing outcomes in melanoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2017; 14(8): 463–482
Tomita S, Castillo PE. Neto1 and Neto2: auxiliary subunits that determine key properties of native kainate receptors. J Physiol 2012; 590(10): 2217–2223
Copits BA, Swanson GT. Dancing partners at the synapse: auxiliary subunits that shape kainate receptor function. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012; 13(10): 675–686
Zhang W, St-Gelais F, Grabner CP, Trinidad JC, Sumioka A, Morimoto-Tomita M, Kim KS, Straub C, Burlingame AL, Howe JR, Tomita S. A transmembrane accessory subunit that modulates kainate-type glutamate receptors. Neuron 2009; 61(3): 385–396
Mennesson M, Orav E, Gigliotta A, Kulesskaya N, Saarnio S, Kirjavainen A, Kesaf S, Winkel F, Llach Pou M, Umemori J, Voikar V, Risbrough V, Partanen J, Castrén E, Lauri SE, Hovatta I. Kainate receptor auxiliary subunit NETO2-related cued fear conditioning impairments associate with defects in amygdala development and excitability. eNeuro 2020; 7(4): ENEURO.0541-19.2020
Sargin D. Heightened fear in the absence of the kainate receptor auxiliary subunit NETO2: implications for PTSD. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019; 44(11): 1841–1842
Xu JC, Chen TY, Liao LT, Chen T, Li QL, Xu JX, Hu JW, Zhou PH, Zhang YQ. NETO2 promotes esophageal cancer progression by inducing proliferation and metastasis via PI3K/AKT and ERK pathway. Int J Biol Sci 2021; 17(1): 259–270
Wang X, Bian Z, Hou C, Li M, Jiang W, Zhu L. Neuropilin and tolloid-like 2 regulates the progression of osteosarcoma. Gene 2021; 768: 145292
Liu JY, Jiang L, He T, Liu JJ, Fan JY, Xu XH, Tang B, Shi Y, Zhao YL, Qian F, Wang Y, Cui YH, Yu PW. NETO2 promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells via activation of PI3K/Akt/NF-κB/Snail axis and predicts outcome of the patients. Cell Death Dis 2019; 10(3): 162
Li Y, Zhang Y, Liu J. NETO2 promotes pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, invasion and migration via activation of the STAT3 signaling pathway. Cancer Manag Res 2019; 11: 5147–5156
Ma H, Groth RD, Cohen SM, Emery JF, Li B, Hoedt E, Zhang G, Neubert TA, Tsien RW. γCaMKII shuttles Ca2+/CaM to the nucleus to trigger CREB phosphorylation and gene expression. Cell 2014; 159(2): 281–294
Xiao C, Yang BF, Song JH, Schulman H, Li L, Hao C. Inhibition of CaMKII-mediated c-FLIP expression sensitizes malignant melanoma cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res 2005; 304(1): 244–255
Chen W, Chen Y, Su J, Kang J, Ding Y, Ai W, Zhang J, Luo H, An P. CaMKII mediates TGFβ1-induced fibroblasts activation and its cross talk with colon cancer cells. Dig Dis Sci 2022; 67(1): 134–145
Chen SP, Sun J, Zhou YQ, Cao F, Braun C, Luo F, Ye DW, Tian YK. Sinomenine attenuates cancer-induced bone pain via suppressing microglial JAK2/STAT3 and neuronal CAMKII/CREB cascades in rat models. Mol Pain 2018; 14: 1744806918793232
Hsu WC, Le HN, Lin YJ, Chen MC, Wang TF, Li CC, Kuo WW, Mahalakshmi B, Singh CH, Chen MC, Huang CY. Calmodulin/CaMKII-γ mediates prosurvival capability in apicidin-persistent hepatocellular carcinoma cells via ERK1/2/CREB/c-fos signaling pathway. J Cell Biochem 2021; 122(6): 612–625
Li B, Rex E, Wang H, Qian Y, Ogden AM, Bleakman D, Johnson KW. Pharmacological modulation of GluK1 and GluK2 by NETO1, NETO2, and PSD95. Assay Drug Dev Technol 2016; 14(2): 131–143
Lian C, Cao S, Zeng W, Li Y, Su J, Li J, Zhao S, Wu L, Tao J, Zhou J, Chen X, Peng C. RJT-101, a novel camptothecin derivative, is highly effective in the treatment of melanoma through DNA damage by targeting topoisomerase 1. Biochem Pharmacol 2020; 171: 113716
Zhang X, Huang Z, Guo Y, Xiao T, Tang L, Zhao S, Wu L, Su J, Zeng W, Huang H, Li Z, Tao J, Zhou J, Chen X, Peng C. The phosphorylation of CD147 by Fyn plays a critical role for melanoma cells growth and metastasis. Oncogene 2020; 39(21): 4183–4197
Guney E, Arruda AP, Parlakgul G, Cagampan E, Min N, Lee GY, Greene L, Tsaousidou E, Inouye K, Han MS, Davis RJ, Hotamisligil GS. Aberrant Ca2+ signaling by IP3Rs in adipocytes links inflammation to metabolic dysregulation in obesity. Sci Signal 2021; 14(713): eabf2059
Gu F, Krüger A, Roggenkamp HG, Alpers R, Lodygin D, Jaquet V, Möckl F, Hernandez C LC, Winterberg K, Bauche A, Rosche A, Grasberger H, Kao JY, Schetelig D, Werner R, Schröder K, Carty M, Bowie AG, Huber S, Meier C, Mittrücker HW, Heeren J, Krause KH, Flügel A, Diercks BP, Guse AH. Dual NADPH oxidases DUOX1 and DUOX2 synthesize NAADP and are necessary for Ca2+ signaling during T cell activation. Sci Signal 2021; 14(709): eabe3800
Tan Y, Mui D, Toan S, Zhu P, Li R, Zhou H. SERCA overexpression improves mitochondrial quality control and attenuates cardiac microvascular ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 2020; 22: 696–707
Monteith GR, Davis FM, Roberts-Thomson SJ. Calcium channels and pumps in cancer: changes and consequences. J Biol Chem 2012; 287(38): 31666–31673
Mookerjee-Basu J, Hooper R, Gross S, Schultz B, Go CK, Samakai E, Ladner J, Nicolas E, Tian Y, Zhou B, Zaidi MR, Tourtellotte W, He S, Zhang Y, Kappes DJ, Soboloff J. Suppression of Ca2+ signals by EGR4 controls Th1 differentiation and anti-cancer immunity in vivo. EMBO Rep 2020; 21(5): e48904
Jia Q, Hu S, Jiao D, Li X, Qi S, Fan R. Synaptotagmin-4 promotes dendrite extension and melanogenesis in alpaca melanocytes by regulating Ca2+ influx via TRPM1 channels. Cell Biochem Funct 2020; 38(3): 275–282
Schwab A, Loeck T, Najder-Nalepa K. STIM2: redox-sensor and effector of the (tumor) microenvironment. Cell Calcium 2021; 94: 102335
Kondratskyi A, Yassine M, Kondratska K, Skryma R, Slomianny C, Prevarskaya N. Calcium-permeable ion channels in control of autophagy and cancer. Front Physiol 2013; 4: 272
Li YJ, Duan GF, Sun JH, Wu D, Ye C, Zang YY, Chen GQ, Shi YY, Wang J, Zhang W, Shi YS. Neto proteins regulate gating of the kainate-type glutamate receptor GluK2 through two binding sites. J Biol Chem 2019; 294(47): 17889–17902
Falcón-Moya R, Losada-Ruiz P, Sihra TS, Rodríguez-Moreno A. Cerebellar kainate receptor-mediated facilitation of glutamate release requires Ca2+-calmodulin and PKA. Front Mol Neurosci 2018; 11: 195
Hansen MR, Bok J, Devaiah AK, Zha XM, Green SH. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinases II and IV both promote survival but differ in their effects on axon growth in spiral ganglion neurons. J Neurosci Res 2003; 72(2): 169–184
Pan K, Xie Y. LncRNA FOXC2-AS1 enhances FOXC2 mRNA stability to promote colorectal cancer progression via activation of Ca2+-FAK signal pathway. Cell Death Dis 2020; 11(6): 434
Shi C, Cai Y, Li Y, Li Y, Hu N, Ma S, Hu S, Zhu P, Wang W, Zhou H. Yap promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis and mobilization via governing cofilin/F-actin/lamellipodium axis by regulation of JNK/Bnip3/SERCA/CaMKII pathways. Redox Biol 2018; 14: 59–71
Lomash RM, Sheng N, Li Y, Nicoll RA, Roche KW. Phosphorylation of the kainate receptor (KAR) auxiliary subunit Neto2 at serine 409 regulates synaptic targeting of the KAR subunit GluK1. J Biol Chem 2017; 292(37): 15369–15377
Wen AY, Sakamoto KM, Miller LS. The role of the transcription factor CREB in immune function. J Immunol 2010; 185(11): 6413–6419
Zhou YQ, Liu DQ, Chen SP, Sun J, Zhou XR, Luo F, Tian YK, Ye DW. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in chronic pain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2017; 363(2): 176–183
Jie Z, Xie Z, Zhao X, Sun X, Yu H, Pan X, Shen S, Qin A, Fang X, Fan S. Glabridin inhibits osteosarcoma migration and invasion via blocking the p38- and JNK-mediated CREB-AP1 complexes formation. J Cell Physiol 2019; 234(4): 4167–4178
Li H, Qiu Z, Li F, Wang C. The relationship between MMP-2 and MMP-9 expression levels with breast cancer incidence and prognosis. Oncol Lett 2017; 14(5): 5865–5870
Brabletz T, Kalluri R, Nieto MA, Weinberg RA. EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 2018; 18(2): 128–134
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82073458, 82173424, 81773341, 81772917, and 81830096). This research also was supported by the Science and Technology Innovation Program of Hunan Province (No. 2021RC4013) and the Program of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities (111 Project, No. B20017)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Susi Zhu, Xu Zhang, Yeye Guo, Ling Tang, Zhe Zhou, Xiang Chen, and Cong Peng declare that they have no competing interests. All institutional and national guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals were followed.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, S., Zhang, X., Guo, Y. et al. NETO2 promotes melanoma progression via activation of the Ca2+/CaMKII signaling pathway. Front. Med. 17, 263–274 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0935-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11684-022-0935-0