Abstract
Purpose
Finding new, reliable biomarkers of cardiovascular risk in hemodialysis (HD) patients is of utmost importance. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) has been recently associated with atherosclerosis in the general population. The relationship between markedly elevated FGF21 levels in HD patients and endothelial dysfunction is unknown. The aim of the study was to assess the determinants of FGF21, the correlation between FGF21 and tumor necrosis factor TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis (sTWEAK) and the correlation between FGF21 and endothelial dysfunction in HD patients.
Methods
A cross-sectional observational study was conducted in 70 HD patients (mean age 59.9 ± 12.5 years, 14.3% diabetes mellitus, 57.1% male) from Nefromed Dialysis Center Cluj. We registered clinical and biological data, and serum FGF21 levels were measured by ELISA. Endothelial function was evaluated by brachial flow-mediated dilation (FMD). An analysis based on stratification of FGF21 values into quartiles was performed.
Results
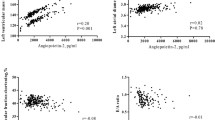
FGF21 levels were directly correlated with sTWEAK, tricipital skinfold thickness (TST), systolic blood pressure (SBP), total cholesterol and triglycerides. In multivariate linear analysis, only sTWEAK and SBP remained significantly associated with FGF21. FGF21 values in the inferior quartile were directly correlated with HDL-cholesterol, while FGF21 values in the superior quartile were directly correlated with SBP, pulse pressure and sTWEAK. FMD was significantly higher in the inferior quartile as compared to the superior quartile.
Conclusions
High FGF21 values in our patients are correlated with atherosclerosis risk factors: hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypertension, increased TST and increased levels of sTWEAK. Endothelial dysfunction is associated with high FGF21 in HD patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beenken A, Mohammadi M (2009) The FGF family: biology, pathophysiology and therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 8:235–253
Kralisch S, Tönjes A, Krause K, Richter J, Lossner U, Kovacs P, Ebert T, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M (2013) Fibroblast growth factor-21 serum concentrations are associated with metabolic and hepatic markers in humans. J Endocrinol 216:135–143
Kharitonenkov A, Wroblewski VJ, Koester A, Chen YF, Clutinger CK, Tigno XT, Hansen BC, Shanafelt AB, Etgen GJ (2007) The metabolic state of diabetic monkeys is regulated by fibroblast growth factor-21. Endocrinology 148:774–781
Li K, Li L, Yang M, Liu H, Boden G, Yang G (2012) The effects of fibroblast growth factor-21 knockdown and over-expression on its signaling pathway and glucose-lipid metabolism in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol 348:21–26
Coskun T, Bina HA, Schneider MA, Dunbar JD, Hu CC, Chen Y, Moller DE, Kharitonenkov A (2008) Fibroblast growth factor 21 corrects obesity in mice. Endocrinology 149:6018–6027
Hermansen K, Davies M (2007) Does insulin detemir have a role in reducing risk of insulin-associated weight gain? Diabetes Obes Metab 9:209–217
Zhang X, Yeung DCY, Karpisek M, Stejskal D, Zhou ZG, Liu F, Wong RLC, Chow WS, Tso AWK, Lam KSL, Xu A (2008) Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes 57:1246–1253
Lin Z, Zhou Z, Liu Y, Gong Q, Yan X, Xiao J, Wang X, Lin S, Feng W, Li X (2011) Circulating FGF21 levels are progressively increased from the early to end stages of chronic kidney diseases and are associated with renal function in Chinese. PLoS ONE 6:e18398. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.001839
Looker HC, Colombo M, Hess S, Brosnan MJ, Farran B, Dalton RN, Wong MC, Turner C, Palmer CNA, Nogoceke E, Groop L, Salomaa V, Dunger DB, Agakov F, McKeigue PM, Colhoun HM, Investigators SUMMIT (2015) Biomarkers of rapid chronic kidney disease progression in type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int 88:888–896
Han SH, Choi SH, Cho BJ, Lee Y, Lim S, Park YJ, Moon MK, Lee HK, Kang SW, Han DS, Kim YB, Jang HC, Park KS (2010) Serum fibroblast growth factor-21 concentration is associated with residual renal function and insulin resistance in end-stage renal disease patients receiving long-term peritoneal dialysis. Metabolism 59:1656–1662
Xiao Y, Liu L, Xu A, Zhou P, Long Z, Tu Y, Chen X, Tang W, Huang G, Zhou Z (2015) Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 levels are related to subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 6:14–72
Chow WS, Xu A, Woo YC, Tso AW, Cheung SC, Fong CH, Tse HF, Chau MT, Cheung BM, Lam KS (2013) Serum fibroblast growth factor-21 levels are associated with carotid atherosclerosis independent of established cardiovascular risk factors. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 33:2454–2459
Shen Y, Ma X, Zhou J, Pan X, Hao Y, Zhou M, Lu Z, Gao M, Bao Y, Jia W (2013) Additive relationship between serum fibroblast growth factor 21 level and coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Diabetol 28:12–124
Lin Z, Wu Z, Yin X, Liu Y, Yan X, Lin S, Xiao J, Wang X, Feng W, Li X (2010) Serum levels of FGF-21 are increased in coronary heart disease patients and are independently associated with adverse lipid profile. PLoS ONE 5:e15534. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0015534
Zhang W, Chu S, Ding W, Wang F (2015) Serum level of fibroblast growth factor 21 is independently associated with acute myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 10:e0129791. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129791
Semba RD, Crasto C, Strait J, Sun K, Schaumberg DA, Ferrucci L (2013) Elevated serum fibroblast growth factor 21 is associated with hypertension in community-dwelling adults. J Hum Hypertens 27:397–399
Hindricks J, Ebert T, Bachmann A, Kralisch S, Lössner U, Kratzsch J, Stolzenburg JU, Dietel A, Beige J, Anders M, Bast I, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M (2014) Serum levels of fibroblast growth factor-21 are increased in chronic and acute renal dysfunction. Clin Endocrinol 80:918–924
Stein S, Bachmann A, Lössner U, Kratzsch J, Blüher M, Stumvoll M, Fasshauer M (2009) Serum levels of the adipokine FGF21 depend on renal function. Diabetes Care 32:126–128
Ulu SM, Yuksel S, Altuntaş A, Kacar E, Ahsen A, Altug A, Celik S, Sezer MT (2014) Associations between serum hepcidin level, FGF-21 level and oxidative stress with arterial stiffness in CAPD patients. Int Urol Nephrol 46:2409–2414
Yilmaz MI, Sonmez A, Ortiz A, Saglam M, Kilic S, Eyileten T, Caglar K, Oguz Y, Vural A, Çakar M, Egido J, Altun B, Yenicesu M, Blanco-Colio LM, Carrero JJ (2011) Soluble TWEAK and PTX3 in nondialysis CKD patients: impact on endothelial dysfunction and cardiovascular outcomes. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6:785–792
Celermajer DS, Sorensen KE, Gooch VM, Spiegelhalter DJ, Miller OI, Sullivan ID, Lloyd JK, Deanfield JE (1992) Non-invasive detection of endothelial dysfunction in children and adults at risk of atherosclerosis. Lancet 340:1111–1115
Ghiadoni L, Faita F, Salvetti M, Cordiano C, Biggi A, Puato M, Di Monaco A, De Siati L, Volpe M, Ambrosio G, Gemignani V, Muiesan ML, Taddei S, Lanza GA, Cosentino F (2012) Assessment of flow-mediated dilation reproducibility: a nationwide multicenter study. J Hypertens 30:1399–1405
Li H, Bao Y, Xu A, Pan X, Lu J, Wu H, Lu H, Xiang K, Jia W (2009) Serum fibroblast growth factor 21 is associated with adverse lipid profiles and gamma-glutamyltransferase but not insulin sensitivity in Chinese subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:2151–2156
Suzuki M, Uehara Y, Motomura-Matsuzaka K, Oki J, Koyama Y, Kimura M, Asada M, Komi-Kuramochi A, Oka S, Imamura T (2008) βKlotho is required for fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 21 signaling through FGF receptor (FGFR) 1c and FGFR3c. Mol Endocrinol 22:1006–1014
Iglesias P, Selgas R, Romero S, Díez JJ (2012) Biological role, clinical significance and therapeutic possibilities of the recently discovered metabolic hormone fibroblastic growth factor 21. Eur J Endocrinol 167:301–309
Eto K (2013) FGF-21, a newcomer in the field of hypertension research. J Hum Hypertens 27:343–344
Tomiyama K, Maeda R, Urakawa I, Yamazaki Y, Tanaka T, Ito S, Nabeshima Y, Tomita T, Odori S, Hosoda K, Nakao K, Imura A, Nabeshima Y (2010) Relevant use of Klotho in FGF19 subfamily signaling system in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:1666–1671
Meighan-Mantha RL, Hsu DK, Guo Y, Brown SA, Feng SY, Peifley KA, Alberts GF, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Richards CM, Winkles JA (1999) The mitogen-inducible Fn14 gene encodes a type I transmembrane protein that modulates fibroblast adhesion and migration. J Biol Chem 274:33166–33176
Moreno JA, Muñoz-García B, Martín-Ventura JL, Madrigal-Matute J, Orbe J, Páramo JA, Ortega L, Egido J, Blanco-Colio LM (2009) The CD163-expressing macrophages recognize and internalize TWEAK: potential consequences in atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 207:103–110
Rusu CC, Racasan S, Kacso IM, Ghervan L, Moldovan D, Potra A, Patiu IM, Bondor C, Caprioara MG (2015) The association of high sCD163/sTWEAK ratio with cardiovascular disease in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 47:2023–2030
Sanz AB, Izquierdo MC, Sanchez-Niño MD, Ucero AC, Egido J, Ruiz-Ortega M, Ramos AM, Putterman C, Ortiz A (2014) TWEAK and the progression of renal disease: clinical translation. Nephrol Dial Transplant 29(Suppl 1):i54–i62
Moreno JA, Izquierdo MC, Sanchez-Niño MD, Suárez-Alvarez B, Lopez-Larrea C, Jakubowski A, Blanco J, Ramirez R, Selgas R, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A, Sanz AB (2011) The inflammatory cytokines TWEAK and TNFα reduce renal klotho expression through NFκB. J Am Soc Nephrol 22:1315–1325
Kim SH, Kang YJ, Kim WJ, Woo DK, Lee Y, Kim DI, Park YB, Kwon BS, Park JE, Lee WH (2004) TWEAK can induce pro-inflammatory cytokines and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in macrophages. Circ J 68:396–399
Diaz-Delfin J, Hondares E, Iglesias R, Giralt M, Caelles C, Villarroya F (2012) TNF-alpha represses beta-klotho expression and impairs FGF21 action in adipose cells: involvement of JNK1 in the FGF21 pathway. Endocrinology 153:4238–4245
Jin QR, Bando Y, Miyawaki K, Shikama Y, Kosugi C, Aki N, Funaki M, Noji S (2014) Correlation of fibroblast growth factor 21 serum levels with metabolic parameters in Japanese subjects. J Med Investig 61:28–34
Dutchak PA, Katafuchi T, Bookout AL, Choi JH, Yu RT, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2012) Fibroblast growth factor-21 regulates PPAR gamma activity and the antidiabetic actions of thiazolidinediones. Cell 148:556–567
Kurosu H, Choi M, Ogawa Y, Dickson AS, Goetz R, Eliseenkova AV, Mohammadi M, Rosenblatt KP, Kliewer SA, Kuro-o M (2007) Tissue-specific expression of beta Klotho and fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptor isoforms determines metabolic activity of FGF19 and FGF21. J Biol Chem 282:26687–26695
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Grant CNCSIS for young research teams, Project No. PN-II-RU-TE-2014-4-1819
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The results of this paper have not been published previously in whole or part.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rusu, C.C., Racasan, S., Kacso, I.M. et al. The metabolic hormone FGF21 is associated with endothelial dysfunction in hemodialysis patients. Int Urol Nephrol 49, 517–523 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1474-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11255-016-1474-x